savanna - BealBio
advertisement

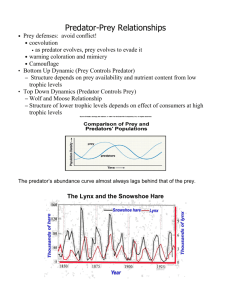
SAVANNA 1. Lions are distributed in clumps because this makes it easier to hunt in packs and capture more prey for the pride. Elephants are also distributed in clumps for protection. Herds are made up of females related by blood and their young. This is called kin speciation, as altruistic behavior is expressed in order to enhance the reproductive success of relatives. Trees such as the acacias tree tend to be distributed randomly because of the extensive savanna fires. 2. The density independent factors are limiting factors that cannot be controlled by the animals within the biome. Density independent factors of the Savanna include risk of fires, a lack of water due to drought, poaching, development, and any other natural disasters. 3. Elephants are K-selected species, as they produce very few offspring. Over their lifetime, a pair of elephants typically produces six offspring. This increases the chance of survival of the offspring because the female and her herd are able to protect the babies better when there are fewer. Elephants also tend to be larger in size and have a long life expectancy, traits common in K-selection. Most insects that live on the savanna are R-selected species. This is because these species have a relatively short life, reach reproductive maturity at a young age, have a low biomass, and have the potential to produce large numbers of small offspring at a time. Insects tend to reproduce rapidly to increase the survival rate of their offspring. Rhinoceroses exhibit Kselection also. Rhinos tend to live in small groups called crashes and only produce one offspring at a time. Parent rhinos are extremely protective of their babies. 4. Commensalism is a relationship between two organisms where one is benefited and the other is not affected. Mutualism is a relationship between two organisms where both are benefitted. Parasitism is a relationship between two organisms where one is benefited and the other is harmed. An example of commensalism is between most large grazers and the egret. The egret feasts on insects that are aroused into flight because of the grazing of the animals. The egret benefits from the food provided by the grazers, while the grazers are neither helped nor harmed. An example of parasitism is between a tick and an elephant. The tick sucks the blood of the elephant, which ultimately harms the elephant and benefits the tick. An example of mutualism is between the African ant and the acacia trees. The ants protect the trees from leaf eating insects, while still allowing for pollinating bees and insects, allowing for reproduction. The tree provides a safe home for the ant, while the ant protects the tree. 5. Batesian mimicry is when a harmless species mimics a harmful species to avoid predation. --in few savannas, the monarch butterfly is abundant, yet very poisonous to predators. Another species of butterfly, the viceroy, is not poisonous and is therefore preyed on more often. In an attempt to protect itself, the viceroy mimics the colors of the monarch in order to deceive predators. Viceroy monarch Cryptic coloration is camouflage which makes prey difficult to spot. -After times of fire on the savanna, many animals are exposed by the juxtaposition of their bright coloring against the charred ground. However, organisms such as the grass hopper have the ability to change their coloring to an ashy coloring than matches the ground, providing camouflage. Deceptive markings are markings that are used to warn predators that the organism unpalatable or noxious and these markings are also used to lure possible prey. This can also be known as aposematism, where markings and coloration is used to ward off predators. -It was very difficult to find an example of deceptive markings, but here is a video on aposematic coloration! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lXi1fQ50Bc8 Mullerian mimicry is when two or more different species resemble each other. Each species gains an advantage because there is an increased number in the possible prey -Leopards and cheetahs exhibit similar coloration and spots, which would confuse prey. The coloration of a cheetah would warn the prey of the impending attack, and this therefore would also prevent leopards from attacking prey. This would be a negative effect.