ANIMAL TISSUES
advertisement
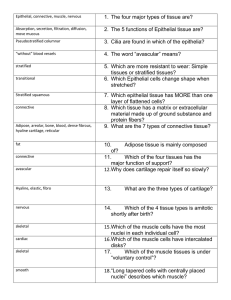
ANIMAL TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES Cells are not usually isolated -- instead they're surrounded by other similar cells: TISSUE. What are tissues?? DEF: Group of similar cells & intercellular substance functioning together to perform a specialized activity. Study of tissues: HISTOLOGY Histio = “tissue” Logos = “study of” All animal tissue can be place in 1 of 4 types. What are the 4 types?? 1) epithelial 2) connective 3) muscle 4) nervous EPITHELIAL TISSUE 2 locations: a) glands b) covering surfaces lining “lumens” Organized in continuous layers ..... thin to thick. Tightly packed .... little intercellular material. Avascular --- not penetrated by blood vessels. Nonneural All epithelial are anchored by a basement membrane. Rules for Naming Epithelia are based on… Number of cell layers Simple (1 layer) Stratified (2 or more layers) Cell shape Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Simple squamous epithelium Simple columnar epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium Some epithelia are simple squamous … others are heavily stratified. Why does this make sense? Examples?? Simple Squamous Epithelia SMALL INTESTINE LINING CONNECTIVE TISSUE Most abundant tissue in body. - Binds (ligaments) - Supports (mesenteries) - Protects (bone) Does not occur on free surfaces (like epithelia). Cells are few ..... fibroblast is a common example. “Matrix” is abundant. Matrix is produced by the CT cells --- nonliving. May be fluid, semifluid, mucus-like, or fibrous. Matrix determines the CT’s quality: - cartilage matrix = firm but pliable - bone matrix = hard & not pliable Matrix often contains protein fibers ... most abundant is collagen. Collagen is produced by fibroblasts. Collagen represents 30 % of total body protein!! Completely inelastic ... greater tensile strength than steel. Another common protein fiber: elastic fiber Loose (= areolar) Connective Tissue Adipose Tissue Dense Regular Connective Tissue Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Hyaline Cartilage Bone Tissue Compact Bone Tissue Blood (a connective tissue!) MUSCLE TISSUE 3 types – 3 locations - Skeletal muscle - Cardiac muscle - Smooth muscle Skeletal (voluntary & striated) muscle Cardiac muscle (striated & involuntary) Smooth muscle NERVOUS TISSUE 2 Main Cell Types - Neurons - Glial cells