Unit 3 Review Sheet - Dr. Vernon-
advertisement
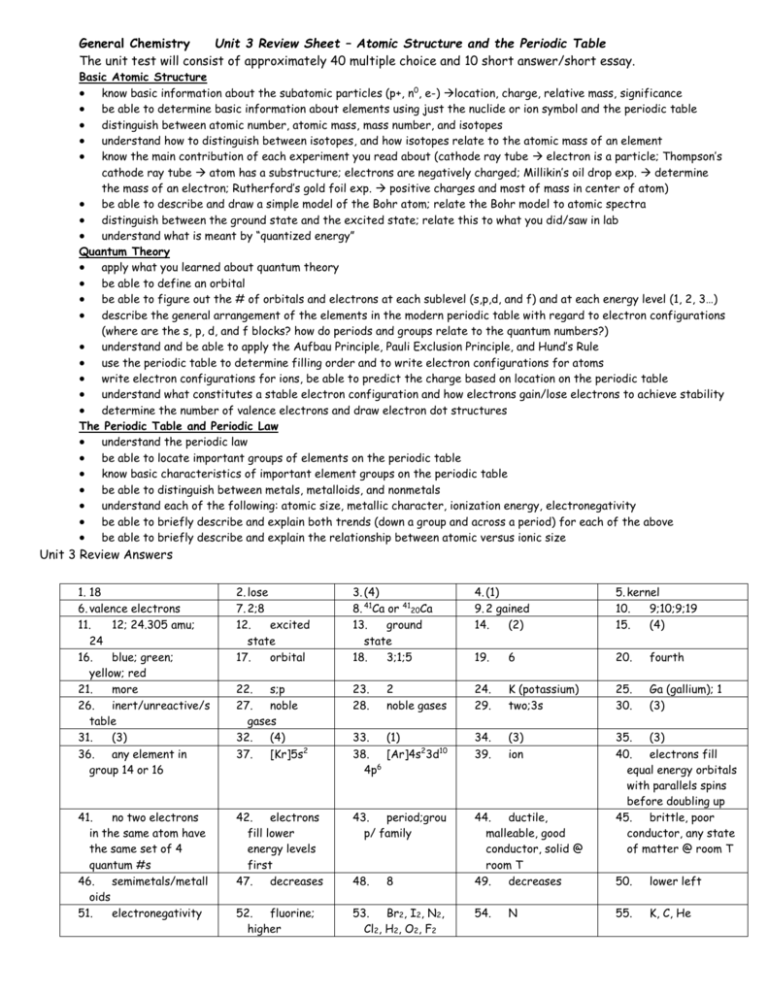
General Chemistry Unit 3 Review Sheet – Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table The unit test will consist of approximately 40 multiple choice and 10 short answer/short essay. Basic Atomic Structure know basic information about the subatomic particles (p+, n0, e-) location, charge, relative mass, significance be able to determine basic information about elements using just the nuclide or ion symbol and the periodic table distinguish between atomic number, atomic mass, mass number, and isotopes understand how to distinguish between isotopes, and how isotopes relate to the atomic mass of an element know the main contribution of each experiment you read about (cathode ray tube electron is a particle; Thompson’s cathode ray tube atom has a substructure; electrons are negatively charged; Millikin’s oil drop exp. determine the mass of an electron; Rutherford’s gold foil exp. positive charges and most of mass in center of atom) be able to describe and draw a simple model of the Bohr atom; relate the Bohr model to atomic spectra distinguish between the ground state and the excited state; relate this to what you did/saw in lab understand what is meant by “quantized energy” Quantum Theory apply what you learned about quantum theory be able to define an orbital be able to figure out the # of orbitals and electrons at each sublevel (s,p,d, and f) and at each energy level (1, 2, 3…) describe the general arrangement of the elements in the modern periodic table with regard to electron configurations (where are the s, p, d, and f blocks? how do periods and groups relate to the quantum numbers?) understand and be able to apply the Aufbau Principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle, and Hund’s Rule use the periodic table to determine filling order and to write electron configurations for atoms write electron configurations for ions, be able to predict the charge based on location on the periodic table understand what constitutes a stable electron configuration and how electrons gain/lose electrons to achieve stability determine the number of valence electrons and draw electron dot structures The Periodic Table and Periodic Law understand the periodic law be able to locate important groups of elements on the periodic table know basic characteristics of important element groups on the periodic table be able to distinguish between metals, metalloids, and nonmetals understand each of the following: atomic size, metallic character, ionization energy, electronegativity be able to briefly describe and explain both trends (down a group and across a period) for each of the above be able to briefly describe and explain the relationship between atomic versus ionic size Unit 3 Review Answers 1. 18 6. valence electrons 11. 12; 24.305 amu; 24 16. blue; green; yellow; red 21. more 26. inert/unreactive/s table 31. (3) 36. any element in group 14 or 16 2. lose 7. 2;8 12. excited state 17. orbital 3. (4) 8. 41Ca or 4120Ca 13. ground state 18. 3;1;5 4. (1) 9. 2 gained 14. (2) 5. kernel 10. 9;10;9;19 15. (4) 19. 6 20. fourth 22. s;p 27. noble gases 32. (4) 37. [Kr]5s2 23. 28. 2 noble gases 24. 29. K (potassium) two;3s 25. 30. Ga (gallium); 1 (3) 33. (1) 38. [Ar]4s23d10 6 4p 34. 39. (3) ion 41. no two electrons in the same atom have the same set of 4 quantum #s 46. semimetals/metall oids 51. electronegativity 42. electrons fill lower energy levels first 47. decreases 43. period;grou p/ family 44. ductile, malleable, good conductor, solid @ room T 49. decreases 35. (3) 40. electrons fill equal energy orbitals with parallels spins before doubling up 45. brittle, poor conductor, any state of matter @ room T 52. fluorine; higher 53. Br2, I2, N2, Cl2, H2, O2, F2 48. 8 54. N 50. lower left 55. K, C, He