Activities to be conducted in the classroom
advertisement

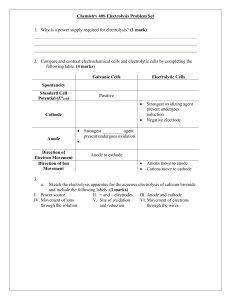
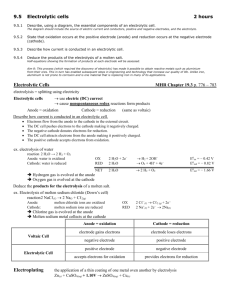
ASSESSMENT 1 QUESTIONS 1. Choose the correct half equations for anode and cathode in electrolysis of lead(II) bromide Anode Cathode A. 2Br- Br2 + 2e 2H+ + 2e H2 + B. 2H + 2e H2 2Br- Br2 + 2e C. 2Br- Br2 + 2e Pb2+ + 2e Pb 2+ D. Pb + 2e Pb 2Br- Br2 + 2e 2. Which A. B. C. D. 3. What is needed to compose an electrolytic cell? I. anode and cathode II. ammeter III. batteries IV. anions and cations A. I and II only B. I , II and III only C. I and III only D. I, II , III and IV 4. During A. B. C. D. the electrolysis of molten sodium iodide, iodide ions move to anode and release electrons. to anode and receive electrons. to cathode and receive electrons. to cathode and release electrons. 5. During A. B. C. D. electrolysis, which of the following energy change occurs? Electrical → light Chemical → heat Electrical → chemical Chemical → electrical of the following statements is incorrect? Cations are formed when neutral atoms release electrons. Electrons flow from cathode to anode in an electrolytic cell. Anions are discharged at the anode when they release electrons. Cations are discharged at the cathode when they release electrons. ASSESSMENT 1 6. Carbon rods Lead(II) chloride The diagram shows electrolysis of molten lead(II) chloride. Which of the results best fit the experiment? A. Small bulb Lights up Anode Shiny grey solid is formed B. Lights up C. Lights up Bubbles of greenish yellow gas is released Shiny grey solid is formed D. Lights up Greenish yellow gas is released Cathode Bubbles of greenish yellow gas is released Shiny grey solid is formed Greenish yellow gas is released Shiny grey solid is formed 7. Which of the following equation occur at the anode during the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide? A. 2Br+ + 2e →Br2 B. 2Br - → Br2 + 2e C. Pb 2+ + 2e → Pb D. Pb → Pb 2+ + 2e 8. An electrolytic cell is made up of the following materials I Salt bridge II Batteries III Electrodes IV Electrolyte A. I and II only B. III and IV only C. I, II and III only D. II, III and IV only ASSESSMENT 1 9. The diagram shows electrolysis of lead(II) bromide. What is the expected observation at the electrodes? A. B. C. D. Anode Cathode Bubbles of colourless gas can be seen A brown gas evolves A reddish brown solid is formed A brown gas evolves Shiny grey solid is formed Shiny grey solid is formed A brown gas evolves Bubbles of colourless gas can be seen 10. What will not happen to the freely moving ions in electrolysis of molten electrolyte? A. Freely moving ions will be discharged at the electrodes B. Freely moving ions will not cluster at the electrodes C. Freely moving ions will move towards the electrode D. Freely moving ions will be selectively discharged 11. What A. B. C. D. happen to cations at the cathode in electrolysis of molten electrolyte? Cations release electrons and become atoms. Cations accept electrons and become atoms. There are two types of cations present. Cations cluster around cathode. ASSESSMENT 1 12. Figure above shows the set-up for the electrolysis of a mixture of molten sodium chloride and molten copper(II) chloride. Which of the following is produced at the cathode during electrolysis? A. Chlorine gas is released B. Only sodium metal is deposited C. Only copper metal is deposited D. Both copper metal and sodium metal are deposited together 13. Which anode A. B. C. D. of the following equation would not represent the reaction occur at the during electrolysis of molten electrolyte? 2H + + 2e H2 2Br- Br2 + 2e 2F- F2 + 2e 2I- I2 + 2e 14. All of these are correct except A. Pb2+ + 2e Pb B. Cations move towards cathode C. Anions are discharged at the anode when they accept electrons D. There are freely moving Pb2+ ions and I ions in molten lead(II) iodide ASSESSMENT 1 15. Which of the following statements are CORRECT about electrolysis? I An electrolyte is made up of an ionic compound which is in molten or aqueous states. II The ionic compound dissociates into free positive and negative ions in all physical states. III The positive ions are attracted to the cathode during electrolysis. IV The negative ions are attracted to the anode during electrolysis. A. I and IV only B. II and III only C. I, III and IV only D. II, III and IV only 16. Carbon rods Iodine crystals A group of students want to conduct an experiment on electrolysis of molten electrolyte. They have the set up as shown in the diagram. However, when the switch is closed, the ammeter does not give any readings. Which of these might cause the problem? A. The electrodes are wrongly connected. B. The ammeter is wrongly connected. C. There are no freely moving ions. D. The electrolyte is not melting. 17. Which A. B. C. D. of the following statements is TRUE for an electrolytic cell? The anode is the more electropositive elements of a metal pair. Anions are discharged at the anode when they accept electrons. Cations accept electrons to achieve noble gas electron arrangement at the cathode. Electrons flow from the cathode to the anode in an electrolytic cell. ASSESSMENT 1 18. The diagram shows the set up of apparatus for the electrolysis of molten lead(II) chloride using carbon electrodes. Which of the following statements are TRUE? I Lead(II) ion accepts two electrons to form lead atom II The gas produced at the cathode is yellowish green in colour. III Lead(II) chloride can only conduct electricity in the molten state. IV Chloride ion donates one electron to form chlorine atom. A. I, II and III B. I, II and IV C. I, III, and IV D. II, III and IV 19. The diagram shows the electrolysis of sodium chloride. However, the ammeter needle did not deflect. Which of the following can be done to enable electric current to flow through the circuit? I Add water to sodium chloride powder. II Add a battery variable resistor to the outer circuit. III Heat sodium chloride powder until it melts. IV Replace carbon electrodes with copper electrodes. A. II and III only B. I and III only C. I, II and III only D. I, II, III and IV ASSESSMENT 1 20. The diagram A. B. C. D. shows an electrolytic cell. Substance X could be glucose solution. molten aluminium oxide. copper(II) carbonate powder hydrogen chloride in methyl benzene.