Name - FJchimie11
advertisement

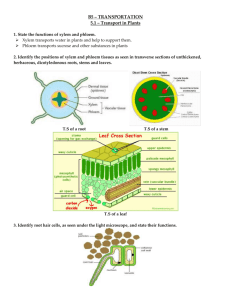
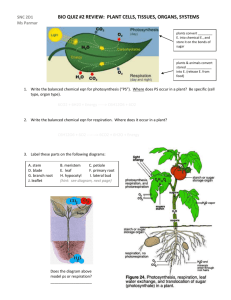
Name: _________________________ Date: ____________________ Plants: Anatomy, Growth & Function Unit Test- Answer Key Knowledge:__/45 Thinking/Inquiry:__/10 Communication:__/10 Application:__/32 Part A: Diagrams (32 marks Application) 1. Label the following diagram of the cross section of a leaf. Write your answers in the blank spaces provided.( 9 marks) a. cuticle b. upper epidermis c. xylem d. phloem e. lower epidermis f. stoma g. guard cell h. spongy mesophyll i. palisade mesophyll 2. Label the following diagram of the cross section of a dicot stem. Write your answers in the blank spaces provided.(7 marks) a. pith b. cortex c. epidermis d. xylem e. cambium f. phloem g. vascular bundle 3. Label the following diagram of a typical flower. Write your answers in the blank spaces provided. (9 marks) a. stigma b. style c. ovary d. pistil e. petals f. anther g. filament h. sepals i. nectary 4. Label the following diagram of the external and internal structures of a dicotyledon seed. Write your answers in the blank spaces provided. ( 4 marks) a. testa (seed coat) b. plumule (embryo shoot) c. radicle (embryo root) d. cotyledons (food storage) 5. Label the following diagram of the apical and lateral meristem. Write your answers in the blank spaces provided.( 3 marks) a. apical meristem b. youngest developing leaf c. developing bud Part B: Multiple Choice (30 marks Knowledge) Choose the best response for each of the following questions or statements. Record your answers on to the scantron card provided.. 1. The primary function of the leaf is to a. b. c. d. 2. Which of the following is true about the cuticle? a. b. c. d. 3. has no chloroplasts. reduces the amount of gas exchange in the leaf tissue. allows rapid diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide through air spaces. reduces water loss in xerophytes. Which of the following outlines the function of guard cells? a. b. c. d. 7. Transport products of photosynthesis. Bring water to replace losses due to transpiration. Open and close to allow CO2 in and O2 out for photosynthesis. Prevent water loss from the upper surface of the leaf. The spongy mesophyll layer a. b. c. d. 6. consist of loosely packed rounded cells with few chloroplasts. consist of densely packed cylindrical cells with few chloroplasts. consist of loosely packed cylindrical cells with many chloroplasts. consist of densely packed cylindrical cells with many chloroplasts. Which of the following is true about the stoma of leaves? a. b. c. d. 5. Thicker on the bottom of the leaf. Found only on the top part of most leaves. Thinner on the bottom of the leaf. Found only at the bottom part of most leaves. Palisade mesophyll cells a. b. c. d. 4. carry out cellular respiration. produce food for the plant. reduce water loss for the plant. store minerals and valuable gases for the plant. Bring water to replace losses due to transpiration. Transport products of photosynthesis out of the leaf. Open or close the stoma to control the amount of water loss out of the leaf. Provide the main gas exchange surface for CO2 and O2 gases. Which of the following is true regarding transpiration? a. b. Plants lose water from their leaves and roots. Plants lose water from their stems and roots. c. d. 8. Which of the following pertains to xerophytes? a. b. c. d. 9. Plants lose water from their roots only. Plants lose water from their stems and leaves. Grow in humid environments. Grow in arid environments. Possess a very thin cuticle layer. Open their stomata during the day. The rate at which plants lose water varies depending on a. b. c. d. external conditions of the plant such as light, temperature, and humidity. internal conditions such as the water potential of plant tissues. both internal and external conditions. primarily wind and humidity conditions. 10. Water diffuses out of the leaf at faster rates when a. b. c. d. there is a sufficient amount of light outside. the temperature inside the leaf is low. the humidity outside the leaf is low. the air just outside the leaf is still. 11. CAM physiology involves a. b. c. d. the opening of stomata in cactus plants during the night. the closing of stomata in cactus plants during the night. the closing of stomata in cactus plants during part of the day. the opening of stomata in cactus plants during part of the night. 12. Cactus plants reduce transpiration by a. b. c. d. possessing spines to reduce the amount of surface area for evaporation to occur. producing larger amounts of abscisic acid when needed to close their stomata more often. opening their stomata during the day and closing them at night to conserve water. possessing larger numbers of stomata to increase the regulation of water loss. 13. The main function of roots is to a. b. c. d. anchor plants into the soil. absorb water from the soil. absorb minerals from the soil. all of the above are correct. 14. Abscisic acid a. b. c. d. is produced when the plant is waterlogged. causes guard cells to lose water which results in the closure of stomata. is produced in the leaves of plants when the plant is dehydrated. is produced by xerophyte plants as a major adaptation in response to water stress. 15. Plant roots absorb potassium, phosphate, nitrate and other mineral ions a. b. c. d. by passive transport. by active transport. by facilitated transport. by proton gradients. 16. Roots of plants produce ATP by a. b. c. d. the process of anaerobic cellular respiration. the process of alcoholic fermentation. the process of aerobic cellular respiration. the process of lactic acid fermentation. 17. The substance that makes xylem vessels hard and durable is called a. b. c. d. schlerenchyma collenchyma meristem tissue lignin 18. Water exits the xylem tissue into adjacent leaf cells through a. b. c. d. sieve tubes along the xylem. pores in the outer cellulose cell wall. the lumen of the tissue. the cytoplasm of the xylem cells. 19. The water that evaporates out of the leaf is pulled out of the xylem vessels and through pores in spongy mesophyll cells was by a. b. c. d. cohesion adhesion capillary action root pressure 20. Low pressure or suction is created inside xylem vessels to force water out of the leaf. This is called a. b. c. d. transpiration pull. capillary action. root pressure. plant sweating. 21. Columns of water molecules are always maintained throughout the xylem tissue because of a principle called a. b. c. d. adhesion. cohesion. surface tension. both a and b are correct. 22. Water sticks to the sides of the xylem walls due to a principle called a. b. c. d. adhesion. cohesion. surface tension. both a and b are correct. 23. For plants, examples of sources are a. b. c. d. stems and leaves. roots. growing fruit. developing seeds. 24. Examples of sinks are a. b. c. d. parts of the plant where photosynthesis occurs. parts of the plant where there might be storages of glucose. parts of the plant where gases are stored and exchanged. parts of the plant where starch is broken down. 25. Female gametes are directly contained in a. b. c. d. pollen grains stigmas ovules stamen 26. Male gametes are found in a. b. c. d. pollen grains stigmas ovules stamen 27. Fertilized ovules develop into a. b. c. d. zygotes. seeds. fruit. seedlings. 28. Ovaries containing fertilized ovules develop into a. b. c. d. zygotes. seeds. fruit. seedlings. 29. The germination of seeds occurs when a. b. moisture levels drop to ideal conditions. oxygen levels exist for anaerobic respiration to occur. c. d. suitable temperatures are reached to maximize enzyme efficiency. none of the above are correct. 30. The bend in the stem of a seedling a. b. c. d. provides energy and nutrients for germination. protects the leaves as the shoot pushes up through the soil. increases the surface area for water absorption helps the seedling burrow effectively into the soil. Part C: True or False (15 marks Knowledge) Choose the best response for each of the following questions or statements. Record your answers on to the scantron card provided. 31. The rate of evaporation of water from a plant doubles for every 10°C increase in temperature. a. b. True False 32. Ions move across root cell membranes by diffusion. a. b. True False 33. Mineral ions can move into fungal hyphae that grow around plant roots in a parasitic relationship, and then from the hyphae to the roots. a. b. True False 34. The movement of water through long unbroken xylem vessels is called transpiration flow. a. b. True False 35. Xylem vessels possess a very thin plasma membrane, so water can move in and out freely. a. b. True False 36. The flow of water through xylem tissue is passive. a. b. True False 37. Sugars and fats are transported inside plants by phloem tissue. a. b. True False 38. The materials located in the phloem are loaded in parts of the plant called sinks. a. b. True False 39. The materials located in the phloem are translocated in parts of the plant called sources. a. b. True False 40. Fertilization of male and female gametes produces a zygote plant. a. b. True False 41. Pollination precedes fertilization. a. b. True False 42. Wind pollination is more popular than animal pollination in the plant kingdom. a. b. True False 43. The first stage in germination is the production of gibberellin. a. b. True False 44. The absorption of water and the rehydration of living cells in the seed allow the cells to become metabolically active. a. b. True False 45. All types of plants are divided into two groups, according to the number of leaves that the embryo plant has, inside the seed. a. b. True False Part D: Short Answers (10 marks Thinking/Inquiry, 10 marks Communication) Please use the space provided below to answer the following questions correctly and accurately. You must use complete sentences to answer each question below. 46. Using the space below, create a Venn diagram to compare and contrast the similarities and differences of plant and animal cells. (5 marks Communication) 47. The cohesive and adhesive properties of water are essential elements in the transport of materials in plants. Predict what would happen if these properties did not exist. Please use full sentences to explain your thinking. (5 marks Thinking/Inquiry) A) The cohesive and adhesive properties of water are essential elements in the transport of materials in plants. If these properties did not exist then it would be nearly impossible for the necessary minerals and nutrients to be transported through the plant. Active transport through osmosis and the diffusion of water require these special properties of water. Most of all, the cohesion-tension model explains how water moves across great distances by being cohesive. Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Use of initiating uses initiating uses initiating uses initiating uses initiating and and and planning and planning and planning planning skills planning skills skills and skills and skills and and strategies and strategies with strategies with strategies with with a high strategies limited some considerable degree of effectiveness effectiveness effectiveness effectiveness 48. You brush up against the leaves of a plant that are covered with small, hair like projections like the ones shown below. By the time you get home, your skin is irritated. Which specialized part of an epidermal cell were you probably exposed to and explain how you know this? ( 5 marks Thinking/Inquiry) A) You were more than likely exposed to root hairs. Root hairs are another example of specialized structures on epidermal tissue. They are tiny extensions of individual epidermal cells on plant roots. Transfer of knowledge and skills 49. Level 1 transfers knowledge and skills to unfamiliar contexts with limited effectiveness Level 2 transfers knowledge and skills to unfamiliar contexts with some effectiveness Level 3 transfers knowledge and skills to unfamiliar contexts with considerable effectiveness Level 4 transfers knowledge and skills to unfamiliar contexts with a high degree of effectiveness Using the space provided below, use a T chart to explain the various differences between the root system and shoot system in plants. ( 5 marks Communication) Root System -made up of the roots of plants -anchors the plant by penetrating into the soil -absorbs water and minerals that the plant needs Expression and organization of ideas and information Shoot System -made up of stems and leaves, 2 of the 3 organs in plants -stems provide structural support -in some cases, stems provide photosynthesis -leaves are specialized for photosynthesis Level 1 expresses and organizes ideas and information with limited effectiveness Level 2 expresses and organizes ideas and information with some effectiveness Level 3 expresses and organizes ideas and information with considerable effectiveness Level 4 expresses and organizes ideas and information with a high degree of effectiveness