Intermediate 2 Biology Revision Unit2
advertisement

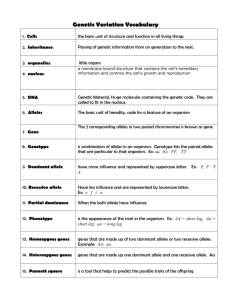
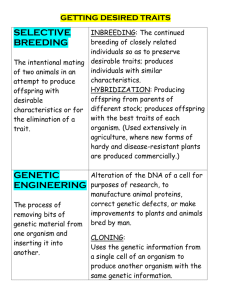
Intermediate 2 Biology Revision Use you Rise section Notes to complete the following tasks 5.1 Ecosystems 1. 2. 3. 4. The place where a living organism lives. The total number of ONE type in a habitat. Made up of all the living organisms of all types in a habitat. The natural unit made up of one or more habitats and the community or communities of plants and animals living there. 5. A group of living organisms that can interbreed, producing fertile offspring. 5.2 Food Chains & Food Webs 1. The feeding relationship showing the flow of energy through a series of organisms. 2. The arrows in a food chain show this. 3. The term given to plants who ALWAYS start the food chain. 4. The process by which plants convert light into chemical energy. 5. A diagram that shows how all the food chains in a community are linked. 6. The term given to all animals because they need to eat to gain energy. 7. The first animal in a food chain. 8. The second animal in a food chain. 5.3 Energy Flow in Food Chains 1. A diagram that represents the number of organisms at each stage in a food chain. 2. Name 2 diagrams that always fit the expected triangular shape. 3. Write a definition for each. 4. State why these two diagrams fit the expected triangular shape. 5.4 Adaptation & Stability 1. The term to describe the role of an organism within its habitat. 2. A feature an organism has that enables it to survive successfully in its habitat. 3. The role of decomposers in a stable ecosystem. 4. Describe the relationship between population size and stability. 5. Describe the relationship between the community size and stability. 5.5 Biodiversity 1. Define biodiversity. 2. Give four reasons why Biodiversity is important to humans. 3. Give four human activities that cause habitat destruction. 4. Name one pollutant and describe how it can cause damage to an ecosystem. 5. Sketch a graph to illustrate the relationship between grazing and species diversity. 6. Describe how grazing impacts on biodiversity. 5.6 Behavioural Adaptations 1. The term used to describe a change in an organism’s surroundings that the organism is sensitive to. 2. The reaction from the organism to an environmental stimulus. 3. Complete the following table for four organisms: Organism Environmental Stimulus Behavioural Response 4. Define ‘survival value’ 5.7 Competition 1. Name 3 resources plants compete for. 2. Name 2 resources animals compete for. 3. Compare the impact of competition between members of the same species and members of different species. 6.1 Sexual Reproduction in Plants 1. 2. 3. 4. Specialised part of female plants that produce sex cells. Specialised part of male plants that produce sex cells. Term for sex cells in animals and plants. Describe the route of a pollen gamete from landing on a plant to the fertilisation of the ovule. 5. The term given to the newly ‘fused’ male and female sex cell 6. In asexual reproduction all the offspring are genetically identical. What does sexual reproduction create? 6.2 Sexual Reproduction in Mammals 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 7. 8. Name the male and female sex cells in animals. Where are female sex cells produced? Where are male sex cells produced? Where does fertilisation take place in mammals? How many sperm can fertilise a single egg cell? No two sperm or eggs are genetically….. Explain why gamete formation means brothers and sisters cannot receive the same combination of parental characteristics 6.3 Genetic Information 1. Define a chromosome 2. Where are chromosome found? 3. 4. 5. 6. What are chromosomes made from? Describe the structure of DNA Name the complementary bases? Define a gene 6.4 Genes & Proteins 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The bases in DNA carry the code to make … These add together in long chains to form … How many bases code for one amino acid? Explain the term ‘genetic code’ How does the structure of a protein relate to its function (hint give an example) 6.5 Gamete Production 1. What is the term given to cells in the reproductive organs that divide to form gametes? 2. Draw a labelled diagram of a chromosome in a gamete mother cell just before it divides 3. Name the process of cell division that produces gametes 4. What happens to the total number of chromosomes during this type of division? 5. What is the term for ‘chromosome shuffling’ 6. How many chromosomes are contained in: 1. Female human gamete? 2. Male human gamete? 3. A zygote? 6.6 Sex Determination 1. How many of the 23 pairs of chromosomes determine sex? 2. Describe the sex chromosomes of females and the sex chromosomes of males. 3. Describe the sex chromosomes that could appear in a male sperm cell. 4. Describe the sex chromosomes that could appear in a female egg cell. 5. Use this genetic cross to explain the sex ratio in the human population 6.7 Genes and Alleles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Define an ALLELE How many alleles do humans have in their body cells for each gene? How many alleles do humans have in their gametes for each gene? What is meant by segregation of alleles? What is meant by the term dominant? What is meant by the term recessive? 7.1 Alleles and Appearance 1. What term is used to describe possessing identical alleles for a characteristic? 2. What term is used to describe possessing different alleles for a characteristic? 3. What term is used to describe the alleles an organism carries for a particular characteristic? 4. How are these alleles represented? 5. What term is used to describe the physical appearance of the characteristic coded for by the genes? 6. What term can be used to describe the genotype of a ‘true breeding’ organism? 7. How do the alleles appear in this organism? 8. What term is used to describe the appearance of different alleles for a characteristic? 7.2 Monohybrid Crosses 1. 2. 3. 4. Define a monohybrid cross. What term is used to describe original parents in a genetic cross? What term is used to describe the offspring from this generation? If these offspring are crossed with their siblings, what term is used to describe this cross? 5. If these offspring are crossed with the homozygous recessive parent, what term is used to describe this cross? 6. Complete this punnet square and calculate a. The genotype ratio b. The phenotype ratio (These ratios are ALWAYS TRUE of F2 generations from true breeding parents) 7.3 Types of Monohybrid cross 1. State why test crosses are performed 2. There are 6 types of monohybrid hybrid cross; list them. 3. What type of diagram can be used to track genotypes through a family? 4. What symbol is used to represent males? 5. What symbol is used to represent females? 6. Complete the labels on this diagram 7.4 Codominance 1. 2. 3. 4. Define codominance Give one example of a trait in animals that shows codominance Give one example of a trait in plants that shows codominance How are the alleles represented in letter form in a codominat genetic cross? 5. Complete this diagram for a codominant genetic cross: 7.5 Polygenic Inheritance 1. What type of variation is described when characteristics fall into distinct categories? 2. How many genes are said to control characteristics showing this type of variation? 3. Give an example of this type of variation in: a. Humans b. Plants c. Another animal 4. Define polygenic inheritance 5. What form of variation is shown by a characteristic coded for by many genes? 6. Give an example of this type of variation in: a. Humans b. Plants c. Another animal 7. Describe the relationship between the number of genes coding for a characteristic and the possible phenotypes 7.6 Drosophila and Genetics 1. Give 4 reasons why drosophila are used in genetic experiments 2. In order to determine a dominant characteristic what must the parental generation be. 3. Complete the table to state the process of performing a genetic cross 7.7 Tobacco Plants and Genetics 1. Give 3 reasons why tobacco plants are used in genetic crosses 2. Which leaf colour in tobacco plants is dominant? 3. Complete the following table for tobacco plant alleles: Possible Genotypes Description of Tobacco seed leaf genotype phenotype 8.1 Development of the phenotype 1. What two factors determine an organism’s phenotype? 2. If identical twins are subjected to different environmental factors, what will happen to their: a. Phenotype? b. Genotype? 3. Name a plant species which has been used in experiments to demonstrate changes in environment alone are NOT enough for evolution to occur. 8.2 Natural Selection and Evolution 1. Name the process by which individuals which are better suited to their environment survive and breed, while those less suited fail to do so. 2. Sexual reproduction produces new combinations of genes, this is termed… 3. Term used to describe the appearance of a new species as a result of natural selection (This takes many, many, many generations! And millions of years) 8.4 Selective Breeding 1. Describe the main difference between selective breeding and natural selection 2. In four bullet points describe how you would improve the milk yield in a population of dairy cattle 3. What is the term given to plants variety produced by cross pollination 4. Give 4 disadvantages of selective breeding 8.5 Genetic engineering 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What are the genes of living organisms are made of? Give a definition of genetic engineering What type of living organism is used in this process? What is the ring of DNA in this organism called? What is the term given to an organism that contains genes from another species? 6. Give four reasons why genetic engineering is better than selective breeding 7. Why can bacterium not be used for some genetically engineered products? 8. Give two examples of how genetic engineering can be harmful 8.6 Uses of Genetic Engineering 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Name two human products of genetic engineering What was a major with problem the original animal sources of Insulin? Name three advantages of GM insulin Name two other ways in which Haemophilia is being treated Name three plants and how GM has improved them 8.7 Issues In Genetic Engineering 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is gene therapy? Name two human diseases where Gene Therapy is being investigated. How are mice being used in gene therapy? Name three problems with GM food What is the name given to transplanting an organ into a human from another species?