Urban Geography Practice MC Exam
advertisement

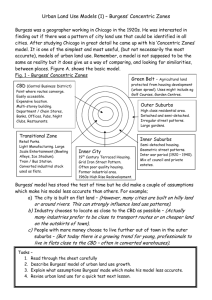
AP Human Geography Chapter 13: Urban Geography (Practice MC Exam) Name: _________________________________________ 1. The process of settlement formation, expansion, and change is called a. suburbanization. b. urbanization. c. post modern expansion. d. city growth. e. all of the above 8. The wide boulevards built in cities in LDCs were most likely built during what era? a. pre-colonial b. colonial c. independence d. medieval e. all of the above equally 2. The physical qualities of the original location for a city is referred to as the a. relative location. b. locational determinants. c. site characteristics. d. situational characteristics. e. none of the above 9. Which of the following is BOTH the least urbanized AND the most rapidly urbanizing realm of the world? a. Middle America b. Africa south of the Sahara c. East Asia d. South Asia e. the Middle East 3. The location of a city relative to its surroundings and other places refers to its a. site b. situation c. genealogy of development d. approximate latitude and longitude e. physical characteristics 10. The most urbanized region in the developing world is a. South Asia b. China c. North Africa d. Southeast Asia e. South America 4. Where did the first urban development originate? a. Southeast Asia b. Southwest Asia c. North Africa d. Western Europe 5. (AP Exam) All of the following were crucial to the emergence of the first cities EXCEPT a. an agricultural surplus b. a stratified social system c. labor specialization d. a system for food storage and distribution e. separation of the ruling system and the religious system 6. (AP Exam) Prior to 1850 the location of all major North American cities was related, chiefly, to the presence of a. transcontinental highways b. defensive sites c. railroad junctions d. navigable waterways e. water power 7. The Industrial Revolution a. had little impact on urban areas. b. spawned vast manufacturing centers. c. began in the Great Lakes region. d. made factory workers obsolete e. caused an urban to rural migration. 11. Higher income people tend to live near the center of the city in all but which of the following regions? a. Latin America b. North America c. South Asia d. Western Europe e. none of the above 12. What is the most noticeable geographic trend in the last 30 years with respect to the world's twenty most populated cities? a. Most of the-20 most populated cities are now located in more developed countries. b. Compared to 30 years ago, a much larger percentage of the cities are now located in Europe. c. Most of the 20 cities are now located in less developed countries. d. Most of the 20 cities are now located in Africa. e. The specific cities have not changed in 30 years; they have only grown in population. 13. Classic ________ cities have narrow, winding streets to maximize shade, open-air markets, many dead ends, and courtyards surrounded by high walls. a. medieval European b. Hindu c. Latin American d. Islamic e. colonial 14. From 1400-1700 many European powers established ___________ , which served as an entrance to or exit from a conquered are a. a colonial city b. an administrative center c. a gateway city d. an outpost e. provisional government 15. (AP Exam) Which of the following models of urban structure pictured above depicts a commercial spine bordered by an elite residential sector extending outward from the central business district? a. Urban realms b. Concentric zone c. Multiple nuclei d. Latin American city e. Southeast Asian city 16. When the models of urban structure which were developed in the US are applied to cities in South America, one conclusion is that a. both lack high income neighborhoods b. the multiple-nuclei model is difficult to classify c. the poorest people live in completely different areas d. the CBDs develop for different purposes e. transportation has an opposite purpose 17. Many Latin American cities conform more or less to the a. theory of ghettoization. b. the sector model. c. the multinode model. d. inner city decay theory. e. the concentric zone model. 18. What factor(s) have contributed to the rapid urbanization in Least Developed Countries (LDCs) since 1950? a. Cities provide opportunity for displaced rural residents. b. Explosive population growth has made it difficult for subsistence farmers to support their families. c. Cultural amenities attract large number of young urban professionals. d. All of the above e. A and B only. 19. If cities in the poorer parts of the world share a common characteristic, it may result from a. an absence of enforced zoning regulations. b. a total lack of industry. c. acute water shortages. d. poor public transportation. 20. Ramshackle houses on the periphery of cities in less developed countries are known as a. squatter settlements b. council estates c. public housing d. zones of transition e. spines of development 21. Which of the following is NOT correct regarding the great metropolises of the developing world? a. They contain both great wealth and tremendous poverty. b. Many retain architectural elements of their colonial past. c. Most have squatter settlements on their outskirts. d. Because their economies are less developed, they rarely suffer from significant pollution. e. They house an increasing proportion of the world's population. 22. (AP Exam) International company headquarters, major global financial functions, and operations that reach beyond state borders, are defining characteristics of a. primate cities b. entrepots c. forward capitals d. world cities e. edge cities 23. The three most important world cities in the world are a. New York, Paris, and Shanghai. b. New York, London, and Tokyo. c. New York, London, and Beijing. d. New York, Paris, and Tokyo. e. New York, Rome, and Shanghai. 24. Which world-class city is the best example of an entrepot? a. Shanghai b. Dubai c. Sao Paulo d. Madrid e. Singapore 25. What is one characteristic of megacities? a. Each city has an efficient form of mass transportation. b. Each has a population of more than 10 million people. c. Each has a world-class airport with connections to each continent. d. Each possesses financial wealth greater than its gross domestic product. e. Each follows a model that is focused around the central business district. 26. When several large urban areas essentially merge together to form an even larger urban complex, it's called a(n) a. urban agglomeration. b. megacity. c. city conglomerate d. megalopolis. e. megatropolis. 27. Megalopolis refers to a. adjacent, overlapping MSAs (metropolitan statistical areas) b. central cities c. consolidated MSAs d. central cities plus urbanized areas e. cities with over 1,000,000 inhabitants 28. Which of the following cities is NOT part of a larger megalopolis? a. New York b. Paris c. Tokyo d. Toronto e. Essen, Germany 29. (AP Exam) The development of high-speed rail lines, highways, and communications systems has created cities that seem to be apart from traditional central-place hierarchies because they have developed complementary functions. Which of the following is an example of these so-called network cities? a. London-Birmingham-Liverpool b. Hong Kong-Shanghai-Beijing c. Moscow-St. Petersburg-Kiev d. Cleveland-Toledo-Chicago e. Tokyo-Osaka-Nagasaki 30. (AP Exam) Which of the following is useful for describing a settlement node whose primary function is to provide support for the population in its hinterland? a. Von Thünen's model of land use b. Concentric zone model c. Core-periphery model d. Rostow's model of economic development e. Christaller's model of central place 31. (AP Exam) Central place theory describes the a. spatial patterns of urban and outlying areas based on the flow of goods and services b. tendency of different ethnic groups to congregate in a single location c. tendency of civilizations to form around certain natural features d. outward radiation of cultural patterns from a central place e. tendency of wealth to concentrate in urban core areas 32. According to central place theory, every settlement is a “central place” surrounded by a a. market area (hinterland) b. threshold c. hierarchy of cities d. zone of limitation e. uniform region 33. A hinterland reveals the ________ of each settlement. a. total population b. working population c. economic reach d. aggregate purchasing power e. quality of agricultural land 34. A “market area” (central city surrounded by hinterland) is a good example of what kind of region? a. cultural b. formal (uniform) c. functional (nodal) d. vernacular (perceptual) e. suburban 35. The maximum distance people are willing to travel for a service is a. hinterland b. range c. threshold d. median e. activity space 36. Within the framework of central place theory, which of the following provides the lowest-order (i.e. lowest range) good or service? a. A furniture store b. An orthodontist c. A gas station d. A jewelry store e. A professional football stadium 37. The minimum number of people needed to support a service in a city is a. hinterland b. range c. threshold d. median e. activity space 38. According to Christaller's Central Place Theory, larger settlements are characterized by a. more services than smaller settlements b. services with larger ranges than smaller settlements c. services with higher thresholds than those in smaller settlements d. the opposite of all of the above e. all of the above, as written 39. According to Christaller’s model of central place theory, larger settlements are ____ numerous and _____________ than small settlements. a. less – farther apart b. more – farther apart c. less – nearer to one another d. more – nearer to one another 40. Central place theory ranks settlements in the following series, from smallest to largest: a. hamlet, town, village, city b. village, town, hamlet, city c. town, hamlet, city, village d. city, town, village, hamlet e. hamlet, village, town, city 41. What geometric pattern is associated with Christaller’s Central Place Theory? a. Square b. Circle c. Hexagon. d. Octagon. e. Pentagon. 42. (AP Exam) According to the rank-size rule, if the largest city in a country has a population of 10 million, the next largest city will have a population of a. 9 million b. 8 million c. 7.5 million d. 5 million e. 3.5 million 43. In a country which follows the rank-size rule – if the largest city had 1,000,000 inhabitants, the fifth largest city will have how many inhabitants? a. 50,000 b. 100,000 c. 200,000 d. 500,000 e. 5,000,000 44. What concerns are there for a developing country if the rank-size rule does not apply? a. Services will be clustered in the primate city. b. Services will not be evenly distributed through out the country. c. Smaller cities find it difficult to compete for services with the primate city. d. People in rural areas and small cities feel compelled to migrate to the primate city for jobs. e. All of the above 45. (AP Exam) An urban center that is disproportionately larger than the second largest city in a country and that dominates the country's social, political, and economic activities can be best classified as a. a megalopolis b. a conurbation c. a primate city d. an edge city e. an imperial city 46. (AP Exam) Which of the following describes a primate city? a. It is economically and politically interconnected to other cities in the world. b. It is disproportionately large in relation to the next largest cities in that country. c. It is surrounded by walls like a fortress. d. It is linked by colonial administrators to an imperial power. e. It is primarily concerned with its role as a religious center. 47. Which of the following lists is comprised of countries with primate cities? a. Germany, Italy, Netherlands, Poland b. United States, Canada, Australia, South Africa c. China, Japan, India, Brazil d. France, UK, Mexico, Argentina 48. The three most famous models of urban structure – concentric zone, sector, and multiple nuclei – were all developed to describe what city? a. New York b. London c. Los Angeles d. Munich e. Chicago 49. The three models of urban structure all agree on one thing: a. There are five major zones in a city. b. Most people tend to prefer to live near others who have the same characteristics. c. Cities and suburbs make up a functional region. d. The models apply to cities all over the world 50. The gravity model when, applied to urbanization, reveals that a. the two largest cities in a country will have the most interaction between them. b. the two closest cities will have the most interaction between them. c. the two cities with the most in common will have the most interaction between them. d. the two cities with the most branch offices will have the most interaction between them. e. the two cities with the most cultural connections will have the most interaction between them. 54. In Burgess' concentric zone model, the zone of transition became a. a suburb. b. deteriorated with more CBD encroachment, low income housing, and warehouses. c. a working class area. d. a gentrified upscale new urban neighborhood. 55. According to the Burgess Model of Urban Development, the outer most ring is the a. extensive agriculture b. extensive commercial agriculture c. the zone of better residences. d. the zone of transition. e. the commuter zone 51. Which of the following models of urban structure (pictured above) describes an urban pattern in which a city grows out from a Central Business District (CBD) in a series of concentric rings each with different land uses based on increasing level of income? a. Urban realms model b. Concentric zone model c. Multiple nuclei model d. Latin American city model e. Primate City model 52. What theory suggests that in an urban setting, the farther a neighborhood is from the central business district, the greater its wealth is? a. Sector model b. Same-size rule c. Multiple nuclei model d. Concentric zone model e. Urban periphery model 53. Which statement would be the most accurate regarding the bid-rent theory? a. Land value is the highest in the central business district, and land value decreases with distance from the CBD. b. Land value is the highest in the suburbs, resulting in bigger houses. c. More space is available in the urban core due to the plight of the inner city. d. More space is available in the suburbs due to higher demand for land there e. Land value is constant throughout the urban area due to the high demand for residential space there 56. Which of the following models of urban geography best describes the above map? a. central place theory b. rank-size rule c. Von Thünen's concentric ring theory d. Sector model of urban development e. Multinucleated model of urban development 57. (AP Exam) According to the sector model of North American city structure, members of low-income groups tend to live in which of the following places? a. The inner city only b. Peripheral temporary settlements c. Linear residential areas radiating from the d. center city outward e. Evenly dispersed throughout the urban area (The suburbs and rural areas only 58. According to the sector model, the best housing is located in a. a corridor from downtown to the edge of the city b. an outer ring around the city c. a node near a university or park d. a renovated inner-city neighborhood e. a suburb 59. The map of Los Angeles above most closely corresponds to which urban model? a. Multiple-nuclei model b. Sector model c. Concentric zone model d. Mixed land use model e. Urban corridor model 60. Large cities develop many nodes around which different types of people and activities cluster. This describes the a. Peripheral Model. b. Multiple Nuclei Model. c. Latin American Model. d. Sector Model. e. Concentric Zone Model. 61. Harris and Ullman's multiple nuclei model of urban structure arose from the idea that __________ was losing its dominant position in the metropolitan city to other competition. a. the exurb b. the edge city c. public transportation d. the suburb e. the CBD 62. According Ullman and Harris's multiple nuclei model, what develops at the outskirts of core cities? a. Airports b. Nucleated cities c. Edge cities d. World cities e. First-ring suburbs 63. (AP Exam) Which of the following is true of an edge city? a. It is located on the edge of a lake, river, or other physical feature. b. It is close to bankruptcy. c. It is an outlet for a region’s trade. d. It is increasingly used for heavy industry. e. It has a large amount of recently developed retail and office space. 64. All of the following describe edge cites except a. they are more convenient places of employment for newer suburban communities. b. they physically resemble a city, because of the prevalence of tall office buildings. c. they typically are located at the intersections of highways. d. other uses such as shopping malls and apartment complexes are also present. e. they make it easier for traffic planners to design mass transit systems. 65. The area of the city where retail and office activities were traditionally clustered is the a. central business district b. central city c. urbanized area d. metropolitan statistical area e. zone in transition 66. The CBD attracts offices primarily because of its a. high accessibility b. high land costs c. more intensive land use d. construction of skyscrapers e. lack of residential areas 67. What types of activities are generally NOT found in CBDs? a. retailers with a high range b. manufacturing industries c. retailers with a high threshold d. face-to-face business services 68. Retail activities which tend to concentrate in the CBD include those which have a. a low range. b. a need for rapid transportation. c. a low threshold. d. service for office workers. e. all of the above 69. An example of the "vertical geography" of a CBD is a. the hilly streets found in downtown San Francisco. b. a barber shop on the bottom floor of a building, an accounting firm occupying the middle floor, and a group of condos on the top floor. c. building height constrained by natural or cultural factors, like earthquakes in Tokyo or zoning codes in DC. d. all of the above e. none of the above 70. The Central Business District is a. attractive to consumer and business services for its accessibility. b. characterized by retail stores with low thresholds and low ranges. c. less important for retail because of changing shopping habits. d. A and B e. A and C 71. European CBDs are similar to those in North America because typically they both contain a. retail and office activities b. extensive residential areas c. skyscrapers d. structure inherited from medieval times e. large parks 72. Compared to the US, poor families in European cities are more likely to be a. clustered in inner-city neighborhoods b. dispersed throughout the city c. clustered in suburbs d. distributed uniformly across the urban area e. living in rural areas 73. When comparing urban models for North American and European cities, what is the difference between where high-class residential neighborhoods area located? a. In European cities they are located near the Central Business District (CBD). b. Both have high-class residential areas adjacent to the main boulevard leading into the CBD c. In North American cities they are typically located on the outskirts of the metro area d. Both have wealthy neighborhoods scattered through out the city. e. A and C only. 74. Grid street patterns are most typical for cities in a. Europe b. South Asia c. Latin America d. North America e. Southeast Asia 75. The process of legally adding land to a city is known as a. annexation b. Council of Government c. metropolitan statistical area d. blockbusting e. urbanization 76. An urban settlement that has incorporated into an independent self-governing unit is a a. metropolitan area b. micropolitan statistical area c. city. d. metropolitan statistical area e. consolidated metropolitan statistical area 77. A Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSA) a. always includes a city of at least 50,000 inhabitants and its county b. includes surrounding counties if over 50% of its inhabitants are employed in the central city c. covers a larger area than the other common definitions of urban settlements d. is the most useful definition of an urban settlement for gathering information about a functional region e. all of the above 78. The city plus its contiguous built-up suburban rings is known as the a. central city b. urbanized area c. metropolitan statistical area d. consolidated metropolitan statistical area 79. Political geography can make it more difficult for metropolitan governments to solve regionally based problems because a. competing municipalities often have conflicting interests. b. political boundaries make it difficult for regional governments to exercise authority. c. each city has its own unique government. d. all of the above e. none of the above 80. Government solutions that help solve regional metropolitan issues include a. establishing cooperative agencies , such as a council of governments. b. forming a federation of municipalities like Toronto. c. consolidations where governments share services. d. altering political boundaries so city and county boundaries coincide e. all of the above 81. (AP Exam) All of the following have helped create ghettos in North American cities EXCEPT a. blockbusting and racial steering b. redlining by financial institutions c. concentration of public housing and social services d. fixed school district boundaries e. Economic Enterprise Zones 82. In US cities the so-called underclass is a. clustered in inner-city neighborhoods b. dispersed throughout the city c. clustered in suburban rings d. distributed uniformly across MSAs e. located mainly in rural areas 83. Compared to whites, African-Americans and other minority groups are more likely to be a. clustered in inner-city neighborhoods b. dispersed throughout the city c. clustered in the suburbs d. distributed uniformly across the MSA e. located mainly in rural fringe areas 84. A process which has resulted in a form of legal segregation in American cities is a. blockbusting b. zoning c. greenbelt construction d. “smart growth” e. redlining 85. Which is the illegal process by which real estate agents encourage the sale of homes because people of certain races have moved into a neighborhood? a. Redlining b. Ghettoization c. Segregation d. White flight e. Blockbusting 86. A process by which banks designate an area within which they refuse to lend money for improvements is a. blockbusting b. filtering c. gentrification d. redlining e. squatting 87. The terms “scattered site” and “projects” are both associated with a. the construction of public housing b. the addition of green spaces to existing cities c. urban renovation d. de-segregation of suburbs e. the multiple-nuclei model of urban structure. 88. The process of change in the use of a house – from single family owner occupancy to eventual abandonment – is a. blockbusting b. filtering c. gentrification d. redlining e. squatting 89. Various cities in North America have used all of the following strategies to revitalize their central business districts except a. by creating pedestrian malls downtown, such as Denver, Colorado, and Eugene, Oregon. b. by building major urban renewal projects. c. by building major sports facilities, such as Camden Yards in Baltimore and Coors Field in Denver. d. by building business parks. e. by turning vacant industrial buildings and warehouses into residential lofts. 90. In the last twenty years the most successful strategy to revitalize central business districts and inner city neighborhoods has been to a. create festival market places. b. build life style malls. c. construct athletic complexes. d. construct more residences downtown. e. encourage more businesses to locate in the area 91. A process which results in the conversion of a lowincome neighborhood to middle- or upper-class housing is a. blockbusting b. filtering c. gentrification d. redlining e. squatting 92. Who is likely to move into revitalized urban downtown area neighborhoods? a. White collar empty nesters. b. Young urban professionals (yuppies). c. Recent college graduates. d. Double income no kids households (dinks). e. All of the above 93. Which of following would be a negative social effect of gentrification in cities? a. Old homes would be converted with updated materials and fixtures. b. Older residents would receive new homes in suburban areas. c. Increased real estate prices and rents would force out poor residents. d. Construction companies would have projects in areas of existing housing. e. Older architecture would be preserved instead of building new structures. 94. In many major metropolitan areas dying or abandoned shopping malls can often be found a. in edge cities. b. outside of urban growth boundaries. c. in the first ring of suburbs built in the 1950s and 1960s. d. in the zone in transition. e. at the intersection of major interstate highways. 95. A recent change in the density gradient of North American cities has been a. a decrease in the number of the people living in the center b. a reduction in the density differences across all zones of the city c. an increase in the extremes between inner and outer areas d. a decrease in the total number of people in the suburban areas e. both A and B 96. Many cities in North America have designed and set aside areas where outdoor concerts, street performers, ethnic events, farmers markets, and cart vendors come together and act as a positive focal point economically and socially for urban life. This recent trend is often referred to as a. an urban park. b. a festival market place. c. a service oriented center. d. a lifestyle mall. e. an urban interface zone. 97. The basic tenants of new urbanism include all of the following except a. a mix of land usages (residential, commercial, office) b. transit based, rather than automobile based, development c. wide streets with cul-de-sacs. d. a wide range of housing and types of employment e. walkable neighborhoods 98. What is the process called when people move away from the central business district due to dissatisfaction with the urban policies and lifestyle? a. Blockbusting b. Redlining c. Counterurbanization d. Decentralization e. Gentrification 99. The largest percentage of the US population lives in a. CBDs b. the zone in transition c. nonmetropolitan areas d. rural areas e. suburban areas 100. (AP Exam) Which of the following was NOT a reason for rapid suburbanization in the United States after the Second World War? a. Mass production of the automobile b. Reduction in long-distance commuting c. Expansion of home construction d. Expansion of the interstate highway system e. Availability of low down payment terms and longterm mortgages 101. (AP Exam) All of the following are reasons for the rise of suburban development in the 1950s EXCEPT a. the building of interstate highways b. loans under the G.I. Bill of Rights c. better public transportation d. the desire for more space e. prefab construction methods 102. Each of the following statements about suburbanization is correct EXCEPT: a. the high number of World War II soldier casualties limited the demand for housing for a decade b. the completion of the interstate highway system made commuting to the workplace easier c. industry was attracted to the suburbs by modern plant facilities and plenty of parking spaces for employees d. service industries developed as a result of the purchasing power and the available suburban labor force e. as people moved to the suburbs, regional shopping centers replaced the CBD retail districts 103. What happened to inner city neighborhoods when many industries shifted geographic location to the suburbs after World War II? a. Neighborhoods declined in population. b. The housing stock deteriorate c. Unemployment rates increased for inner city residents. d. Business services declined for inner city residents. e. All of the above 104. People are attracted to suburbs in part because suburbs are characterized by a. the best accessibility to the central city b. lower opportunity for home ownership c. private land surrounding the house d. more social heterogeneity e. the availability of gentrified neighborhoods 105. Suburban developments suffer from a. a lack of diversity. b. social isolation. c. a lack of green space d. deteriorating schools. e. A and B only. 106. How are North American suburbs segregated? a. according to land use b. by social class c. through the use of zoning ordinances d. all of these 107. (AP Exam) Which of the following most closely describes the leading trend in retailing in the United States during the 1950s, 1970s, and 1990s? a. 1950's: Downtown business district; 1970's: Shopping mall; 1990's: "Big box" superstore b. 1950's: Downtown business district; 1970's: "Big box" superstore; 1990's: Shopping mall c. 1950's: Shopping mall; 1970's: Downtown business district; 1990's: "Big box" superstore d. 1950's: "Big box" superstore; 1970's: Downtown business district; 1990's: Shopping mall e. 1950's: "Big box" superstore; 1970's: Shopping mall; 1990's: Downtown business district 108. Even though land use in North American Central Business Districts (CBDs) is characterized by skyscrapers and high-density uses, a sizable percentage of land is still devoted to a. recreation. b. arts and entertainment. c. museums. d. industry. e. automobiles. 109. Auto-centered cities emerged during the post World War II era in a. Eastern North America b. Northwestern Europe c. Central Japan. d. Upper Midwest. e. Southwestern United States. 110. Public transportation is better suited for commuting to the CBD primarily because a. it is less expensive b. it is more space and energy efficient c. commuters desire to use it d. the population of the CBD has declined 111. Because so few people live in the CBD, urban areas are characterized by a high degree of a. blockbusting b. commuting c. threshold d. skyscrapers e. apartments 112. The US government has encouraged the use of cars in part by a. building interstate highways b. charging high gasoline prices c. constructing new subways d. protecting prime agricultural land through legislation e. eliminating tax breaks for home owners and giving them to renters 113. Public transportation is more extensive in Western European cities than in the US primarily because a. Europeans can’t afford cars b. European governments heavily subsidize this from of transport c. the overall density in urban areas is lower d. the central cities contain few high rises e. US cities have numerous pedestrian areas in the central city 114. The major exception to the decline of the use of public transport in American cities is a. the automobile b. buses c. rapid transit (subways) d. streetcars and trolleys e. none of the above 115. The decline in density and the spread of cities associated with the building of freeways in the second half of the twentieth century has been pejoratively (negatively) referred to as a. suburbanization. b. urban sprawl. c. exurbanization. d. new urbanism. 116. Sprawl is best described as the a. change in density within an urban area from the center to the periphery b. development of new housing sites not contiguous to the existing built up area c. land maintained as open space surrounding an urban area d. period in the morning and evening with the heaviest volumes of traffic 117. Urban sprawl is responsible for a. loss of biodiversity. b. loss of open space c. increasing vehicle miles driven. d. increasing auto emissions. e. all of the above 118. Urban growth boundaries are most commonly associated with the movement known as a. smart growth. b. new urbanism. c. transit oriented development. d. urban renewal. e. low density development. 119. The UK has less urban sprawl than the U.S. in part because British cities are surrounded by undeveloped space known as a. greenbelts b. public housing c. sprawl d. squatter settlements e. brownfields 120. Which of the following best describes "exurbia"? a. Usually found in Europe and Asia b. Generally located along freeways, on the outskirts of major cities c. Made up of small, isolated communities consisting mostly of telecommuters d. Usually designed by the Beautiful City tradition e. Lies outside of urban zoning restrictions