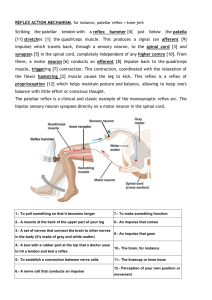
Reflex Arc.
advertisement

Synapses and Reflex Action Synapse • Neurons are not continuous • Synapse is “The junction across which a nerve impulse passes from an axon terminal to a neuron, muscle cell or gland” • Two types of Synapses: o Excitatory o Inhibitory Reflex Action • In Groups of 3. • 2 people face each other, looking at each other • The third person stands off to the side. • Anytime from 1 Sec till 10 Seconds the third person will clap • Two people record what the other does. What is a Reflex action?? Reflex actions • “An action that is performed without conscious thought as a response to a stimulus” • The signals from the receptors do not travel to the brain, instead they travel through what we call a Reflex Arc. • Spinal reflexes or Brain Reflexes • Stimulus – receptor – sensory neuron – association neuron – motor neuron – Effector Response Try These?? • Draw one reflex arc for your body’s response to touching a hot object. • Draw one reflex arc for your body’s response to standing on something sharp. • Draw one reflex arc showing your body’s response to a loud noise. Stimulus Response Model. • How does our body react to normal stimulus?? • In a reflex: o Stimulus – Receptor – Messenger – Association neuron – Messenger – Effector - Response • In a normal response: o Stimulus – Receptor – Messenger - Coordinating system - Messenger – Effector - Response Try These?? • Draw a stimulus response model for how the body would handle a change in temperature? • Draw a stimulus response model for how the body may respond to a drop in water concentration? • Draw a stimulus response model for how the body may respond to a drop in sugar levels? • Hypothalamus (links our nervous and endocrine systems): o o o o o Control Metabolic Activities Water Balance Sugar Metabolism Body Temperature Hormone Secretion Nervous System Review 1. Name the Two parts of the nervous system, and provide there acronyms? 2. Draw and Label the Key Structures of a Motor Neuron? 3. What are the two components of the CNS? 4. What are the two types of matter that make up our CNS? 5. How many Neurons does our brain contain? 6. Name three parts of the Brain? 7. How much space does the Cerebrum take in our brain? 8. What does PNS stand for and what are the two components? 9. What are two examples of Receptors? 10. What function does our Somatic Nervous System play? 11. What are the two types of Photoreceptors found in the eye? 12. Apart from sound, what other function does our ear play in our body coordination? 13. What are 3 examples of stimuli our skin can detect?