Acids, Bases & Salts
advertisement

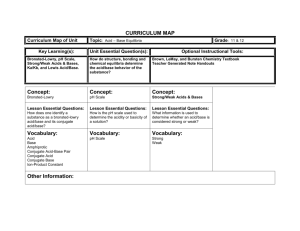
NOTES: 19.1 – Acid-Base Theories Acids & Bases have distinctive properties… Properties of Acids and Bases: ACIDS: BASES: Change the color of many indicators Change the color of many indicators Conduct an electric current Conduct an electric current The Arrhenius Theory of Acids & Bases: ● An acid is a compound that contains an H+, and Example: In Reality… HCl + H2O H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Hydronium Ion (can be used interchangeably with H +) ● A base is a compound that contains an OH- group and . Example: Neutralization: the combination of ● Commentary on Arrhenius Theory… One problem with the Arrhenius theory is that it’s not comprehensive enough. Some compounds act like acids and bases that don’t fit the standard definition. Bronsted-Lowry Theory of Acids & Bases: ● An ACIDis a ● A BASE is a for example… HCl(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq) another example… NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) Conjugate acid-base pairs ● Conjugate acid-base pairs **A conjugate acid is the particle formed when a base gains a proton. **A conjugate base is the particle that remains when an acid gives off a proton. Examples: In the following reactions, label the conjugate acid-base pairs: a) H3PO4 + NO2- HNO2 + H2PO4- b) CN- + HCO3- HCN + CO32- c) HCN + SO32- HSO3- + CN- d) H2O + HF F- + H3O+ Amphoteric Substances ● A substance that can act as both an acid and a base (depending on what it is reacting with) is termed AMPHOTERIC. ** The Lewis Theory of Acids & Bases ● Lewis acid: a substance that can accept an electron pair to form a covalent bond ( ). ● Lewis base: a substance that can donate an electron pair to form a covalent bond ( ). Example 1: ionization of NH3: Example 2: auto-ionization of water: Example 3: reaction of NH3 with HBr (is a Lewis AND a Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reaction): SUMMARY OF ACID-BASE THEORIES: Theory: Acid definition: Base definition: Brǿnsted-Lowry Theory Any substance which ______________________ in water solution. Any substance which __________________________. Any substance which ______________________ in water solution. Any substance which __________________________. Lewis Theory Any substance which can ____________________________. Any substance which can ____________________________. Arrhenius Theory