P2 – The main tissue types of the body and the role these play in two
advertisement
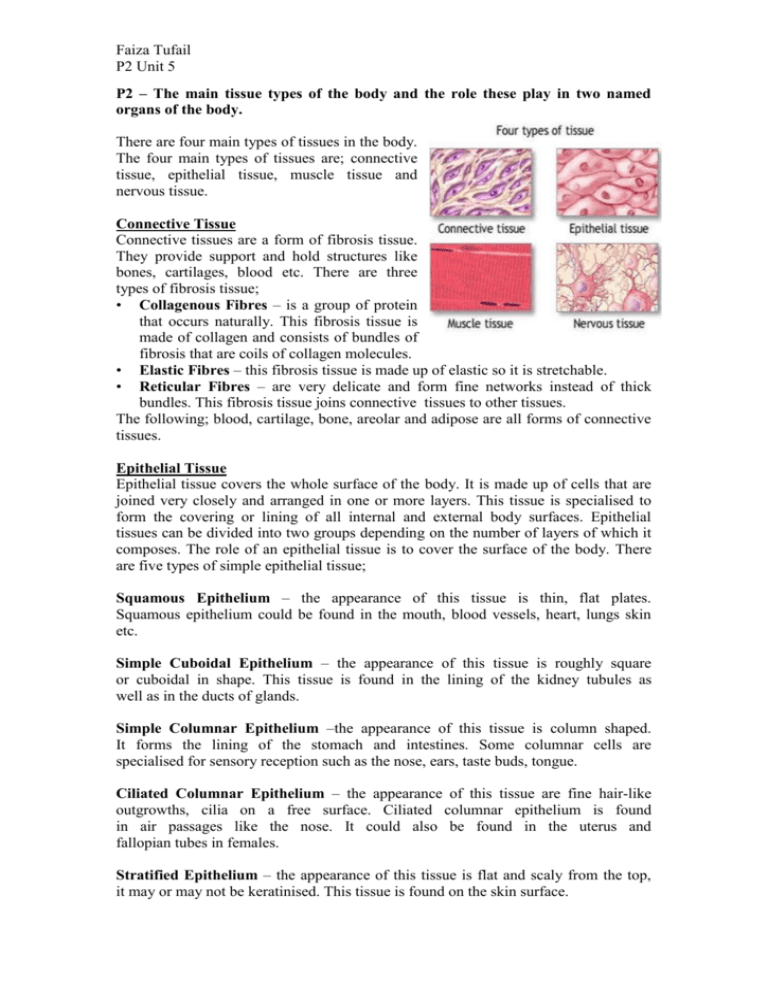
Faiza Tufail P2 Unit 5 P2 – The main tissue types of the body and the role these play in two named organs of the body. There are four main types of tissues in the body. The four main types of tissues are; connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Connective Tissue Connective tissues are a form of fibrosis tissue. They provide support and hold structures like bones, cartilages, blood etc. There are three types of fibrosis tissue; • Collagenous Fibres – is a group of protein that occurs naturally. This fibrosis tissue is made of collagen and consists of bundles of fibrosis that are coils of collagen molecules. • Elastic Fibres – this fibrosis tissue is made up of elastic so it is stretchable. • Reticular Fibres – are very delicate and form fine networks instead of thick bundles. This fibrosis tissue joins connective tissues to other tissues. The following; blood, cartilage, bone, areolar and adipose are all forms of connective tissues. Epithelial Tissue Epithelial tissue covers the whole surface of the body. It is made up of cells that are joined very closely and arranged in one or more layers. This tissue is specialised to form the covering or lining of all internal and external body surfaces. Epithelial tissues can be divided into two groups depending on the number of layers of which it composes. The role of an epithelial tissue is to cover the surface of the body. There are five types of simple epithelial tissue; Squamous Epithelium – the appearance of this tissue is thin, flat plates. Squamous epithelium could be found in the mouth, blood vessels, heart, lungs skin etc. Simple Cuboidal Epithelium – the appearance of this tissue is roughly square or cuboidal in shape. This tissue is found in the lining of the kidney tubules as well as in the ducts of glands. Simple Columnar Epithelium –the appearance of this tissue is column shaped. It forms the lining of the stomach and intestines. Some columnar cells are specialised for sensory reception such as the nose, ears, taste buds, tongue. Ciliated Columnar Epithelium – the appearance of this tissue are fine hair-like outgrowths, cilia on a free surface. Ciliated columnar epithelium is found in air passages like the nose. It could also be found in the uterus and fallopian tubes in females. Stratified Epithelium – the appearance of this tissue is flat and scaly from the top, it may or may not be keratinised. This tissue is found on the skin surface. Faiza Tufail P2 Unit 5 Muscle Tissue Muscle tissue is responsible for the movements of the body and the various parts of the body. Smooth Muscle Tissue – this muscle tissue is found in various parts of the body such as the arteries, bladder, digestive tract, blood vessels, gut, internal tubes etc. The role of a smooth muscle tissue is to contract organs such as blood vessels, bladder and uterus. Skeletal Muscle Tissue – this muscle tissue is attached to bones by tendons and is associated with the body voluntary movements. This muscle is a striated muscle. Cardiac Muscle Tissue – this muscle tissue is found in the heart. Calls are joined to one another by intercalated discs which allow the synchronization of the heart beat. Cardiac muscle is branched and a striated muscle. Nervous Tissue Nervous tissues are cells that can convert stimuli (a change in the internal and external environment) to epithelial impulses and conduct those impulses for example; Temperature - a person may pull away from an object with a high temperature. This is known as the reflex arm. Light – An individual’s eye may become bigger in the dark as it is trying to find light to see better and a little clearer. The pupil will become bigger in the dark and smaller in the light. There are two types of nervous tissues; Neurons -Billions of neurons vary in size, in which human bodies consist of. Neurons could be broken down into the cell body, which contains each neuron’s nucleus, mitochondria, and nerve processes. Neurons, nerve cells are very sensitive to various types of stimuli such as heat/cold, light/dark pressure. Neuroglia -The Neuroglia also known as ‘glia’, maintains homeostasis, from myelin, and provides support and protection for the brains neurons. Some ‘glia’ cells maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for the brain's neurons. Faiza Tufail P2 Unit 5 Muscle Tissue - Heart The heart is a large pump, which pumps blood around the body. The muscle tissue around the human heart, like all tissues in the body relies on blood supply to deliver oxygen and nutrients and to remove waste products such as CO2. The left side of the heart has to pump blood around the whole body therefore, it has thicker muscle tissue, as the blood has to travel a longer distance. The right side of the heart has thinner muscle tissue, because it only has to pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs, which is close to the heart, therefore the heart does not have to pump as much as the left side. Nervous Tissue – Brain A brain is a Nervous Tissue as it controls and regulates body functioning. This is because messages are sent to and from the brain. When a message comes into the brain from any part of the body, the brain tells the body how to react for example, if a person accidentally touch the hot iron, the nerves in their skin will shoot a message of pain to their brain. The brain monitors and regulates the body's actions and reactions. It continuously receives sensory information, and rapidly analyzes this data and then responds accordingly by controlling bodily actions and functions. The brainstem controls breathing, heart rate, and other autonomic processes that are independent of conscious brain functions.









