Teacher Notes on Homeostasis
advertisement

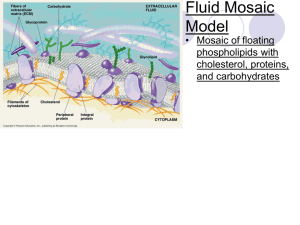
Student Notes on Homeostasis Biology *All living things must maintain a conditions regardless of Homeostasis: the process of maintaining environment, a to change Important terms to know: Solute: substance being quantity) and in the cell’s in another substance (often the lesser Solvent: substance that another substance Ex. Koolaid, Which is the solute and which the solvent? Mixture vs. Compound Compound: be easily separated by methods The chemical/physical properties are totally different than the properties of the parts NaCl Na-very , whitish, Cl- , green gas We know this compound as . H2O2 H2- explosive gas, O2-flammable gas We know this compound as Mixture: . be easily separated by methods The chemical/physical properties remain the same Types: 1. Solution: two or more is evenly * in a single phase, does not out, it molecules are smaller than in the ex. 2. Suspension: larger than will over time, unless the mixture is constantly stirred or agitated out ex. separated water-mud settles when not 3. Colloid: particles of and *small , particles can be are mainly the same size, remain ex. types of emulsionsmoke, fog-liquid in gas , Each of these mixtures is in our body: Solution: Suspension: Colloid: Major part of cells that maintain homeostasis: 1. Plasma Membrane: a. Function: of out-too much can be harmful Cells need nutrients- between cell and its environment, allows steady to come into the cell and excess , , b. Selective permeability: allows some in and others out c. Structure: phospholipid bilayer: two layers of back to back glycerol, fatty acids, phosphate Nonpolar: Polar: , no charge can dissolve other substances (like dissolves like so Water is cell) Fatty acids Hydrophobic: water Hydrophilic: water can only dissolve , so it can interact with water (face ) (facing outside of the of cell membrane) d. Fluid mosaic model: membrane is a pattern on the membrane surface , proteins Transport proteins: allow needed or move through the membrane, movement of substances in a mixture to Processes used to maintain homeostasis: 1. Diffusion: net movement of concentration to an area of from an area of concentration until it reaches equilibrium -results due to the movement of particles, a slow process 3 Key factors of diffusion 1. concentration: more , more rapid 2. Temperature: increase in temp. molecules and then up the movement of 3. Pressure: increase in and , accelerate molecule Goal of cell is to have: Dynamic Equilibrium: and out of the cell, but no movement of molecules, concentration change Concentration gradient: difference in across space 2. Osmosis: diffusion of -water flows to side of cell with *water continues to on both sides of the membrane rate in across a semi-permeable membrane water, where water is low until it is in 3 types of solutions, osmosis in cells 1. Isotonic solution: The of inside and outside the cell are the same, so water moves in and out of the cell at the same * and of the cell are normal, do not experience osmosis, water concentration is the same in and out of the cell 2. Hypotonic: solute concentration is concentration or amount is lower the cell outside the cell, water the cell so water moves * and pressure increases, can cause of cell swells beyond normal Result: animal cells can , plant cells become pressure 3. Hypertonic: solute concentration outside the cell is cell, so concentration or amount is cell, so water moves of the cell *size of cell decrease for animal cells, causes Result: animal cell shrinks, plant due to than in the outside the , in plant cell Turgor pressure vs. plasmolysis vs. cytolysis Turgor pressure: in cells, when water moves the pressure and makes cell rigid Plasmolysis: water cell and cell Cytolysis: cells take in cells much water and cell , only in Water regulation in organisms 1. Single celled: most found in and environments, *Want to avoid bursting, have that act as a pump and remove water by contracting 2. Higher level animals: cells in a environment, no water Small portion of cells in the brain shrink and cause salt in *Cells in environment drink too much , low *Small patch of cells in brain when they trigger and cause kidney tubules to open up and produce more Passive transport: no the membrane Ex. is needed to move the across and Facilitated diffusion: passive transport of -Moves sugars and amino acids Active transport: of with the help of through a