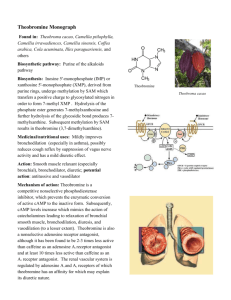
Document

1
Chemistry 151
Professor Whitesell
Essay Code C2
RW: C2
The Joys of Chocolate and Theobromine
Chocolate has become a part of everyday life throughout the world. Many enjoy different chocolate selections such as cake, ice cream, chocolate bars, etc. as desserts. Eating and giving chocolate is also a common occurrence during holidays such as Valentine’s Day, Easter,
Halloween and Christmas. It is no wonder why chocolate has grown into a more than $80 Billion a year industry. Europeans, specifically individuals from Switzerland, consume the greatest amount of chocolate. Europeans are said to consume an average of 24 pounds of chocolate per person, per year. Americans on the other hand are said to consume an average of 11 pounds of chocolate per person, per year [9]. It takes about twelve cocoa seeds to make one ounce of dark chocolate, while it takes about four cocoa seeds to make one ounce of milk chocolate [6]. The primary alkaloid in cocoa beans is Theobromine and is present in the cocoa bean, throughout the production of chocolate and in the chocolate product [7]. This is a good introduction paragraph.
You might want to add why people like chocolates and how theobromine effects the brain.
Theobromine Structure [7]
Many people eat chocolate but are unaware of the long process of changing the cocoa bean into the chocolate we eat. The majority of cocoa in the world is produced in Africa, South
American and the Ivory Coast [9]. Cocoa beans are found in pods which grow on Theobroma cacao trees. In order to begin the process of making chocolate, the cocoa beans as well as the pulp which surrounds the beans are removed from the pods. The cocoa beans and the pulp are then left in baskets or containers for anywhere from two to eights days in order to ferment together. The fermentation allows the flavors of the beans to blend and mellow together. The beans would become too bitter if the fermentation process was unable to occur. The time variation in the fermentation process is associated with the quality of chocolates which the beans will go on to produce. A longer fermentation process is usually correlated with higher quality chocolates, while a shorter fermentation process is usually correlated with lower quality chocolates [8]. Try to elaborate how fermentation effect the quality of chocolate. Does the theobromine structure change? How does the chemistry work with fermentation?
2
Cocoa Beans and Pulp in Pod [1] Cocoa Beans Drying in Sun [1]
After the desired fermentation process is complete, the beans are taken out of the containers and are left to dry by spreading the beans out into a single layer and left in the sunlight. This drying process are often times done on wooden floors or electric dryers and can take anywhere from one to two weeks. During this time, the beans change their color from a reddish brown to a darker brown. After the drying process is complete, the beans are then able to be sent around the world to various chocolate manufactures [1]. For the drying process, is there a difference between the colors and the quality of chocolate? From the previous paragraph, fermentation time effects the quality of chocolates. Does reddish brown color show shorter or longer duration fermentation?
Once the cocoa beans are at different chocolate manufacturing plants, the beans are roasted for various lengths of time and temperatures in order to reveal more of the bean’s color and flavor. After roasting the beans, they are transferred to a machine called a winnower. The winnower removes the bean’s shells and the beans are then called nibs. These nibs contain cocoa butter, the fat, and are ground together to create a paste which begins to smell and resemble the typical chocolate we consume [8]. The paste made by the nibs has pressure applied to it in order to remove the cocoa butter so that only about 10-25% of the cocoa butter still remains [1]. The leftover paste is pulverized and becomes cocoa powder [8]. Perhaps add pictures of the structure of cocoa butter and fat.
Depending on the type and quality of chocolate which is going to be made, different ingredients are then added to the cocoa powder. Lower quality chocolate is produced by mixing the cocoa powder with vegetable fats, sugar and other flavorings. Higher quality chocolate on the other hand is produced by mixing cocoa powder with re-added cocoa butter, milk, sugar, vanilla, etc. The mixed chocolate solution (cocoa powder and added ingredients) is then smoothed out by rollers and sent to the conching machines. The conching machines massage and knead the chocolate mixtures from anywhere from hours to a couple of days. The conching process determines the texture and flavor of the final chocolate product due to the variation of length, temperature and speed of the conching process. After the conching process, the chocolate mixture is tempered(cooled at a precise temperature) in order to produce a smooth and shiny appearance. Finally, the chocolate is able to be molded and shaped, wrapped and shipped out for other to enjoy [8]. Perhaps give examples of lower quality and higher quality brand name chocolates such as milky way, lindt chocolates.
3
As stated before, Theobromine is present in cocoa beans, through out the chocolate making process, and the end chocolate product. Depending on the type of cocoa beans, the amount of Theobromine varies. The amount of Theobromine in cocoa beans can be anywhere from 300-1200 mg/ounce [7]. The amount of Theobromine also varies by the type of chocolate made. White chocolate contains the least amounts of Theobromine of any type of chocolate [2].
Milk chocolates and chocolate syrups contain the second least amount of Theobromine. Cocoa powder, dark chocolates and unsweetened baking chocolate contain the most amount of
Theobromine. To give a comparison, a regular Hershey’s milk chocolate bar contains about 64 mg of Theobromine, while a Hershey’s dark chocolate bar contains about 215 mg of
Theobromine [3]. Try to explain how would the amount of theobromine effect the chocolate bar.
Would it taste bitter or sweet? Which one would be healthier to eat?
Product
Serving
(g)
Theobromine
(mg) 2
HERSHEY’S Milk Chocolate
HERSHEY’S BLISS Dark Chocolate
REESE’S Peanut Butter Cups
1.55 oz (43 g)
6 pieces (43 g)
2 cups (42 g)
64
215
26
YORK Peppermint Pattie 1 piece (39 g) 53
Amount of Theobromine Found in Different Chocolate Products [3]
Society may be curious of the different effects Theobromide has on the human body.
Theobromine is responsible for the feel good sensation individuals get from eating chocolate.
Theobromine is very similar to caffeine, but the effects which Theobromine elicit are on a much smaller scale to caffeine’s effects [4]. Theobromine is a mild stimulant like caffeine, but does not affect our central nervous system as much as caffeine does [2]. Theobromine is a mild diuretic, which increases urine production. Theobromine also dilates blood vessels so more blood is able to get through veins and arteries quicker. Lastly, Theobromine aids in relaxing the smooth muscle and bronchi of the human lungs [7]. From the previous paragraph, compare which chocolate bar is recommended to consume. Does consuming a chocolate bar with more theobromine amount is better for health reason?
While Theobromine is common in chocolate, this molecule is common in other foods and drugs. Theobromine is also found in tea, cola nuts and is also used to flavor some soft drinks. As stated before, Theobromine affects the human body in many different ways. While Theobromine is sold as a supplement, Theobromine can and is used in many different drugs. It is sometimes used in medications which treat asthma because it helps to relax the smooth muscles of the lungs.
It is also sometimes suggested to eat some chocolate when one has a cough because
Theobromine is known as a mild cough suppressant [4]. Theobromine is used in some medications used to treat high blood pressure because its ability to dilate blood vessels. Also,
Theobromine is sometimes used in medications which help patients suffering from cardiac
4 failure. When a individual with cardiac failure has an accumulation of body fluids, Theobromine helps rid the fluid, due to its’ diuretic properties [7].
This paragraph is good.
Although Theobromine provides many benefits for the human body, too much
Theobromine, like too much of anything else, can cause Theobromine poisoning. Theobromine poisoning is more common in animals but only affects a small amount of humans. Early stages of Theobromine poisoning in humans may cause symptoms such as sweating, trembling, headaches and nausea. In more extreme cases, individuals may need to be hospitalized; it is more common that the elderly with poisoning needs to be hospitalized. Theobromine is said to be many times fatal if an individual has contains more than 1000mg/kg of Theobromine in their body [2].
Perhaps adding a sentence or two of having 5 Hersey’s dark chocolate bar in a day is fatal because they would have consume more than 1000mg of theobromine. A sentence proving people have actually have died consuming too much.
While Theobromine is many times fatal for humans who have more than 1000mg/kg in their body, for animals Theobromine is much more dangerous. Theobromine is especially dangerous for dogs and the amount of Theobromine needed to become fatal in dogs is significantly less than that for humans. Amounts of Theobromine as low as 20mg/kg can cause agitation, hyperactivity, vomiting and diarrhea. Theobromine amounts greater or equal to about
40mg/kg can cause high blood pressure, increased heart rate and possible heart arrhythmias.
Theobromine amounts greater or equal to about 60mg/kg can cause twitching, tremors and seizures. It is believed that at amounts of 100mg/lb or greater, Theobromine in dogs can cause fatalities. To give an example, a fifty pound dog that eats 8 ounces of milk chocolate can show signs of poisoning [5]. Good.
Animals are affected more profoundly to Theobromine due to difference of half lives.
The amount of Theobromine in humans is half the amount after six to ten hours, but animals take two times to amount of time humans do in order to have half the amount [7]. Due to this difference, it can take animals several hours to develop signs of Theobromine poisoning and several days for the symptoms of the poisoning to go away [5]. It is also important to remember that different types of chocolate contain more Theobromine than others. Even if an animal has less amounts of dark chocolate, it is still more likely to do more damage than larger amounts of milk chocolate. Good. Perhaps this paragraph can be combine with the previous paragraph.
If an animal does have Theobromine poisoning, there are different treatment options for them. One common treatment for animals is to be given medication to induce vomiting. Another treatment is to be given charcoal in order to block Theobromine absorption. Animals may also be given a fluid therapy to dilute the Theobromine and help to excrete it faster [5]. What about human poisoning? Is there other treatments or the same? Or don't consume too much in a day?
As stated before, Theobromine is the primary alkaloid in cocoa beans and chocolate.
More specifically, Theobromine belongs to methlyxanthines, which are a class of alkaloids.
Other methlyxanthines include caffeine in coffee and theophylline in tea [7]. Other well known alkaloids include nicotine, cocaine and quinine [4]. Short paragraph, perhaps compare theobromine to caffeine.
5
The Theobromine found in cocoa beans is present throughout the process of making chocolate and is present in the chocolate which we enjoy. Dark chocolate was found to have more Theobromine in it than other types such as milk and white chocolate. Although
Theobromine does have some benefits to the human body such as dilating blood cells and being a cough suppressant, too much Theobromine can cause poisoning. In human individuals
Theobromine poisoning is not very common, but chocolate indulgers must be careful that animals do not digest it because this molecule is very dangerous, especially for dogs. Chocolate has become a part of everyday life for many people around the world and continues to satisfy our sweet tooth. Overall, this essay is good. There are a few questions and statements that need to be thought about in this essay. Great job!
Works Cited
1.
"About Cacao Beans, Cocoa and Chocolate." Cacaoweb.net
. N.p.. Web. 22 Feb 2014.
<http://www.cacaoweb.net/cocoa-chocolate.html>.
2.
Blum, Deb. "The Poisonous Chemistry of Chocolate." Wired . N.p., 14 02 2013. Web. 22 Feb
2014. <http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2013/02/the-poisonous-nature-of-chocolate/>.
3.
"Caffeine and Theobromine." The Hershey Company . N.p.. Web. 22 Feb 2014.
<https://www.thehersheycompany.com/nutrition-and-wellness/nutritioninformation/ingredients/caffeine-theobromine.asp&xgt;.
4.
"Chemistry in its Element-Theobromine." Royal Society of Chemistry . N.p., 14 02 2013.
Web. 22 Feb 2014.
<http://www.rsc.org/chemistryworld/podcast/CIIEcompounds/transcripts/theobromine.asp>.
5.
"Chocolate Poisoning for Dogs." VCA Animal Hospitals . N.p., 14 02 2013. Web. 22 Feb
2014. <http://www.vcahospitals.com/main/pet-health-information/article/animalhealth/chocolate-poisoning-for-dogs/537>.
6.
"Exhibit Archive- Chocolate Facts." California Academy of Science . California Academy of
Sciences. Web. 22 Feb 2014.
<https://www.calacademy.org/exhibits/chocolate/chocolate_facts.php>.
7.
Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D. "Theobromine Chemistry- Theobromine Is Chocolate's
Caffeine Relative." About.com
. N.p.. Web. 22 Feb 2014.
<http://chemistry.about.com/od/factsstructures/a/theobromine-chemistry.htm>.
8.
LaBau, Elizabeth. "From Bean to Bar: How Chocolate is Made." About.com Candy . N.p..
Web. 22 Feb 2014. <http://candy.about.com/od/workingwithchocolate/a/beantobar.htm>.
9.
"Who Consumes the most chocolate?." CNN Freedom Project . 17 01 2012: n. page. Web. 22
Feb. 2014. <http://thecnnfreedomproject.blogs.cnn.com/2012/01/17/who-consumes-themost-chocolate/>.