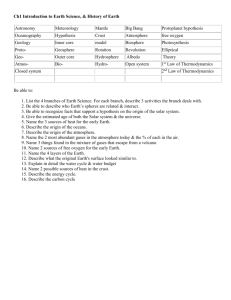
Part 1 - cosee now
advertisement
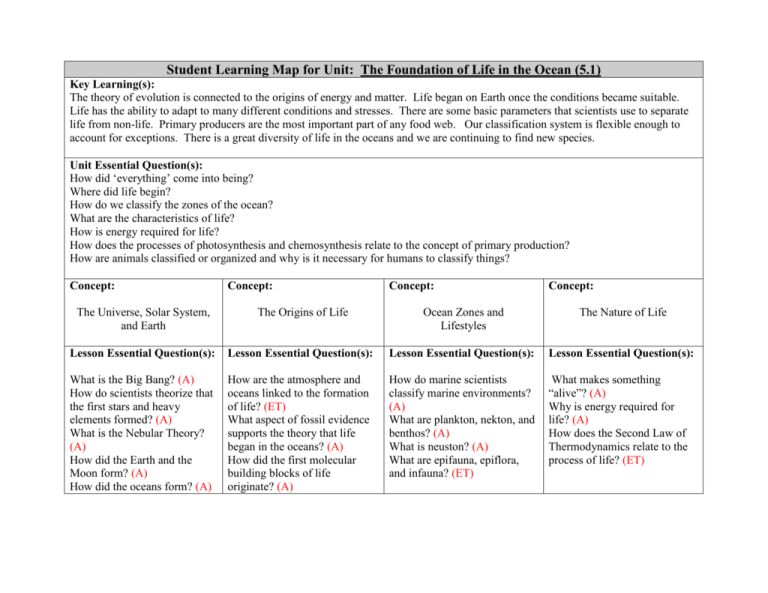
Student Learning Map for Unit: The Foundation of Life in the Ocean (5.1) Key Learning(s): The theory of evolution is connected to the origins of energy and matter. Life began on Earth once the conditions became suitable. Life has the ability to adapt to many different conditions and stresses. There are some basic parameters that scientists use to separate life from non-life. Primary producers are the most important part of any food web. Our classification system is flexible enough to account for exceptions. There is a great diversity of life in the oceans and we are continuing to find new species. Unit Essential Question(s): How did ‘everything’ come into being? Where did life begin? How do we classify the zones of the ocean? What are the characteristics of life? How is energy required for life? How does the processes of photosynthesis and chemosynthesis relate to the concept of primary production? How are animals classified or organized and why is it necessary for humans to classify things? Concept: Concept: Concept: Concept: The Universe, Solar System, and Earth The Origins of Life Ocean Zones and Lifestyles The Nature of Life Lesson Essential Question(s): Lesson Essential Question(s): Lesson Essential Question(s): Lesson Essential Question(s): What is the Big Bang? (A) How do scientists theorize that the first stars and heavy elements formed? (A) What is the Nebular Theory? (A) How did the Earth and the Moon form? (A) How did the oceans form? (A) How are the atmosphere and oceans linked to the formation of life? (ET) What aspect of fossil evidence supports the theory that life began in the oceans? (A) How did the first molecular building blocks of life originate? (A) How do marine scientists classify marine environments? (A) What are plankton, nekton, and benthos? (A) What is neuston? (A) What are epifauna, epiflora, and infauna? (ET) What makes something “alive”? (A) Why is energy required for life? (A) How does the Second Law of Thermodynamics relate to the process of life? (ET) What is the common theory about how the early atmosphere formed? (A) KEY: (A) – Acquisition Lesson (ET) – Extended Thinking Vocabulary: Accretion Astrology Astronomy Atmosphere Density stratification Nebular Star What are heterotrophs and autotrophs? (A) Why is oxygen important to life? (A) What is the Theory of Evolution? (A) How does evolution explain the origin of the different organisms that exist today? (A) Vocabulary: Abiogenesis Atmosphere Autotroph Heterotrophy Hypothesis Photosynthesis Model from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2008) Vocabulary: Abyssalpelagic Bathypelagic Benthic Epifauna Epiflora Epipelagic Hadalpelagic Littoral Mesopelagic Nekton Neritic Pelagic Plankton Supralittoral Vocabulary: Cells Element Energy Entropy Machine Matter Thermodynamics