Corticospinal Tract
advertisement

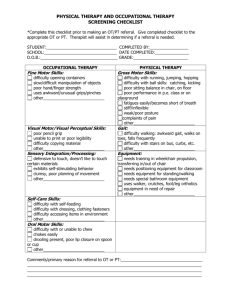
COMPARISON OF MOTOR SYSTEMS with examples from NeuroLogic Exam Website: http://library.med.utah.edu/neurologicexam/html/home_exam.html Normal examination samples are also on the same site. Lower Motor Neuron in Spinal Cord Upper Motor Neuron in Cortex Corticospinal Tract Cerebellum influences Basal Ganglia influences Efferent part of monosynaptic reflex Muscle tone by inhibiting antagonists Maintains muscle fibers (trophic factors) Voluntary willed movement Rapid coordinated alternating skilled movements that are learned Facilitates intentional movements and inhibits extraneous movements Muscle tone. Inhibition of lower motor neurons, so there is not too much muscle tone Fine control, espec. finger flexors Eye-head movements Autopilot for motor activities Posture and Gait Automatic movements such as walking, eating, running, drinking, dressing Normal Balance, equilibrium, orientation in space Timing, duration, and amplitude of movements 533581572 COMPARISON OF MOTOR SYSTEMS with examples from NeuroLogic Exam: http://library.med.utah.edu/neurologicexam/html/home_exam.html Lower Motor Neuron Spinal Cord Upper Motor Neuron Corticospinal Tract Cerebellum Basal Ganglia Weakness or paralysis Weakness or paralysis; spastic paralysis http://library.med.utah.edu/neurologi cexam/movies/gait_ab_08_x2.mov Hyperreflexia Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes http://library.med.utah.edu/neurologi cexam/movies/motor_ab_09_x2.mov No weakness No weakness Truncal ataxia, http://library.med.utah.edu/neuro logicexam/movies/coord_ab_10_ x2.mov gait ataxia http://library.med.utah.edu/neuro logicexam/movies/coord_ab_11_ x2.mov Nystagmus, Dizziness, http://vimeo.com/7563593 Shuffling or festinating gait, small steps, hard to turn or start moving typical of Parkinson’s Disease http://library.med.utah.edu/neurologi cexam/movies/gait_ab_12_x2.mov Abnormal Fasciculation http://library.med.uta h.edu/neurologicexa m/movies/motor_ab _01_x2.mov Muscle Atrophy http://library.med.uta h.edu/neurologicexa m/movies/cranialner ve_ab_25_x2.mov Flaccid paralysis 533581572 Babinski- extensor plantar reflex http://library.med.utah.edu/neurologi cexam/movies/motor_ab_10_x2.mov Spasticity http://library.med.utah.edu/neurologi cexam/movies/motor_ab_02_x2.mov Masked facies, few blinks see in video above Dysmetria- ataxia of arms Difficulty turning or starting, http://library.med.utah.edu/neuro hypokinetic = bradykinesia logicexam/movies/coord_ab_02_ x2.mov Decomposition of movement Paucity of associated movements Lower Motor Neuron Spinal Cord Upper Motor Neuron Corticospinal Tract Cerebellum Dysynergia Dysdiadochokinesia- inability to do rapid alternating movements http://library.med.utah.edu/neuro logicexam/movies/coord_ab_05_ x2.mov Hypotonia- pendular reflexes Intention tremor Scanning speech http://library.med.utah.edu/neuro logicexam/movies/coord_ab_01_ x2.mov 533581572 Basal Ganglia Chorea, athetosis, hyperkinetic typical of Huntington’s Disease http://library.med.utah.edu/neurologi cexam/movies/gait_ab_13_x2.mov Rigidity (cogwheel), lead-pipe Resting tremor seen in first video Soft speech