Plant Water Transport: Cohesion-Tension Theory Worksheet
advertisement

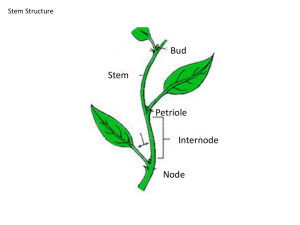
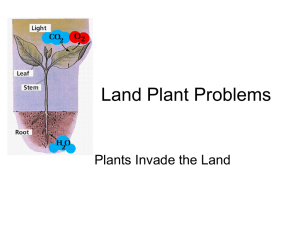
Name: _________________________________ Period: ____ A.P. BIOLOGY – Bulk Transport Reading / Response Bulk Transport of Water in Plants: Cohesion-Tension Theory Chapter 36 (pp. 772 – 776) Concept 36.3 Water and minerals are transported from roots to shoots 1. What is transpiration? (page 772) 2. There are two mechanisms that pull water up through the plant, from roots to leaves: root pressure and transpiration-cohesion-tension. a. Explain root pressure. (page 773) b. The second mechanism that pulls water up through the plant is transpiration-cohesion-tension. Refer to Figure 36.13, p. 775, in your text. Note that water is moving from a region of high water potential to a region of lower water potential. The arrow on the left side of the figure shows this gradient. Explain how water moves from the roots to the leaves of a plant. Include each of these terms in your explanation, and label them on the figure: lower water potential, higher water potential, hydrogen bonding, adhesion, cohesion, xylem tubes, and stomata. ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Tissue Organization of Leaves (pp. 750 – 751) 3. Describe the function of stomata and their associated guard cells. 4. Explain why the organization of cells in the spongy mesophyll differs from that of the palisade layer. How do their respective structures correlate with their functions? Concept 36.4 Stomata help regulate the rate of transpiration 5. Leaves generally have large surface areas and high surface-to-volume ratios. Give an advantage and disadvantage of these traits. advantage disadvantage 6. Plants lose 95% of their water through stomata! What controls the amount of water loss? 2 7. On the sketches, label the guard cell, stomata, K+, and H2O. Explain why the stoma opens when K+ accumulates in the guard cells. 8. Three types of stimuli can cause guard cells to open. Name and explain how each one works. Water-conducting Cells of the Xylem (p. 745) 9. Describe the structure and function of vessel elements and tracheids. 10. List four different physiological or morphological adaptations of xerophytes, and explain how each of them reduces water loss. 3 Adaptations to Reduce Water Loss 4