Notes Lesson 6
advertisement

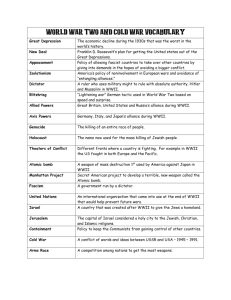
World History Mr. Reed Question Answer Stalin Communist dictator of Soviet Union during WWII Mussolini Fascist dictator of Italy during WWII Hitler Nazi dictator of Germany during WWII Chiang Kai-Shek Nationalist leader of China during WWII Churchill Prime minister of England during WWII DeGaulee Led Free-French forces in WWII F.D. Roosevelt President of the U.S. during most of WWII; died in 1945 Tojo Fascist dictator of Japan during WWII Eisenhower United States General; made Supreme Allied Commander in Europe Truman U.S. President after Roosevelt; decided to use atomic bombs against Japan Appeasement policy of giving in to a nation's demands to avoid war Non-aggression pact two countries agree not to attack one another Axis Powers Germany, Italy, and Japan during WWII Embargo a stoppage of all trade with a country Allied Powers Great Britain, France, Soviet Union, China, and the U.S. Gestapo Hitler's secret police, mainly used to hunt and torture Jews Holocaust the Nazi policy of deliberately murdering Jews and other non-Aryans Genocide deliberate attempt to kill an entire people Concentration Camps prison-like camps designed to "hold" Jews and others till they were murdered Blitzkrieg "Lightning War" German tactic of using airplanes and tanks to surprise the enemy Vichy part of France unoccupied by Germans, but controlled by proGerman French Lend-Lease (1941) United States policy of "loaning" war materials to Allied countries Island Hopping United States strategy in the Pacific where the U.S. would by-pass Japanese strongholds and attack smaller islands Manhattan Project secret code-name for the U.S. atomic weapons program developed during WWII United Nations created after WWII by the victorious Allies; intended to prevent the rise of dictatorships and future wars; still in existence today Israel Jewish "free" state created by the Allies after WWII in Palestinian territory; became and independent nation in 1947 Nuremburg Trials series of court hearing at the end of WWII to convict Nazi war criminals Radar (GB) used to detect airplanes and later, ships Sonar (GB) underwater version of radar, used to detect submarines Bazooka shoulder-launched rocket designed to let an infantryman disable a tank Jet Aircraft (Ger)advanced engine designs allowed fighters to fly MUCH faster than propeller-driven aircraft Aircraft Carrier (US, Japan) large ship designed to carry airplanes; THE weapon in the Pacific LST (US) large ship used to transport tanks and other large vehicles directly onto a beach during an invasion V-1 Rocket (Ger) terror weapon, world's fist cruise missile V-2 Rocket (Ger) terror weapon, world's first ballistic missile Atomic Bomb (US) worked under Einstein's theory of splitting an atom; used on Hiroshima and Nagasaki; forced Japan to surrender Air-to-Surface Rocket (Ger) first "smart" weapon; TV-guided rocket fired from a bomber to destroy naval targets Long-Range Bombers (US, GB) large aircraft designed to destroy enemy cities and industries Magnetic Mines (US, Ger) underwater mines designed to detonate whenever a ship got close Napalm (US) Highly flammable jelly-like substance used in flame-throwers and bombs Acoustic Torpedoes (Ger) specialized submarine weapon that only had to be aimed near its target Rocket Artillery (Ger, S.U.) rapid-firing artillery that was used as a terror weapon against troops Computer (US) developed to rapidly calculate artillery aiming and trajectory Assault Rifle (Ger) fully automatic hand-weapon; gave each soldier the firepower of a machine gun Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 Japan sneak attack on United States Naval Forces; U.S. enters war Battle of Stalingrad August 1942; stopped German drive into Soviet Union, THE turning point battle on the Eastern Front Battle of El August 1942; British defeat Italy and Germany, THE turning point Alamein of the battle in Africa Battle of Midway June 1942; THE turning point battle in the Pacific; U.S. stops Japan's drive on Hawaii Operation Overlord (D-Day) June 6, 1942; Allied invasion of Normandy, France; establishes 2nd front in Europe; larges amphibious invasion in history Battle of the Bulge December 1944; last German offensive of WWII; Germans use up their remaining military supplies and largest US battle of WWII Battles of Iwo Jima and Okinawa Spring and Summer 1945; US invades islands to secure bases to invade Japan; costly victory here plays role in US decision to use atomic bomb Causes of WWII *Germany blamed for WWI by Treaty of Versailles*League of Nations too weak to stop aggression*Great Britain and France's policy of appeasement toward Hitler*U.S. policy of isolationism Aggression by totalitarian dictators Axis Powers Germany*Italy*Japan and "Others" Allied Nations Great Britain*France*Soviet Union*United States*China*"Other Nations" Turning Points Battle of Britain*German Invasion of Soviet Union*Japan Attacks Pearl Harbor*Battles on specific "Fronts" Impact of WWII Cold War begins*Nuremburg War Trials*Division of Germany and Korea*Creation of United Nations*Establishment of Jewish free state (Israel)*HUGE amounts of new technology