References
advertisement

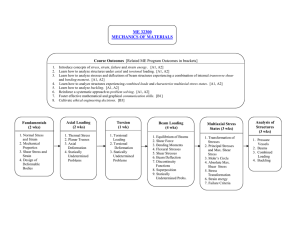
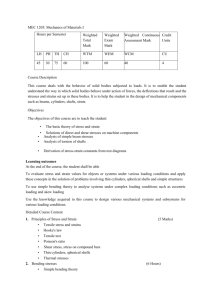
EMA 3702 Mechanics of Materials (3) Spring 2011 A mid-level course addressing the selection of engineering materials based on static and dynamic loadings, environmental analysis and the experimental analysis of mechanical systems. Emphasis on metals and composite materials. Professor: Cesar Levy Office EC3474 Class T 1230-315pm and R 1230-145pm in EC1110 Office hours: T and W 1530--1700. Use my office hours as a resource as well. Tel: (305) 348-3643 (voice mail) e-mail: levyez@fiu.edu PLEASE NOTE UPDATED EMAIL ADDRESS Textbook: Beer, Johnston, DeWolf and Mazurek, Mechanics of Materials, 5th Ed., McGraw Hill References: There are plenty of books at the FIU Library on the subject. Here is a list of a few books on the subject available at the library. Engineering mechanics of solids. Egor P. Popov. Englewood Cliffs, N.J. : Prentice Hall, c1990. Mechanics of materials. James M. Gere, Stephen P. Timoshenko. 3rd ed. Boston : PWS-KENT Pub. Co., c1990. Problem solver in strength of materials and mechanics of solids staff of Research and Education Association ; M. Fogiel, director. Rev. print. Piscataway, N.J. : The Association, 1988, c1980. Engineering considerations of stress, strain, and strength, Robert C. Juvinall, New York, McGraw-Hill [1967]. Elements of mechanics of materials Gerner A. Olsen. Englewood Cliffs, N.J. Prentice-Hall, c1982. Course Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Identify mechanical properties and the characteristics of elastic behavior for material types. Calculate the stress and strain configuration at a point for a specific loading arrangement. Transform plane stress and strain configurations and identify principal stress and Principal Axes. Use the appropriate failure criteria for diverse situation and/or materials (elastic behavior only). Design prismatic beams. Determine the deflection at any point of a beam, given the loading and end conditions Determine the load, shear and moment diagrams for a beam given the loading and end conditions. Topics By Week 1. 2. 3. 4. Introduction. Shear and Bending Moment Diagrams. Relation among load, shear and bending moment Normal and Shear stresses. Bearing stresses. Stress on an oblique plane. Stresses under general conditions Transformation of Stresses. Principal Stresses. Stress and Strain – Axial Loading. Stress vs. strain. Hooke’s law. Fatigue and deformations of members under axial load. Transformation of Strains. EXAM 1 5. Thermal Stresses, Poisson ratio. Generalized Hooke’s law 6. Saint Venant’s Principle. Stress Concentration. Torsion. Stresses in a shaft Deformations and angle of twist 7. Statically indeterminate shafts. Stress concentration in circular shaft 8. EXAM 2. Analysis and Design of Beams. Pure Bending. Stresses and deformations in the elastic range 9. Bending on members made of several materials. Stress Concentration. General case of eccentric axial loading 10. Prismatic beams for bending. EXAM 3. 11. Quick Review of Transformation of Stresses and Strains. Principal Stresses. Mohr’s Circle: Plane Stress. General State of Stress 12. Stresses in Thin-Walled pressure vessels. Mohr’s Circle: Plane Strain. Strain Rosette 13. Deflection of Beams. Beam deflection by integration. Statically indeterminate beam. 14. Superposition Method. EXAM 4. Columns. Euler’s formula. 15. Extension Euler’s formula. Design of columns: centric and eccentric load. Failure Criteria Homeworks are going to be assigned and some problems will be collected, unless specified in class. These problems should be neatly worked out, on engineering paper/graph paper, one problem to a page. One or more of the assigned problems will be chosen randomly for grading. In preparing the homework, use the “Given, Required, Solution” format and completely draw appropriate diagrams and coordinate systems. All numerical answers should have the appropriate units. The collected HW grade may be used to replace your Exam 1 quiz grade and it would behoove you to do all problems as the exam questions will be similar in nature. You must keep up with the homework in order to do well in class. Exams: as you see below we have 4. No make-up exams will be given except for medical reasons. If you know you will be out, for example for work reasons, you need to tell me BEFORE the exam, not after. You can inform me (or have a parent or wife or best friend inform me) by email (levyez@fiu.edu) or by phone (305-348-3643). CHEATING: Cheating will not be tolerated; it is an ethics violation. Also, you don’t learn anything by cheating. All instances of cheating will automatically result in a zero grade, especially exams, and will result in disciplinary action against ALL cheaters. Grading Exam 1 or HW grade Exams (2-4: 21%, 21%, 22% each) Final Exam Total 6% 64% 30% 100% Grades will be assigned based on your performance on the activities above. Final letter grades will be assigned as follows: 100 – 93 87-92.99 84-86.99 80-83.99 A AB+ B 77-79.99 73-76.99 70-72.99 67-69.99 BC+ C C- 63-66.99 60-62.99 Below 60 D+ D F FINAL EXAM (Cumulative): Will be announced as soon as the new exam schedule is released. NOTE: This is a preliminary syllabus and it might be changed during the semester. Any change will be announced in class.


![Applied Strength of Materials [Opens in New Window]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009007576_1-1087675879e3bc9d4b7f82c1627d321d-300x300.png)