REVISED Review 4 - Bonham Chemistry
advertisement

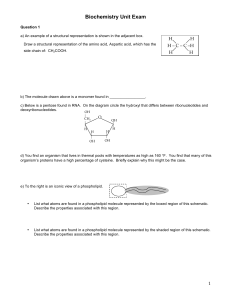
CHE 2100 Fall 2013 General Organic & Biological Chemistry Review IV A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won’t improve your answer— just answer clearly, succinctly, and in your own words. 1. How many different triose sugars exist? 2. How many chiral carbons are present in the straight chain form of Glucose? What about the cyclic ring form? 3. If the following structure or D-glucose? Circle the feature(s) that determine this designation. 4. The two simplest sugars are glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone. Dihydroxyacetone does not rotate the angle of plane polarized light. Why? 5. A glycosidic bond occurs when a ____________ functional group on a sugar reacts with a __________________ functional group on another sugar. 6. Draw the reaction which results in trans fatty acids in processed foods. 7. An 1,4 glycosidic bond is found in what types of molecule in plants? 8. In your own words, explain why people with type AB bloodgroup are often called “universal acceptors”. 9. Grass-eating animals require symbiotic relationships with gut bacteria. In molecular terms, what can these bacteria do that the animal cannot do itself? 10. Name three roles of lipids. 11. What are the components of a triglyceride? What type of functional group links these components? 12. Stearic acid is very common in both plant and animal tissues, while oleic acid is much more common in plant tissues. How does oleic acid differ from stearic acid? 13. Describe the structure of phosphatidylcholine. What class of lipid is it, and what role does it serve in the body? 14. If the weather outside is cold, why does your body’s usage of cholesterol increase? 15. Which carbon in the ring structure of fructose is the hemiacetal carbon? 16. Draw the straight-chain form of D-Allose, a C-3 epimer of D-Glucose. Then draw the correct ring form of this molecule. 17. What feature makes a given carbohydrate reducing or non-reducing? List an example of both types. 18. Glycogen is structurally very similar to what other material? 19. Why are lipids insoluble in water? 20. What poly-acohol is a component of all triglycerides? Give both it’s common and IUPAC name. 21. Lipid membranes surrounding cells have how many layers? Draw the general structure/arrangement of a lipid membrane. 22. Describe the sequence of reactions needed to go from a starting material of propane to isopropoxy 2-propanol. 23. What is the minimum number of carbon atoms in an -amino acid? 24. From the list of amino acids below, identify the following structures: Alanine, Cysteine, Serine, Phenylalanine 25. In your own words, explain what a Zwitterion is. 26. Circle the amino acid below that you would expect to have the largest pI, isoelectric point. 27. How many amino acids have acidic side chains? 28. Draw the hydrolysis reaction of a pair of amino acids. 29. How many atoms form the “backbone” of the repeating unit of a polypeptide? 30. If the following pentapeptide is put in a gel electrophoresis unit with buffer at pH 3, will it migrate towards the positive or negative electrode? 31. What are the two most common forms of protein secondary structure? 32. When naming a polypeptide chain, you begin at the __________________ and go towards the ______________________. 33. The identity of the R groups contributes most significantly to the ____________ structure of proteins. 34. Explain why soap would effectively denature many proteins. 35. Draw the following molecules: 2-amino propanoic acid Do they look familiar? 2-Amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid 36. What are three roles of proteins in the body? 37. Explain what is wrong with the following statement: “Enzymes shift the chemical equilibrium to more heavily favor products.” 38. Why does having an enzyme recognize the transition state result in lowered activation energy? 39. Given the graph of enzyme kinetics below, estimate the Km. 40. In the reaction mechanism of acetylcholinesterase, which product is temporarily covalently bound to the enzyme? 41. In competitive inhibition, does the inhibitor bind to the active site or to an allosteric site? Is this an example of reversible or irreversible inhibition? 42. Name 2 examples of commercially used enzymes and what products they help create. 43. Draw a Lineweaver-Burke plot for a typical enzymatic reaction. Label where you would find the KM and Vmax.