Chemistry
advertisement

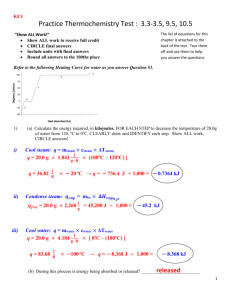
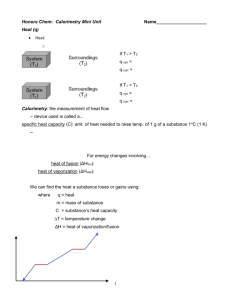
Calorimetry Problems Worksheet 2 1. A reaction occurs in a calorimeter containing 200.0 g of water with an initial temperature of 22.0oC. The temperature of the water changes to 17.5oC. a) Was the reaction endothermic or exothermic? Explain. b) Calculate H in kilojoules. 2. Exactly 4.50 kJ of heat energy was released by a reaction in a calorimeter. The temperature of the water changed by 34.0oC. Calculate the mass of water in the calorimeter. 3. When 450. J of heat energy was added to a 25.0 g certain substance, its temperature increased from 23.0oC to 25.0oC. Determine the specific heat of this substance. 4. A calorimeter contains 250.0 g of water at an initial temperature of 25.0 oC. A reaction occurring in the calorimeter absorbs 850. J of heat energy. Determine the final temperature of the water. 1 5. A reaction occurring in a calorimeter containing 100.0 g of water produces a temperature change from 21.0oC to 34.0oC. a) Was the reaction endothermic or exothermic? Explain. b) Determine the quantity of heat energy involved. 6. Exactly 2.77 g of a hydrocarbon was burned in a calorimeter containing 100.0 g of water. The temperature of the water increased from 23.0oC to 74.5oC. a) Calculate the amount of heat energy involved in the reaction. b) Express your answer above in kJ/g of hydrocarbon. c) If the hydrocarbon has a molar mass of 192 g/mol, express your answer in kJ/mol of hydrocarbon. 7. A 3.50 g sample of nickel metal at a temperature of 88.0oC is placed into a 50.0 g sample of water at 25.0oC. What will be the final temperature of both the metal and water after “thermal equilibrium” is reached? The specific heat capacity of nickel is 0.444 J/goC. 2