Key People in Psych
advertisement
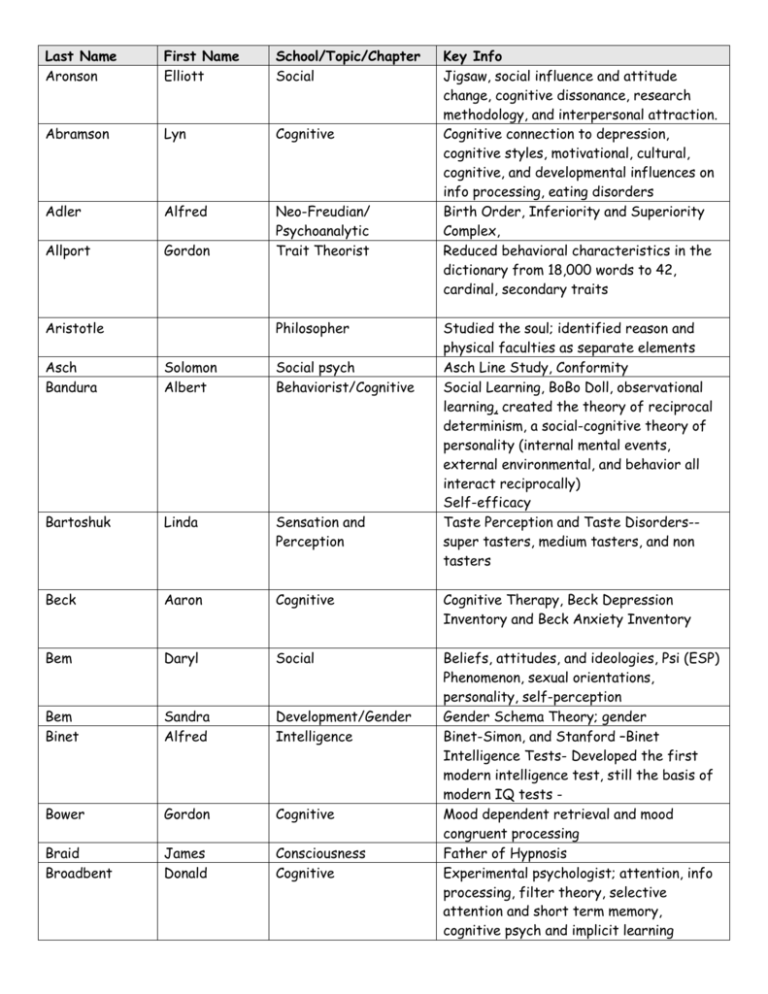
Last Name Aronson First Name Elliott School/Topic/Chapter Social Abramson Lyn Cognitive Adler Alfred Allport Gordon Neo-Freudian/ Psychoanalytic Trait Theorist Aristotle Philosopher Key Info Jigsaw, social influence and attitude change, cognitive dissonance, research methodology, and interpersonal attraction. Cognitive connection to depression, cognitive styles, motivational, cultural, cognitive, and developmental influences on info processing, eating disorders Birth Order, Inferiority and Superiority Complex, Reduced behavioral characteristics in the dictionary from 18,000 words to 42, cardinal, secondary traits Studied the soul; identified reason and physical faculties as separate elements Asch Line Study, Conformity Social Learning, BoBo Doll, observational learning, created the theory of reciprocal determinism, a social-cognitive theory of personality (internal mental events, external environmental, and behavior all interact reciprocally) Self-efficacy Taste Perception and Taste Disorders-super tasters, medium tasters, and non tasters Asch Bandura Solomon Albert Social psych Behaviorist/Cognitive Bartoshuk Linda Sensation and Perception Beck Aaron Cognitive Cognitive Therapy, Beck Depression Inventory and Beck Anxiety Inventory Bem Daryl Social Bem Binet Sandra Alfred Development/Gender Intelligence Bower Gordon Cognitive Braid Broadbent James Donald Consciousness Cognitive Beliefs, attitudes, and ideologies, Psi (ESP) Phenomenon, sexual orientations, personality, self-perception Gender Schema Theory; gender Binet-Simon, and Stanford –Binet Intelligence Tests- Developed the first modern intelligence test, still the basis of modern IQ tests Mood dependent retrieval and mood congruent processing Father of Hypnosis Experimental psychologist; attention, info processing, filter theory, selective attention and short term memory, cognitive psych and implicit learning Last Name Broca Calkins First Name Paul Mary School/Topic/Chapter Brain History consciousness Key Info Broca’s Area—production of speech First Female President of the APA Self Psychology Cannon Cartwright Walter Rosalyn Motivation and Emotion Consciousness Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion/ Dreams as connected to psychologically traumatic events; depression, dreaming and the brain, Sleep Researcher Sleep apnea, parasomnias Cattell Raymond Trait Theorist Charcot Jean Martin Brain Chomsky Noam Development/Language Clark Kenneth Educational psychologist Social Cover-Jones Mary Behaviorist Dewey John Used factor analysis to determine surface traits and 16 source traits Considered by some to be the founder of modern neurology, studied hysteria— believed that hypnosis was a biological not psychological state. Freud and Binet were his students Language—Innate language acquisition device Doll studies on racism ; testified in Brown v. Board, prejudice , First African American to earn a doctorate in psychology at Columbia Counter conditioning—Peter-- The “mother of behavior therapy Thinking and reflection in education Ebbinghaus Herman Memory Ekman Ellis Erikson Paul Albert Erik Emotion Cognitive Psychoanalytic Eysenck Hans Trait Theorist Fechner Gustav Experimental psychologist Festinger Freud Leon Anna Psychoanalytic Freud Sigmund Psychoanalytic Forgetting and Learning Curves, one of first researchers on memory; nonsense syllables Facial Expressiveness, universal and innate RET/REBT Therapy Psychosocial Development—8 Stages, NeoFreudian Coined the “Big 3” dimensions of personality: Psychoticism, Extraversion, Neuroticism Sensation and perception, color perception, JND—just noticeable difference Cognitive Dissonance child psychoanalysis, ego psychology Father of Psychoanalysis, id, ego, se; defense mechanisms, unconscious, dream interpretation Last Name Fromm First Name Erich School/Topic/Chapter Psychoanalytic Key Info Blend of Freud and Marx and freedom (biological determinism + socioeconomic determinism + freedom) Galton Sir Francis Evolutionary eugenics, and differential psychology Darwin’s cousin…evolutionary psych Gardner Gazzaniga Gilligan Howard Michael Carol Intelligence Brain Development Guilford JP Cognitive Hall G. Stanley History Development Harlow Harry Development Hebb Donald Hilgard Holmes Horney Ernest Thomas Karen Consciousness Stress Psychoanalytic Hull Clark Behaviorism Hume Izard David Carroll Philosopher Emotion James William Jung Carl Functionalism/Early Theories Psychoanalytic Kinsey Koffka Alfred Kurt Gestalt Multiple Intelligences Split Brain Research Moral Development—critiques Kohlberg— males=black and white thinking; females=relationship based decisions Structure of Intellect, convergent v. divergent thinking First President of the APA, developmental psychology; described adolescence as a period of “sturm und drang” Attachment; cloth/wire monkey experiment (infant had stronger bond with cloth monkey – need for affection creates a stronger bond) Nature v. nurture, brain damage and intelligence, psychology of individual differences Hypnosis—the hidden observer Holmes-Rahe--SRRS Neo-Freudian, Groundbreaking work on neuroticism; concept of womb envy, criticism of penis envy, moving toward , away, and against Reinforcement, drive-reduction, stimulus, response, incentive motivation Empiricism and perception Emotional Development and facial expressiveness , Found that facial expressions of emotions are constant across cultures American Psychologist, First Psych Textbook, Functionalism Collective v personal unconscious, anima v animus, archetypes, synchronicity Sex researcher Published an early textbook on Gestalt psychology (which studied perception, and how humans combine parts into wholes) Last Name Kohlberg First Name Lawrence School/Topic/Chapter Development Kohler Wolfgang Gestalt Kubler-Ross Lashley Elisabeth Karl Development Brain/Memory Lazarus Richard Emotion Kurt Lewin Social Locke Loftus Lorenz John Elizabeth Konrad Maslow May Abraham Rollo McClelland David Mesmer Milgram Franz Stanley Miller Miller Mischel Alice George Walter Murray Henry Myers David Olds Pavlov Perls Piaget James Ivan Frederick Jean Key Info Moral Development—pre-conventional, conventional, post-conventional (6 stages/3levels) Published an early textbook on Gestalt psychology (which studied perception, and how humans combine parts into wholes) Insight learning Stages of Dying localization of brain function and rats Memory Trace/Engram Cognitive Appraisal and Emotion Leadership styles, experiential learning and group dynamics Philosopher Tabula Rasa Memory Eyewitness id, memory problems, Development Imprinting and Critical Periods, innate behaviors; evolutionary perspective Humanist Humanism, Hierarchy of Needs Humanist/Existentialist Existentialism, the individual must bravely face life as it is. He also talked about 4 stages of development: innocence, rebellion, ordinary, and creative Motivation Achievement Motivation, developed scoring system for TAT Consciousness Hypnosis Social Psych Milgram Obedience Study, social psych, norms Child abuse and the impact on society Memory Memory, short term memory 7 +/-2 Personality Personality—behavior is based on situational influences, did the Marshmallow test, self/emotional regulation Considered a trait Developed TAT, psychogenic needs—power, theorist affiliation, and achievement Social Psych psychology and religion connection, positive psych, hearing loss Biological Rewards system in the brain Behaviorist Classical Conditioning, Dogs, Therapy Gestalt Therapy Cognitive/Development Cognitive development, assimilation v accommodation, sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operations, formal operations, Last Name Plato First Name School/Topic/Chapter Philosopher Plomin Premack Rahe Robert David Richard Biological Rank Otto Psychoanalyst Rescorla Rogers Robert Carl Behaviorism Humanism Rorschach Schachter Herman Stanley Personality Assessment Emotion Seligman Martin Seyle Hans Stress Simon Herbert Cognitive Skinner B.F. Behaviorist Socrates Solomon Richards Philosopher Behaviorial Spearman Sperry Sternberg Charles Roger Robert Intelligence Biological Intelligence Love Szasz Thomas Abnormal Terman Lewis Intelligence Thorndike Edward Behaviorist Thurstone Louis Intelligence Stress Key Info Described levels of consciousness in his “Cave” Twin Studies and Behavior Genetics Primate Research, symbol use in chimps Stress, SRRS, worked with prisoners of war, hostages Initially Freud’s favorite son, he later broke with Freud and emphasized the conscious mind and current experience Cognitive connection to learning Humanism, real vs. ideal, Client-Centered Therapy inkblots Schacter-Singer Theory of emotion, Twofactor theory of emotion: generalized arousal and appraisal Learned helplessness; also known for his research on optimism, biological preparedness Stress—GAS—alarm, resistance, exhaustion Organizational decision making, problem solving, informational processing Operant conditioning, operant chamber, air crib Opponent process theory, Perception , avoidance learning, punishment, drug addiction—Rescorla and Seligman were his students G Factor—Intelligence Nobel prize winner—split brain research Triarchic theory of love and intelligence— Love: (intimacy, passion, commitment) intelligence: (creative, analytic and practical) “there is no such thing as mental illness” It allows for labeling—“you have problems with living” Intelligence—Revised Binet-Simon (Mental / Chronological X 100) Law of Effect—first to experimentally study animal behavior…active behaviors are influenced by their consequences 7 primary mental abilities; intelligence Last Name Titchener First Name Edward Key Info Structuralism—Wundt’s student Edward School/Topic/Chapter Structuralist/Early Theories Behaviorism Tolman Von Helmholz Herman S/P Vygotsky Watson Lev John Social/Development Behaviorist Weber Wechsler Weisel Ernst David Tortsen S/P Intelligence/Cognitive Biological Wernicke Wertheimer Karl Max Wolpe Wundt Joseph Wilhelm Brain Gestalt—Early Theories Behaviorist Structuralism/Early theories Young-Helmholtz—Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision Social and cultural influences Classic conditioning, Little Albert, advertising Psychophysics and JND WAIS , WISC Sensation and Perception—visual cortex, visual processing, specialized cells Understanding language Gestalt Yerkes Robert Zimbardo Phillip Social Latent Learning and Cognitive Maps Systematic Desensitization First Psych Lab, introspection, structuralism Intelligence—chimps v humans, eugenics, Yerkes-Dodson—arousal to performance Stanford Prison study, Shyness, Discovering Psych Series, Power of the Situation, most recent--heroes