CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. 0 Document No
advertisement

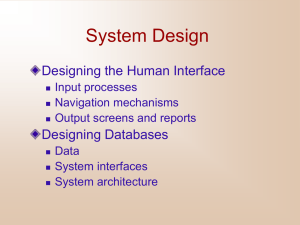
CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: Author: : Norjihan Abdul Ghani Date: : <dd/mm/yy/> Subject Title: : System Analysis & Design/System Analysis & Design Subject Code : CICT1033/CCPS2103 Lesson Title : 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 Version: 1.0 User Interface Design Introduction: Ani1 Ani1: A picture of people are designing an interface Learning Outcome: In the end of this lesson, you will be able to: define the important of user interface design list and explain several types of user interface explain and design the user interface based on the principles design a dialogue diagram List of Topic No 1. Topic Title Overview of user interface design 2. Types of user interface 3. Principles for good user interface design 4. Designing a dialogue Terminology No Word Definition <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 1 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE 1. Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 Command An interface types whereby users enter explicit statements into a system to language interfaces invoke operations 2. Dialogue A sequence in which information is displayed to and obtained from user 3. Menu An interaction methods in which a list of system options is provided and a specific command is invoked by a user selection 4. 5. 6. Natural language An interface types it permit users to interact with the computer in their interfaces everyday or natural language Question-and- An interface type where the system displays a question to the user on the answer dialogue screen User interface A method by which users interact with an information system Reference: <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 2 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 Content Topic Title : Topic 1: Overview Of User Interface Design Interface is an interaction between user and system. a method which users interact with an information system. A user interface should provide a friendly interface which users can interact with the system to process inputs and obtain an output Interface design is where we integrate both input and output design into an overall user interfaces that established the communication between users and system. Interface design focuses on how information system is provided to and captured from users to an information system Ani2 Ani2: A picture from Figure 11-1. When mouse over to the “System Desin”; this text appears (in a callout): Files and Database Output Design Input Design √ User Interfaces <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 3 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Topic Title : Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 Topic 2: Types Of User Interface various types of methods which users can interact with the system Although output design involves a separate set of physical design issues, it is an integral part of a larger concept called user interface. A user interface describes how users interact with an information system, and it consists of hardware, software, screens, menus, functions, and output and features hat affect two way communications between user and information system User interface consisted of process-control screens that allowed the users to send commands to the system A user interface is based on basic principles of human-computer interaction (HCI). User interface design is the specification of a dialogue or interaction between user and information system. User interface design is the specification of a dialogue or conversation between the system user and the information system. Most today’s user interfaces are graphical are graphical. The graphical user interface(GUI) is provided within either the computer operating system or the internet browser The most popular used of graphical user interfaces are menus. 11.2.1: Menus the most commonly employed in information system. is an interface types in which a list of system options is provided and a specific command is invoked by user selection of a menu option. A specific command is invoked or another menu is activated. two methods for positioning menus; pop-up menu and drop down menus. Most applications combine these two types of methods; pop-up and drop down menu. Pop-up menus A menu-positioning method that places a menu near the current cursor position; so users don’t have to move the position or their eyes to view system options. Gfx1 <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 4 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 Gfx1: A picture from Figure 11-2 Drop-down menus A menu-positioning method that places the access point of the menu near the top line of the display; when accessed, menus open by dropping down onto the display. a list of available menus drops down from the main top line of the menus when accessed. Drop down menus have become popular since it provide consistency in menu location and operation among applications and efficiently use display space. Gfx2 Gfx2: A picture from Figure 11-3 good menu design for menu options in Student Registration System. Gfx3 Gfx3: A picture from Figure 11-4 11.2.3: Question-and-Answer Dialogue the system displays a question to the user on the screen. to communicate, users need to answer the question by using keyboard or mouse. Then, the computer acts on the input information in a preprogrammed manner, typically by moving to the next questions. two types of common question-and-answer interface; First, users answering the question and the information system directs the question in sequence basis. Second, by using a dialog box. Users are prompted with questions to which they supply the answer. Gfx4 Gfx4: A picture from Figure 11-5 Question-and-answer dialogues are popular in a web based applications. 11.2.4 : Forms The purpose of forms it to allow users to fill in the blanks when working with a system. <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 5 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 form was used to get input and present the information. A good form should have self-explanatory title and field headings, followed by fields that have been organized into grouping with boundaries to differentiate them. also need to minimize the need to scroll down the windows. Form-fill interfaces consist of on-screen forms or web-based forms displaying fields containing data items or parameters that need to be communicated to the users. 11.2.5: Command Language Interfaces is an interface types whereby users enter explicit statements into a system to invoke operations. For example; to copy a file name database.doc from C location to disk A using DOS can be done by using the statement : COPY C:DATABASE.DOC A:DATABASE.DOC requires user to remember the syntax, names and operation to be done. Command-language manipulates the computer as a tool by allowing the users to control the dialog. When user gives a command to the computer using a command language, it is executed by the system immediately. Activity A (Courseware Activity) Match each of the following terms with its definition. a. Menu interface b. pop-up menu c. drop-down menu d. Command language interface e. Form interface f. Natural language interface g. Questions-and-answer interface 1. A menu positioning method that places a menu near the current cursor position. b 2. A type of interface whereby data fields are formatted in a manner similar to paper-based forms. e 3. An interface type where the system displays a question to the user on the screen. In order to communicate, users need to answer the question by using keyboard or mouse. g 4. An interface type where a list of system options is provided and a specific command is invoked by user selection of a menu option. a <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 6 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 5. A menu positioning method that places the access point of the menu near the top line of the display; when accessed, menus open by dropping down onto the display. c 6. An interface type whereby inputs to and outputs from a computer-based application are in a conventional speaking language such as English. f 7. An interface type where users enter explicit statements into a system to invoke operations. d Activity B (Group Activity) Contrast the differences between form interface and menu interface. Form interaction is a highly intuitive human-computer interaction method where data fields are formatted in a manner similar to paper-based forms. Menu interaction is a human-computer interaction method where a list of system options are provided and a specific command is invoked by user selection of a menu option. <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 7 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Topic Title : Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 Topic 4: Principles For User Interfaces Design The goal of designing a good user interface is to make the user interface pleasing to the eye and easy to use, and at the same time minimizing the user effort in accomplishing their task 11.3.1: Easy to Use the most important things in designing a good interface is it should be designed clearly labeled with all controls, buttons and icons. select only images that users can understand easily. Gfx6 Gfx6: Figure 11-7: Icon and Commands The interface also need to provide on-screen instructions that are logical, concise and clear. A good interface design is an interface which is easy to navigate or return to any level in the menu structure. 11.3.2: An Attractive Layout The important element in any user interface design is the basic layout of the screen, form, or report. should have and follow a standard formats for computer-based forms and reports similar to those the paper-based one. Most of the screen is divided with at least three main components : Header Body or data details Comments or signatures When designing layouts to records or display information from a paper-based forms, we should try to make is as similar as possible with computer-based forms and reports. A good layout with creative and attractive design can attract users in using the system. Use appropriate colors in order to highlight different areas of the screen, but need to avoid gaudy and bright colors. The use of animations and sound might be effective in some situations, but not too many special effects. Arrange the layout title of the screen accordingly in a consistent manner together with its messages and instructions. When a user enters data, please ask the users to reconfirm their input before it goes to the next field. Ensure that all the available commands have same meaning such as NEXT control button <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 8 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 always indicates that the next screen will appears 11.3.3: Minimize Input Errors One objective of user interface design is to reduce data input errors so steps must be taken to ensure that the input is valid. It’s important to provide data validation checks. we must anticipate the types of errors users may make and design features into the system’s interface to avoid, detect, and correct data input mistakes. several validation tests that can be conducted such as class or composition, combination, expected values, missing data, range, self-checking digits, size and values. It is a need and easier to correct the data before permanently stored in a system. The other way is, the system can notify users of input errors as data are being entered. Field formatting and the data entry prompt should make easier and clear the type of data being requested. The use of input mask, which is a template or pattern that make it easier for users to enter data. In other words, a caption describing the data to be entered should be in a same format to the requested data field. 11.3.4: User Feedback and Help When designing interfaces, providing appropriate feedback is an easy method for making a user’s interaction more enjoyable. there are three types of system feedback : Status information a technique for keeping users informed of what is going on within a system. Providing information while the system processing the operation is important especially when the processing takes longer time. Gfx7 Gfx7: A picture from Figure 11-8 Prompting cues a system feedback used to display prompting cues. With a prompt, system designer assumes that the user knows exactly what to enter. For example : Enter your Matric Number (XXX12345): ________ Error or warning messages <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 9 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 a system feedback display messages that is specific and free of error codes. This message should guide the users toward a resolution. For example : Sorry, No Student Found with the Matric Number Besides feedback, it’s good if we can provide helps to user. When designing help, we need to put ourselves in the user’s place. Activity A (Courseware Activity) Activity B (Group Activity) When designing a user interface, what are the main considerations that need to use as a principles in building an internal control into user interface design. Guidelines and considerations to take into account in building internal controls into the user interface design include: Passwords should never be displayed on screen; asterisks are the preferred convention. A standard security authorization screen should be displayed for log-in failures. User interface screens may need to be customized for different categories of users, depending upon their access and security privileges. For web applications, a website certification icon should be displayed and users should be able to view the authentication certificate at any point in their transaction. Exercise Answer TRUE or for FALSE for each of the questions below. 1. The goal of designing a good user interface is to make it attractive and easy to use. TRUE 2. The use of images will make the user interface complex and difficult for users. FALSE 3. Interface should follow a standard formats for computer-based forms and reports similar with the paper-based. TRUE 4. The use of input mask is good to assist users about the template of the input, so it easy for user enters data. TRUE 5. System feedback provides status information, prompting cues, and error or warning messages. TRUE <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 10 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Topic Title : Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 Topic 4: Designing Dialogue is a sequence in which information is displayed to and obtained from user. Dialogue design is a process of designing the overall sequences that user needs to follow to interact with an information system. As a system designer, we have to understand how users use the system and from there we can transform these activities into a formal dialogue specification. Dialogue diagram is a formal method used when designing and representing dialogues. By using dialogue diagram, we can easily represent the sequencing of displays, selection of displays in a system. three types of connection; sequence, iteration and selection. Gfx8 Gfx8: A picture from Figure 11-9 Activity A (Courseware Activity) Activity B (Group Activity) What are three steps involved when designing a dialogue? The three major steps in dialogue design are: (1) designing the dialogue sequence; (2) building a prototype; and (3) assessing usability. A case can be made for the importance of all steps. Yet, designing the dialogue (with input from the user) is likely the most important step because this is where you collect and structure the users’ requirements. Exercise Answer TRUE or for FALSE for each of the questions below. 1. Dialogue is a sequence in which information is displayed to and obtained from user. TRUE <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 11 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 2. Dialogue diagram have one symbol, a box with a four sections. FALSE 3. Dialogue diagram can be drawn after understanding in a way how users will use the system. TRUE 4. Using a dialogue diagram, make it easy to represent the sequencing of displays, selection of displays in a system. TRUE 5. Three types of connection in a dialogue diagram; sequence, iteration and repetition. FALSE <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 12 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 Summary In the end of this lesson, you have learned that: overview of user interface types of user interface principles for good user interface design designing a dialogue Self Assessment Fill in with the correct answer 1. ________________________ focuses on how information is provided to and captured from users. Interface design 2. A ________________________ is a menu positioning method that places a menu near the current cursor position. pop-up menu 3. _______________________________ syntax allows users to enter questions and commands in their native language. Natural-language interface 4. ________________________ refers to a human-computer interaction method where users enter explicit statements into a system to invoke operations. Command language interface 5. A(n) _______________________________ dialogue style is primarily used to supplement either menu-driven or instruction-driven dialogues. Users are prompted with questions to which they supply answers. question-and-answer interface 6. ____________________________ moves the displayed information up or down on the screen, one line at a time. Scrolling 7. ________________________ refers to graphical pictures that represent specific functions within a system. Icon <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 13 CONTENT WRITING TEMPLATE Revision No. Document No. Effective Date: 0 CWT/ISDT/001 Sept 2008 8. Referencing interface ________________________, the standard screen navigation that users use to move between fields should be from left-to-right and top-to-bottom. layout guidelines 9. ________________________, ________________________and ________________________ are three types of system feedback. Status information; prompting cues error; warning messages 10. The sequence of interaction between a user and a system is called a ________________________. dialogue Reference Lonnie D. Bentley, Jeffrey L. Whitten. 2007, Systems Analysis and Design Methods, 6th Edition, McGraw Hill. (Bentley et. al., 2007) Jeffrey A Hoffer, Joey F. George and Joseph S. Valacich. 2005. Modern Systems Analysis and Design. 4th ed. Prentice Hall. (Hoffer et. al., 2005) Shelly, Cashman, and Rosenblatt. 2006. System Analysis and Design, 6th Edition, Thomson. (Shelly et. al., 2006). George M, Marakas, 2001. Systems Analysis and Design: AN Active Approach, 1 st Edition, Prentice hall, Inc. (George ,2001) Dennis, A., & Wixom, B. H. (2003). System Analysis and Design (2 ed.): John Wiley & Sons., (Dennis et.a l. 2003) Ending In the next lesson, we will discuss the fourth phase involved in system development life cycle; system implementation. The purpose of system implementation is to build a properly working system, install it in organization, replace and old systems, preparing system and user documentation and train users. <User Interface Design> < System Analysis & Design > | Private and Confidential 14