Station 1: Species Interactions Part 1: Responses to Predation For
advertisement

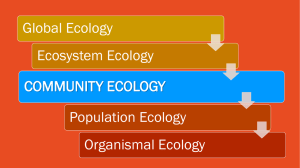
Station 1: Species Interactions Part 1: Responses to Predation For each of the following statements or pictures determine the correct response from the following list: Camoflauge Warning Coloration Mimicry Moment of truth Defenses (action by prey) Deceptive Markings Alluring Coloration Picture Description 1. This a spider, Synemosyna formica, that looks like an ant species to avoid predation from birds mimicry 2. This lizard’s tail is blue to attract predators to a non vital body part. Alluring coloration 3. The moth has markings that look like eyes. Deceptive markings 4. The peacock flounder can change colors to match its surroundings. camouflage 5. Bright orange color tells predators that they are toxic. Warning coloration 6. The beetle releases a strong odor to distract predators. Action by Prey Part 2: Species Relationships For each of the following statements or pictures determine which type of relationship is occurring: Mutualism Predation Commensalism, Parasitism Intraspecific Competition Interspecific Competition Competitive Exclusion. Niche/Resource Partitioning 7. 11. Remora fish eats left over’s that the shark catches. commensalism 8. Parasitism 12. Male giraffes compete for mates. Intraspecific competition 9. 10. Competitive exclusion 13. Different plant species having different root depth. Niche/resource partitioning Ants hollow out the large thorns of the 14. Acacia trees for nests and feed on sweet secretions from leafs. The ants in return protect the trees from herbivores that would eat the leaves. With a movement of the branch, ants emerge and release a nasty odor and attack the herbivore. mutualism predation Two different species compete for the same limited resource Interspecific competition Station 2: Community Ecology Part 1: Community Properties 1. Which site has higher species richness? Why? A. because it has more species 2. Which site has more evenness? Explain why? B. because the relative abundance of each species is the same. 3. Which site has more biodiversity? Site B because it has more than one species and it even. 4. What is the trend in species richness as you move closer to the equator? It increases 5. Name the concept shown in this graph (above). Species-area-effect 6. Explain this concept. The larger the island, the more species are found on it. Part 2: Succession 7. Define Succession. Sequential growth of an ecosystem. 8. Create a double bubble comparing and contrasting Primary and Seconday succession. Must have one similarity and two differences. Part 1: Ecosystem Station 3: Biomes 1. Describe which parts of Earth are found in each of the following: a. Geosphere b. Hydrosphere c. Atmosphere d. Biosphere Part 2: Biomes 1. Complete the following chart Biome Name Temperature Tundra Taiga Temperate Forest Tropical Rainforest Desert 2. Using the following graphs: Identify each biome. A. rainforest B. Tundra C. grassland D. Desert Precipitation Soil Description permafrost Station 4: Humans and the Environment Part 1: Environmental Solutions 1. Define the following: a. Biodiversity Hotspot b. Ecological (Carbon) Footprint c. Sustainability 2. What is ecotourism and how does it benefit the environment? Part 2: Environmental Issues 1. Using the image to the right: Explain how DDT in the water ends up harming the fish-eating bird. (Must use the terms bioaccumulation and biomagnification in your explanation). 2. What causes acid precipitation to become acidic? Burning of fossil fuels creates sulfuric and nitric acid gas which mixes with the water vapor in the atmosphere lowering it’s pH. 3. What are the health risks to humans if we destroy the ozone (O3) layer (hint: what does the ozone layer absorb)? Skin cancer 4. Using the image below: a. What environmental issue is being demonstrated? Global warming b. Explain how green house gases keep the planet warm. they trap heat from the sun