Higher Human Biology Chapter 5 Questions
advertisement
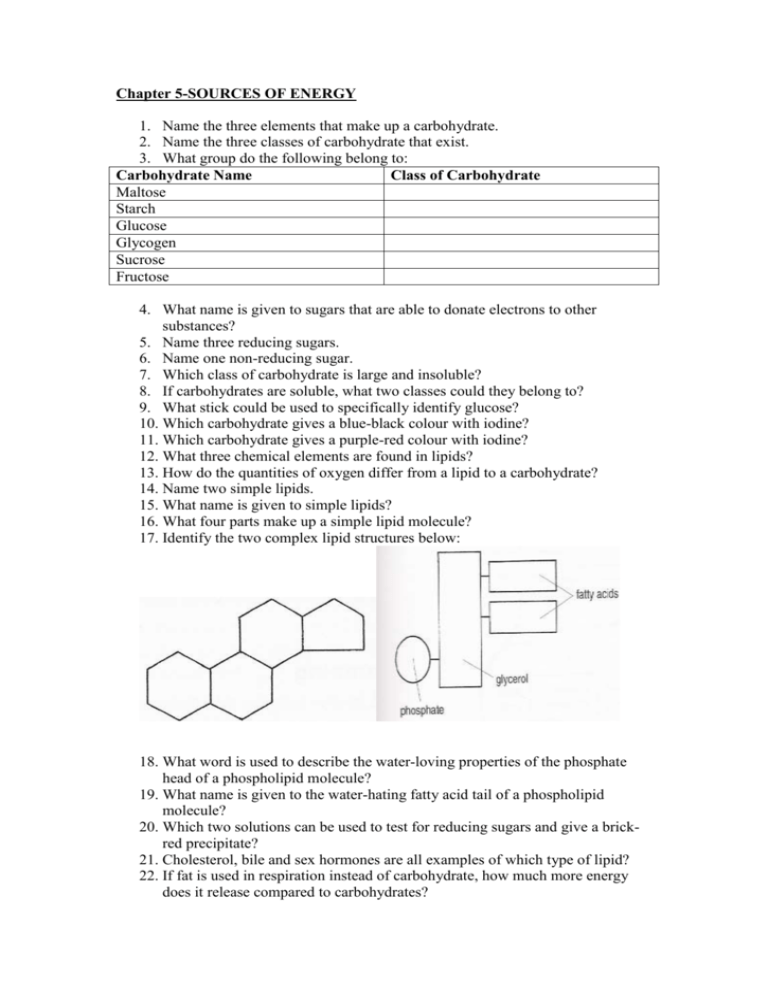
Chapter 5-SOURCES OF ENERGY 1. Name the three elements that make up a carbohydrate. 2. Name the three classes of carbohydrate that exist. 3. What group do the following belong to: Carbohydrate Name Class of Carbohydrate Maltose Starch Glucose Glycogen Sucrose Fructose 4. What name is given to sugars that are able to donate electrons to other substances? 5. Name three reducing sugars. 6. Name one non-reducing sugar. 7. Which class of carbohydrate is large and insoluble? 8. If carbohydrates are soluble, what two classes could they belong to? 9. What stick could be used to specifically identify glucose? 10. Which carbohydrate gives a blue-black colour with iodine? 11. Which carbohydrate gives a purple-red colour with iodine? 12. What three chemical elements are found in lipids? 13. How do the quantities of oxygen differ from a lipid to a carbohydrate? 14. Name two simple lipids. 15. What name is given to simple lipids? 16. What four parts make up a simple lipid molecule? 17. Identify the two complex lipid structures below: 18. What word is used to describe the water-loving properties of the phosphate head of a phospholipid molecule? 19. What name is given to the water-hating fatty acid tail of a phospholipid molecule? 20. Which two solutions can be used to test for reducing sugars and give a brickred precipitate? 21. Cholesterol, bile and sex hormones are all examples of which type of lipid? 22. If fat is used in respiration instead of carbohydrate, how much more energy does it release compared to carbohydrates? 23. Fat can be used as an insulator to conserve body heat- true or false? 24. The insulating fat around a nerve fibre is called myelin and can increase the speed of nerve impulses-true or false? 25. Name three areas of the body that have fat pads. 26. Lipoproteins transport lipids and what vitamins in lymph and blood plasma? 27. What is the name of the process that breaks down amino acids to form urea as they cannot be stored in the body? 28. During prolonged starvation, once all fat and glucose have been used up, what acts as a source of energy? 29. During marathon running what substance is used in the first few minutes of a race before glycogen and fats are used?