Ch.3 Density Assessment
advertisement

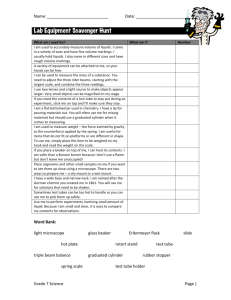
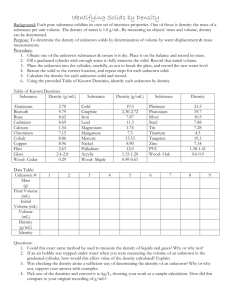
Name________________________ Date______________Pd.________ Ch. 3 Assessment- Density Column Objective- To demonstrate your skills in measuring volume, calculating densities, and using proper significant figures in experimental calculations. Procedure- Each group will obtain 20.0ml of the four (4) solutions. Using these solutions you will make a density column: 1. First you will calculate the densities of the four solutions. a. Find the mass of 4 empty 100ml beakers. Label A, B, C, D b. Obtain 20.0ml of each solution (A, B, C, D) in the previously massed beakers i. Make sure you use the correct instrument to measure out 20.0 ml. c. Find the mass of each beaker again. 2. Create a chart that organizes your data. ALL data and equations should be shown and in the correct amount of significant figures. 3. After you have figured out the densities and organized your data, create the actual density column in your 100ml graduated cylinder. (Use densities calculated in chart below) 4. Draw and label the density column. 5. Now, find the density of a rubber stopper. 6. Call Mr. Focht over to your group. You are going to predict at which layer the rubber stopper is going to stop when dropped in the graduated cylinder. Data Beaker A B C D Empty Beaker Beaker w/ liquid Mass of Liquid Volume of liquid Density of Liquid Name________________________ Date______________Pd.________ Density Column ** Use the graduated cylinder below to label your density column Density of rubber stopper ______________________. Which layer will the rubber stopper stop at. __________ Correct: yes / no Questions 1. What type of mixture did you create in your graduated cylinder? Explain your answer. Sample A B C Use the chart to answer questions 2-3 Volume Experimental Actual Density Density 2.0 ml 4.5 g/ml 4.3 g/ml 2.0 ml 5.5 g/ml 6.0 g/ml 2.0 ml 6.5 g/ml 8.5 g/ml 2. Which sample has the smallest Percent Error? (Show all work and equations. You should figure out all three Percent Errors) Name________________________ Date______________Pd.________ 3. All of the samples have the same volume. Discuss what is the reason for their different densities. Include interpretive drawings for samples A,B,C and the word “molecules” in your written answer. 4. Why is water a unique substance? Explain how the density of water changes from a liquid to a solid, and how this is different from other substances. Why? (Use pg. 448) 5. What are two types of error that you might encounter in an experiment?