1 - Rosshall Academy
advertisement

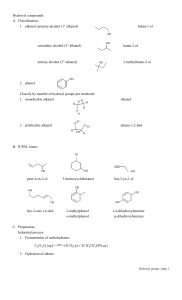
2.3 Alkanols, Alkanoic Acids & Esters Learning Outcomes In all cases pupils should be able to: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 State that fermentation is the breakdown of glucose to form ethanol and carbon dioxide. State that an enzyme in yeast acts as a catalyst for the reaction. State that ethanol, for alcoholic drinks, can be made by the fermentation of glucose derived from any fruit or vegetable. State that the concentration of ethanol produced during fermentation is limited. State that distillation is a process used to increase the concentration of ethanol in ‘spirit’ drinks. State that alcoholic drinks, if taken in excess, can have damaging affects to health and mind. State that to meet market demand, ethanol is made by means other than fermentation. State that industrial ethanol is manufactured by the catalytic hydration of ethane. State that ethanol can be converted back to ethane by dehydration. State that ethanol, mixed with petrol, can be used as fuel for cars. State that ethanol obtained from sugar cane is a renewable source of energy. Identify an alkanol as containing the hydroxyl functional group (-OH) State that alkanols are a homologous series based on the corresponding parent alkanes Write systematic names for alkanols, incorporating the position of the hydroxyl group, from shortened and full structural formulae C1 to C8 Draw full & shortened structural formulae for straight chain alkanols given the names C1 to C8 Identify an alkanoic acid from the carboxyl functional group and the ‘-oic’ name ending. State that alkanoic acids are a homologous series based on the parent alkanes 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 Write systematic names for straight chain alkanoic acids given the shortened or full structural formula C1 to C8 Draw full & shortened structural formulae for straight chain alkanoic acids given their name C1 to C8. State that esters are formed by the condensation reaction between an alkanoic acid and an alkanol. State that, in a condensation reaction, the molecules join together by the reaction of the functional groups to make water. State that the ester link is formed by the reaction of a hydroxyl group with a carboxyl group to make water. Identify an ester from the ester group and the ‘-oate’ ending. Name esters given the name of the alkanol & alkanoic acid or from shortened & full structural formulae. Draw full & shortened structural formulae for esters given the names of the alkanol & alkanoic acid or the names of esters. State that esters can be broken back down into an alkanol and an alkanoic acid in a process called Hydrolysis. State that the formation and hydrolysis of an ester is an example of a reversible reaction. Name the products of hydrolysis of an ester given the name of the ester. Draw the full structural formula or shortened structural formula of the products of hydrolysis given the name, full or shortened structural formula of the ester.