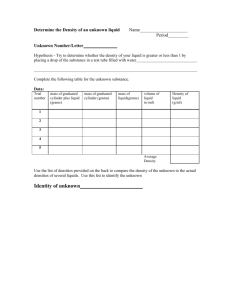
PRE-AP CHEMISTRY: Semester 2 Final Review
advertisement

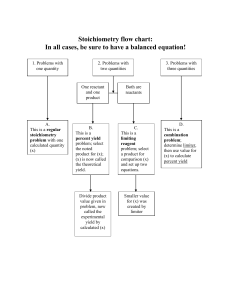
PRE-AP CHEMISTRY: Semester 2 Final Review Final: June 8 (period 7); June 9 (period 6) Review days after school: Monday June 1, Wednesday June 3, Thursday June 4 *You have come a long way this year! You should celebrate your successes and continue to work hard until the end. Let me know how I can help you! **You can also use a periodic table and your reference sheets from the semester. ***Your binder contains your work from the whole semester (maybe even the whole year!) You can study from your semester’s old worksheets, practice problems within the chapters, labs, quizzes, or tests, or look in my folders for extra worksheets/practice. I. SEMESTER 1: a. Significant figures: rules for measuring, rounding, etc. i. Why do we need them? ii. How can you tell how many sig figs are in a measurement? b. Scientific notation, converting metric units i. 5.64 x 105 = ________________ ii. 0.000374 = ________________ iii. 5000 grams = __________kg iv. 0.345 L = ____________mL c. Physical/chemical changes (in Ch. 9 again) d. Structure of an atom: numbers of protons, neutrons, electrons i. What are isotopes? ii. How do you identify the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom? e. Electron configurations i. Use the Aufbau principle to write e- configs for any element on P-table ii. Know electron configurations for ions: what has changed? Why do atoms become ions? f. Arrangement of periodic table i. Names of specific groups on table: halogens, alkali metals, noble gases, metals, nonmetals II. UNIT 5 IONIC BONDING (Chapter 4/12) i. How do positive ions form? Negative ions? ii. What is the octet rule? How does ionic bonding happen? iii. Naming and writing formulas, including those with transition metals 1. MgCl2 = __________________ 2. KF = ________________ 3. Iron (III) oxide = _____________ iv. Common polyatomic ions 1. Na2CO3 = __________________ 2. Aluminum hydroxide = _________________ III. UNIT 5: COVALENT BONDING a. What is the octet rule? How does covalent bonding happen? b. Single, double, triple bonds + valence electrons c. Naming and writing formulas (system of prefixes) d. VSEPR: predicting shapes of molecules e. Polar/nonpolar: what is it, how do you know? i. Draw Lewis structures for the following molecules and identify the shape and polarity: 1. H2O 4. SF6 2. NH3 5. SO4 -2 3. CH4 IV. UNIT 6/7: CHEMICAL REACTIONS a. What is a chemical reaction? V. VI. b. Balancing chemical reactions (conservation of mass) i. __ H3PO4 + __ NaBr __ HBr + __ Na3PO4 ii. __ CF4 + __ Br2 __ CBr4 + __ F2 c. State 5 observations that a chemical reaction has occurred. d. Writing reactions from words: i. Sodium bicarbonate decomposes into sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water. ii. Lead (II) iodide and potassium chloride react to form lead (II) chloride and potassium iodide. e. ID 5 Types of reactions: synthesis, decomposition, combustion, single replacement, double displacement i. P4 + 3 O2 2 P2O3 _________________________ ii. Na3PO4 + 3 KOH 3 NaOH + K3PO4 ____________________ iii. O3 O. + O2 _________________________ iv. SeCl6 + O2 SeO2 + 3Cl2 _________________________ f. Activity series for SR rxns (know how to use, on reference sheet) g. Solubility rules (What is a precipitate?) h. Predicting products for all types of reactions i. __ HCN + __ CuSO4 ii. __ C4H8 + __ O2 iii. __ Cu + __Ag2SO4 UNIT 8: THE MOLE a. Molar mass calculations: Use the Periodic Table i. Calculate the molar mass of calcium phosphate, Ca3(PO4)2. b. Grams-moles-particles calculations and relationships (1 mole = 6.022 x 10 23 particles) i. Calculate the number of atoms in 2.00 g of platinum. ii. What is the mass in grams of 3.01 x 1019 molecules of iodine, I2? c. % Composition i. Quartz has the chemical formula SiO2. What is the percentage composition of this compound? d. Empirical/Molecular formulas i. What is the empirical formula for a compound of aluminum and fluorine that is 32% aluminum and 68% fluorine? ii. The empirical formula of a compound is CH. The experimental molar mass is 78.12 g/mol. Determine the molecular formula of the compound. UNIT 9: STOICHIOMETRY a. DEFINE (and know relationships between): Limiting reagent, excess reagent, percentage yield, actual yield, theoretical yield b. Mole Ratios: Use a balanced equation c. Grams A to grams B calculations d. Limiting/Excess reactant/% yield problems i. Consider the reaction: 2 Al + 3 S Al2S3 83.7 grams of aluminum, Al, and 195.2 grams of sulfur, S, are put into a container and allowed to react according to the above equation. Calculate the following: Excess reactant is __________________ Limiting reactant is __________________ Amount of Excess reactant left over __________________ Amount of product expected to be made (TY) _____________ Amount of product actually made: 200 g Al2S3 (AY) Percent yield = AY/TY x 100%