3.3 What are the subatomic particles
advertisement

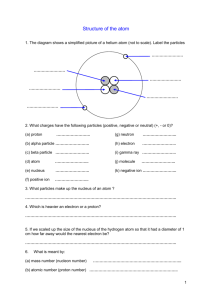
NAME:_______________________ 3.3 What are the subatomic particles? DATE:____________ AHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109/110 UNIT 3 ATOMIC CONCEPTS 3.3 What are the subatomic particles? AIM: DO NOW: Based on our study of the ATOMIC THEORY, draw an atom the way you understand it. Your Atom Version 1 REVIEW: ATOM Shape? Your Atom Revised Version Dense? THREE MAJOR SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Proton Label your proton with as much information as you can: Neutron Label your neutron with as much information as you can: Electron Label your electron and energy levels with as much information as you can: Size? Nucleus Label your nucleus with as much information as you can: Contains? Dense? Diameter? Mass? Directions: Use the information from the notes to fill the chart. Subatomic Particle Protons p+ + p Neutrons N0 p+ Where are they found? p+ Mass Charge (attitude) Draw a simple model of the Atom (label it) Electrons NAME:_____________________________ DATE:__________ 3.3 Independent Practice AHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 ATOMIC CONCEPTS 3.3 What are the subatomic particles? 1. Describe the structure of a typical atom. Identify where each subatomic particle is located (verbally or visually). 2. Compare and contrast JJ Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model with Rutherford’s nuclear atomic model. 3. A student constructs a model for comparing the masses of subatomic particles. The student selects a small, metal sphere with a mass of 1 gram to represent an electron. A sphere with which mass would be most appropriate to represent a proton? a. 1g b. ½ g c. 1/2000 g d. 2000g 4. How did you arrive at your answer to #3?________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Which statement correctly describes the chare of the nucleus and the charge of the electron cloud of an atom? a. The nucleus is positive and the electron cloud is positive. b. The nucleus is positive and the electron cloud is negative. c. The nucleus is negative and the electron cloud is positive. d. The nucleus is negative and the electron could is negative. 6. How did you arrive at your answer to #5?_________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 7. A proton has a mass that is opposite the charge of______________________________________________