Security Devices / Trust Deed
advertisement
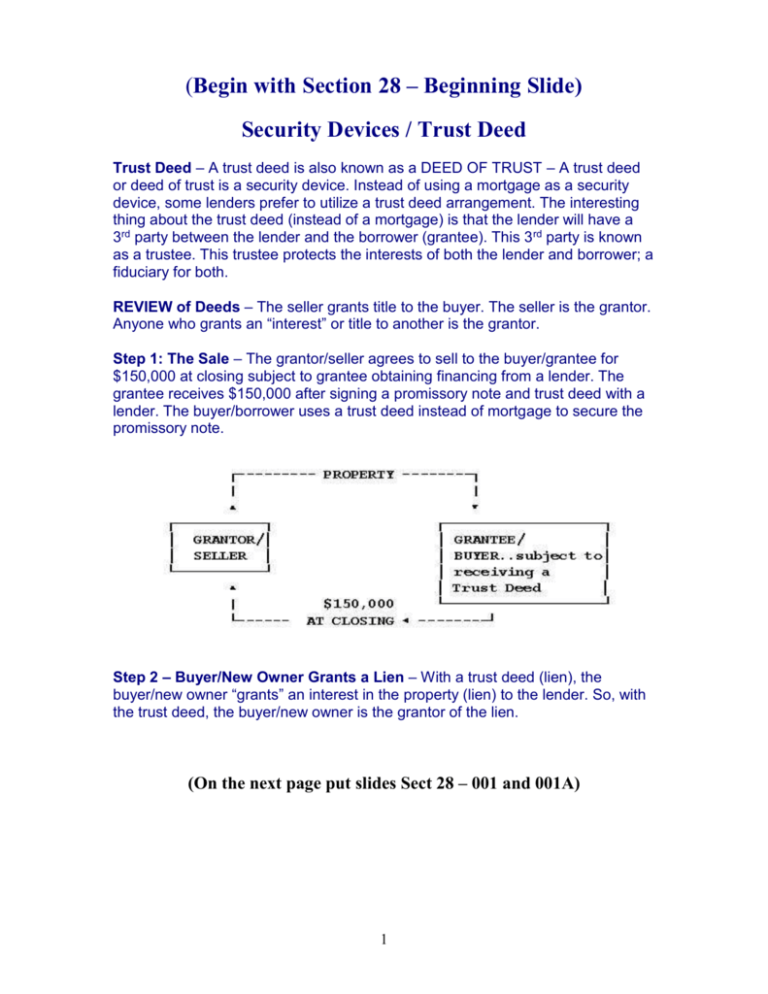
(Begin with Section 28 – Beginning Slide) Security Devices / Trust Deed Trust Deed – A trust deed is also known as a DEED OF TRUST – A trust deed or deed of trust is a security device. Instead of using a mortgage as a security device, some lenders prefer to utilize a trust deed arrangement. The interesting thing about the trust deed (instead of a mortgage) is that the lender will have a 3rd party between the lender and the borrower (grantee). This 3 rd party is known as a trustee. This trustee protects the interests of both the lender and borrower; a fiduciary for both. REVIEW of Deeds – The seller grants title to the buyer. The seller is the grantor. Anyone who grants an “interest” or title to another is the grantor. Step 1: The Sale – The grantor/seller agrees to sell to the buyer/grantee for $150,000 at closing subject to grantee obtaining financing from a lender. The grantee receives $150,000 after signing a promissory note and trust deed with a lender. The buyer/borrower uses a trust deed instead of mortgage to secure the promissory note. Step 2 – Buyer/New Owner Grants a Lien – With a trust deed (lien), the buyer/new owner “grants” an interest in the property (lien) to the lender. So, with the trust deed, the buyer/new owner is the grantor of the lien. (On the next page put slides Sect 28 – 001 and 001A) 1 Formation of a Loan - Step 2 The borrower gives a promissory note to the lender for $150,000. The lender gives the $150,000 needed by the borrower at closing. In the formation of the trust, the borrower becomes the trustor (giver of the trust deed). The lender now becomes the beneficiary of the trust. The trustee/3rd party will look after the lender regarding contracted payments by the borrower. 1. Borrower/Trustor - The borrower receives title to the property; lien theory state. The borrower/trustor gives a trust deed instead of a mortgage. So, instead of being known as the mortgagor, the borrower is known as the trustor. He/she is the trustor in issuing the trust deed. He/she gives the trust deed to a neutral 3rd party known as the trustee (receives the trust deed). 2. Trustee - A neutral 3rd party (referee) between the borrower and the lender. This trustee can only receive instructions from the beneficiary (lender) and the trustor (buyer). If the buyer or lender want to communicate, it goes through the trustee (3rd party). a. Trust Deed - A trust deed is not a deed. It does not convey interest in a property. It conveys the ability to sell property without having to go to a court to foreclose. If the borrower defaults on the promissory note and the lender/beneficiary tells the trustee that it is necessary to foreclosure, the neutral 3rd party (trustee) has to the power to sell the property (no sheriff's sale) under the power of sale clause. b. Naked Title - Because foreclosure does not require going before a judge, this is also referred to as naked title. The trustee has the stripped down rights to do a forced sale without going before a judge/court. 2 Performance (Paying Off) of a Loan - Step 3 Performance of a loan means the borrower has made all the contracted payments under the promissory note. The promissory note has been paid off. The owner must get something to record showing that the trust deed has been paid off. 1. Beneficiary/Lender - When the borrower has made all the payments or paid off the promissory note, this is called performance. The beneficiary/lender notifies the trustee that the debt is paid off. 2. Reconveyance Clause - Inside the trust deed (deed of trust) there is a clause called the reconveyance clause. This requires the trustee to reconvey the naked title back to the owner. The recordable document sent by the trustee to the borrower/ owner is a deed of reconveyance. This simply reconveys the complete title back to the owner in full. The power to sell is taken away from the trustee; no possible foreclosure. Mortgage vs. Trust Deed: 1. Full Payment - The mortgage has a defeasance clause and the trust deed has a reconveyance clause. Both release the lien that was placed on the title back to the owner when the debt is paid off. 2. Recordable Document - The mortgage release document is called a "satisfaction of mortgage" and the trust deed release document is called a "deed of reconveyance". 3 Foreclosure On a Trust Deed When the borrower/trustor defaults on the promissory note, the trustee will have to foreclose on the borrower/owner. The trustee cannot do this on his/her own. She/he must get instructions. The (promissory) note is being held by the beneficiary/lender. If the borrower defaults, the lender must notify the trustee/referee to foreclose on the trust deed. The following would occur: 1. Notification - The trustee must notify the borrower that he/she is late on their payments. The trustee must provide the borrower with 30 days notice of possible foreclosure. 2. Foreclosure by the Lender - The lender can foreclose on a trust deed or deed of trust. The lender would notify the trustee. The trustee can then sell under the power of sale clause in the trust. 3. 2 Methods of Foreclosure - The lender has two methods to foreclose on the borrower. They are Judicial Foreclosure and Sale as well as Advertisement and Sale. We will begin with Judicial Foreclosure and Sale. 4. Judicial Foreclosure and Sale - This is exactly the same as a mortgage. This involves the use of a sheriff's sale. The trustee would have to give proper notice. The trustee would have to go before a judge/court. The judge rules there is breach of contract (promissory note). The judge gives a writ of execution to the sheriff. The sheriff would sell. a. Right of Redemption - In most States the owner/borrower has a 1 year right of redemption. The borrower can come forward and pay off the promissory note and the expenses of the lender during this period. The buyer at auction would get their money back and the owner/borrower would gain back the title. b. Deficiency Judgment - Some States allow a deficiency judgment under a trust deed. If the sale money is not enough to cover the lenders promissory note and costs, the borrower has to make up the difference. 4 Foreclosure On a Trust Deed cont. Continued procedure and foreclosure of the trust deed. Instead of using the Judicial Foreclosure and Sale, the lender/beneficiary can have the trustee utilize Foreclosure by Advertisement and Sale. This method protects the lender's interest far more. 1. Foreclosure by Advertisement and Sale - This does not require the trustee to go to court or appear before a judge. This means the lender can foreclose without going to court. This is sometimes called a trustee sale. Trustee procedure under this lender option: a. Trustee Gives Proper Notice. Anywhere from 30 to 60 days depending on the State laws (we will look at your State later). b. Becoming Current - The owner/borrower has this time period to become current. 2. Trustee Invokes the Acceleration Clause - The trustee calls the debt due and payable and starts advertising of the sale to the highest bidder. The trustee must advertise a minimum of once a week for 4 weeks. 3. Trustee Sale - The trustee must wait 20 additional days after the 4th advertisement and then can hold a trustee sale. The owner/borrower has the right to reinstate the loan up until 5 days prior to the trustee sale. When it is 4 days before the sale, there is nothing the borrower/owner can do. The trustee holds the sale (no sheriff). The highest bidder will receive a trustee's deed on the spot. There is NO statutory right of redemption after the sale. No additional 1 year to redeem by the borrower/owner. He/she must immediately move out of the property foreclosed. 4. Buyer Possession - The new buyer will gain possession of the property after 10 additional days beyond the trustee sale. 5. Time Period of Foreclosure - A borrower under a trust deed could lose possession of the property within 78 days instead of 1 year. 30 days to notify the owner. 4 weeks (28 days) of advertising. And 20 days before the trustee sale. Renew the Loan - The owner can only renew the current loan up until 5 days prior to the trustee sale. This gives the borrower/owner 73 days to renew the loan. 5 Trust Deed - Foreclosure Procedures The following is a summary of the foreclosure options that the trustee can pursue on behalf of the lender as stated in the Power of Sale clause in the Trust Deed (Deed of Trust). Option 1: Judicial Foreclosure and Sale - "A trust deed may be foreclosed as if it were a mortgage". This option would have all the same characteristics. 1. Notice - 30 days to notify of foreclosure. 2. Court - The Court issues a Writ of Execution (to have sheriff sell the property). 3. Sheriff's Sale - Sheriff sells to the highest bidder. If it doesn't pay off the debt and legal costs a deficiency judgment can be issued against the owner/borrower. Some States restrict the right to a deficiency judgment. 4. Purchaser - Bidder is given a Certificate of Sale. The borrower now has an additional year of possession under the 1 year Period of Redemption. 5. Total Time of Foreclosure - The total process has been known to take a total of 2 years before the borrower has to move out. 6 Trustee's Sale Foreclosure By Advertising & Sale Trustee advertises for bids on the subject property. The procedure under this foreclosure method is as follows: 1. Notice - Proper notice to borrower to bring the lien current. This time period varies from State to State; 30 to 60 days. 2. Trustee Acts - If the borrower does not bring the lien current during the notification period, the trustee invokes acceleration clause. 3. Advertisement - There is a 4 week advertisement period in a newspaper of general circulation. After the 28 day period of advertising, the trustee waits 20 additional days to hold the trustee sale. 4. Trustee's Sale - The highest bidder receives a trustee's deed. 5. Possession - Purchaser gains possession 10 days after the sale. 6. No Right of Redemption - The owner has no redemption right, only a loan reinstatement right that ends 5 days before the trustee's sale. 7







