Osmotic Solutions: Hypotonic, Hypertonic, Isotonic Cell Effects
advertisement
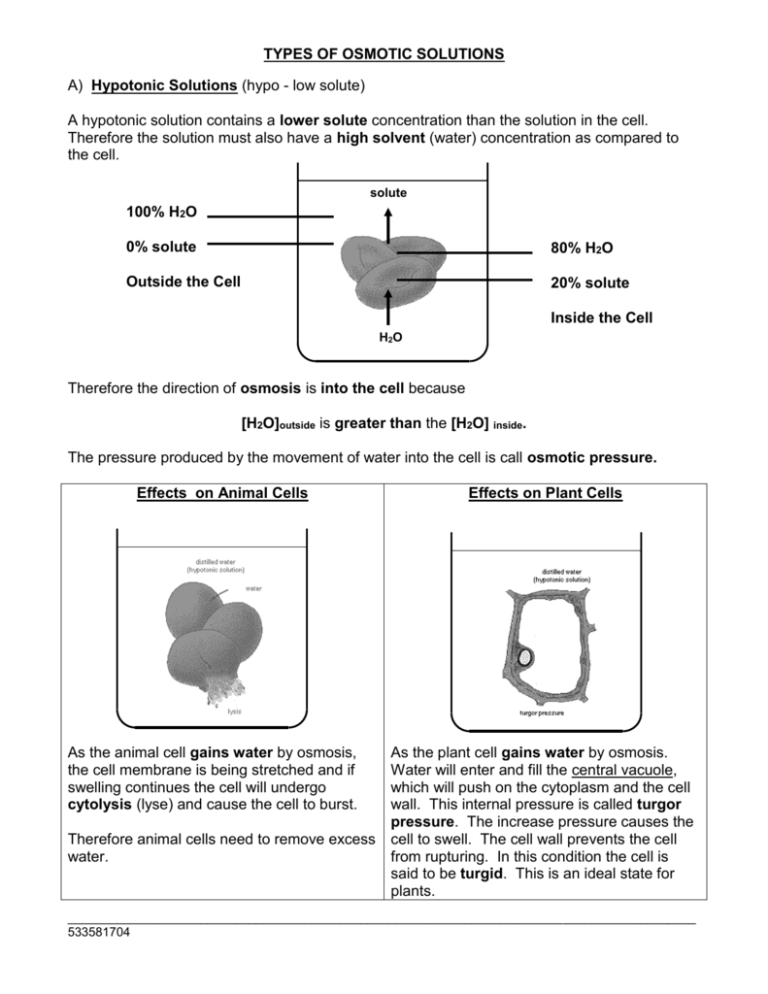
TYPES OF OSMOTIC SOLUTIONS A) Hypotonic Solutions (hypo - low solute) A hypotonic solution contains a lower solute concentration than the solution in the cell. Therefore the solution must also have a high solvent (water) concentration as compared to the cell. solute 100% H2O 0% solute 80% H2O Outside the Cell 20% solute Inside the Cell H2O Therefore the direction of osmosis is into the cell because [H2O]outside is greater than the [H2O] inside. The pressure produced by the movement of water into the cell is call osmotic pressure. Effects on Animal Cells As the animal cell gains water by osmosis, the cell membrane is being stretched and if swelling continues the cell will undergo cytolysis (lyse) and cause the cell to burst. Therefore animal cells need to remove excess water. Effects on Plant Cells As the plant cell gains water by osmosis. Water will enter and fill the central vacuole, which will push on the cytoplasm and the cell wall. This internal pressure is called turgor pressure. The increase pressure causes the cell to swell. The cell wall prevents the cell from rupturing. In this condition the cell is said to be turgid. This is an ideal state for plants. __________________________________________________________________________________________ 533581704 B) Hypertonic Solutions (hyper - high solute) A hypertonic solution contains a high solute concentration than the solution in the cell. Therefore the solution must also have a low solvent (water) concentration as compared to the cell. solute 90% H2O 10% solute 99% H2O Outside the Cell 1% solute Inside the Cell H2O Therefore the direction of osmosis is out of the cell because [H2O]outside is less than the [H2O] inside. Effects on Animal Cells An animal cell will lose water by osmosis. The cell will shrivel or crenate. A cell can conserve water by pumping out salt (solute). i.e. Bony fish in sea water Effects on Plant Cells As the plant cell loses water by osmosis, the central vacuole will shrink causing the turgor pressure to drop. The cell membrane will come away from the cell wall causing the cell to be less rigid. This condition is called plasmolysis. If the cell reaches this state it will be lethal and the cell may not recover. __________________________________________________________________________________________ 533581704 C) Isotonic Solutions An isotonic solution contains an equal solute concentration as the one found inside the cell. solute 75% H2O 25% solute 75% H2O Outside the Cell 25% solute Inside the Cell H2O Therefore rate of osmosis into the cell is equal to the rate of osmosis out of the cell because [H2O]outside is equal to [H2O] inside. Therefore the net movement of molecules is zero. Effects on Animal Cells The volume of the animal cell remains unchanged since there is a dynamic equilibrium across the cell membrane. Effects on Plant Cells Since there is no net movement of water across the membrane of the cell, the size of the cell remains the same. The cell membrane is just touching the cell wall. The plant cell has become flaccid (limp) and therefore the plant cell will lose some of its structural support do to low turgor pressure. __________________________________________________________________________________________ 533581704