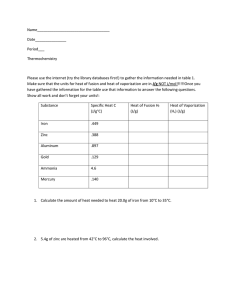
Heat Transfer Worksheet: Specific Heat Calculations

Name: Date: Period:
Ch 11 Worksheet 2 -
May 6, 2008
Heat Transfer
1.
A sample of mercury is heated from 25.5
C to 52.5
C. In the process, 782 J of heat are absorbed. What mass of mercury was in the sample? The specific heat of mercury is 0.138 J/g
C.
2.
A piece of erbium metal weighing 100.0 g and heated to 95.0
C is dropped into
200.0 g of water initially at 20.0
C. The final temperature of the mixture is 21.5
C. What is the specific heat of erbium metal?
3.
A 21.5 g block of titanium was placed in a Bunsen burner for 10 minutes and heated to some unknown temperature. The block was then placed into 100.0 ml of water at an initial temperature of 20.0
C. The final temperature of the mixture was 39.5
C.
How hot did the titanium block get? (C
Ti
= 0.523 J/ g
C)
4.
A block of rhenium metal (specific heat = 0.138 J/g
C) is heated to 88.2
C and then dropped into 100.0 g of water initially at 26.4
C. The final temperature of the mixture is 32.4
C. What was the mass of the block of rhenium?
5.
(Extra Credit) What is the final temperature of 250.0 g of water whose initial temperature is 25.0
C if 80.0 g of aluminum (initially at 70.0
C) is dropped into the water? The specific heat of aluminum is 0.900 J/g
C.
Answers: 1) 210. g 2) 0.171 J/g
C 3) 766
C 4) 326 g