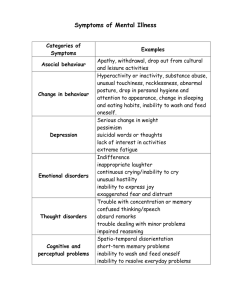
F.A.T. City Workshop (handout)
advertisement

F.A.T. City Workshop Outline Corresponds with the video Understanding Learning Disabilities: How Difficult Can This Be? I. Experiencing Frustration, Anxiety and Tension LD students experience these feeling when teachers: A. Use throwaway sarcasms which may make the rest of the class laugh, but create a victim out of the LD student. What is the definition of exclusion? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ B. Move through question and answer periods so rapidly that LD students cannot keep up and choose not to volunteer, or when called on, cannot answer. C. Become intimidating, and expect LD students to look at them when they speak to them. Anxiety affects performance in the classroom. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ II. Inability to Process Language LD students’ inability to process language as rapidly as others may make it necessary for teachers to: A. Move less rapidly through classroom discussion, especially the question and answer periods. B. Take the LD student aside and promise only to call on him/her when standing in front of the student’s desk. That way, only the teacher and the LD student know when the student is required to answer. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ III. Risk Taking Sometimes intimidating situations in the classroom make LD students hesitant to take risks. This leads to: A. Lack of participation in classroom discussion for fear of giving a wrong answer which will be ridiculed. B. LD students developing into LD adults who are reluctant to take chances. If teachers respond positively to answers that students give, then LD students might not be so reluctant to raise their hands and volunteer answers. This is a form of encouragement. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ IV. Visual Perception The visual perception problems of LD students make it difficult for them to immediately understand what they are looking at. This problem is exacerbated by teachers who: A. Urge the LD student to “try harder” to understand what he/she is having trouble making sense of. B. Engage in “blaming the victim” by accusing the LD student of not trying hard enough. Seeing is different than perceiving. Why does Mr. Lavoie emphasize this concept? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ V. Reading Comprehension A. LD students have trouble with reading comprehension even if they know and recognize individual words within a sentence. B. They may be dyslexic or might not have a grasp of the background information required to understand what they are reading. Comprehension often depends on background. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ VI. The Effect of Visual Perception on Behavior Often, the LD student gets into trouble and does not know what he/she did wrong. Misperceptions of visual stimuli can lead the LD student to give incorrect answers or respond inappropriately to situations. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ VII. Visual-Motor Coordination Difficulties with visual-motor coordination often make the writing process difficult for LD students. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ VIII. Oral Expression The inability to retrieve stored linguistic information the way others can is called dysnomia. Teachers can help with this problem by giving the LD student more time to answer and respond to questions. What is dysnomia, according to Richard D. Lavoie? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ IX. Reading and Decoding LD students are often dyslexic and they cannot decode information as quickly as others can. Teachers should try not to ask students rhetorical questions; they shut down communication between the teacher and student. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ X. Auditory and Visual Capabilities LD student often need to hear a written passage before they are able to comprehend it. Many LD students benefit from having books or lectures on tape. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ XI. Fairness Teachers are urged to reexamine the notion of what is “fair.” “Fair” does not mean that every student gets the same treatment, but that every student gets what he/she needs. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________