UNIT: 1
advertisement

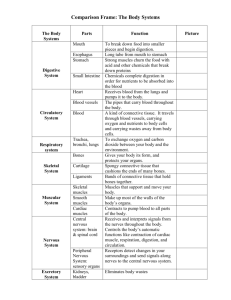
UNIDAD: 3.- INTERACCIÓN Y COORDINACIÓN ¿QUÉ ES LA INTERACCIÓN? Todos los seres vivos interactúan con el medio ambiente y con otros seres vivos para sobrevivir. La interacción implica diferentes elementos: Interaction involves different elements: Estímulos: Son cambios detectables en el medio ambiente. Por ejemplo, un estímulo es el olor de una flor o la imagen de un edificio. Receptores: Son estructuras que reciben estímulos del medio ambiente. En los animales, los receptores son los órganos de los sentidos. Sistema de coordinación: Está compuesto por los órganos que procesan la información recibida por los receptores y produce la respuesta. Órganos responsables: Son estructuras que llevan a cabo las respuestas, como los músculos y las glándulas en los animales. ¿CÓMO FUNCIONAN LOS RECEPTORES? Receptores son estructuras sensoriales que detectan estímulos externos e internos. Los órganos de los sentidos son: Vista: Los ojos detectan la luz. Olfato: La nariz detecta sustancias químicas disueltas en el aire. Gusto: La lengua detecta sustancias químicas disueltas en el agua. Oído: Las orejas detectan sonidos. Tacto: La piel detecta presión, tacto, dolor y cambios de temperatura. ¿CÓMO FUNCIONA LA COORDINACIÓN EN LOS ANIMALES? Los sistemas de coordinación trabajan juntos para procesar la información recibida de los estímulos, y producir la respuesta apropiada. Los animales tienen dos sistemas de coordinación: El sistema nervioso regula y coordina las actividades del cuerpo y las respuestas. El sistema endocrino regula y coordina las funciones del cuerpo principalmente por sustancias químicas llamadas hormonas. ¿CÓMO FUNCIONA EL SISTEMA NERVIOSO? El sistema nervioso recibe información, la interpreta, y transmite una respuesta a los órganos efectores. El sistema nervioso en los vertebrados incluye: El sistema nervioso central: Consta de cerebro y la espina dorsal. El cerebro analiza la información y decide una apropiada respuesta. El sistema nervioso periferico: Consta de nervios que se originan en el cerebro y en la espina dorsal. Los nervios llevan impulsos nerviosos desde los centros nerviosos a todas las partes del cuerpo. Los nervios pueden ser clasificados como: - Nervios aferentes (sensoriales): Llevan la información desde los órganos de los sentidos hasta el sistema nervioso central. - Nervios eferentes (motores): Llevan la información sobre la respuesta desde el sistema nervioso central hasta los órganos responsables. ¿CÓMO FUNCIONAN LOS ÓRGANOS DE RESPUESTAS? Hay dos tipos de respuestas a estímulos. Respuestas motoras: La respuesta es movimiento. El sistema motor consta de un sistema óseo (los huesos sostienen al cuerpo) y un sistema muscular (los músculos son órganos contráctiles unidos al hueso por tendones). Respuestas endocrinas: La respuesta es la liberación de hormonas. Se controla por glándulas en el sistema endocrino. Estas glándulas producen hormonas que se liberan en la sangre y controlan y coordinan actividades por todo el cuerpo. ¿CÓMO FUNCIONA LA COORDINACIÓN EN LAS PLANTAS? Las plantas no tienen un sistema nervioso ni un sistema endocrino. Las respuestas a los estímulos en las plantas son coordinadas por hormonas. Las plantas responden a muchos factores como: luz, gravedad, agua y temperatura. ¿QUÉ ES TROPISMO? Tropismo es un tipo de respuesta en las plantas el cual cambia permanentemente la dirección de un crecimiento de la planta. Hay dos clases de tropismo: Tropismo positivo: La planta crece en la dirección de la fuente del estímulo. Tropismo negativo: La planta crece en dirección contraria a la fuente del estímulo. Algunos tropismos son: geotropismo (gravedad), fototropismo (luz), hidrotropismo (agua), tigmotropismo (contacto), etc. ¿QUÉ SON LAS NASTIAS? Hay respuestas temporales de alguna parte de la planta a estímulos externos. La planta después vuelve a su posición original. Nastia son, por ejemplo: - Algunas flores se abren al atardecer y se cierran durante el día, otras flores hacen lo contrario. - Los tulipanes se abren y cierran según la temperatura. - Algunas plantas se mueven cuando se tocan, etc. NAME:_________________________________________ DATE:__________ 2º ESO___ (Bilingual) UNIT: 3.- INTERACTION AND COORDINATION WHAT IS INTERACTION? All living beings interact with their environment and with other living beings to survive. Interaction involves many different elements: Stimuli: These are detectable changes in the environment. For example, a stimulus is the smell of a flower or the sight of a building. Receptors: These are structures which receive stimuli from the environment. In animals, the receptors are the sense organs. Coordination system: This consists of organs which process information received by the receptors and they produce a response. Responsive organs: These are structures which produce responses, such as muscle and glands in animals. 1.- Copy below this information. 2.- Translate the following words: Interaction: Stimuli: Environment: Living being: Receptor: Sense organs: Muscle: System coordination: Gland: Responsive organs: 3. – What is the difference between stimulus and stimuli: 4.- Fill-in the blank: ___________: These are detectable ___________ in the _______________. ___________: These are ____________ which receive ___________ from the _______________. ______________________: This consists of _________ which process ________________ by the ___________ and they produce a _____________. ______________________: These are ______________ which produce ____________, such as ________ and ________ in animals. 5. – Complete with vowels: R__c__pt__rs: Th__s__ __r__ str__ct__r_ s wh__ch r__c__ __v__ st__m__l__ fr__m th__ __nv__r__nm__nt. __n __n__m__ls, th__ r__c__pt__rs __r__ th__ s__ns__ __rg__ns. 6.- Write “stimulus” or “receptor” or 1both below each picture: ________________ __________________ _______________ ________________ _________________ _________________ _______________ _______________ _______________ __________________ _______________ 7.- What are stimuli? Write an example: 8.- What are receptors? Draw a receptor. 9.- What is a coordination system? 10.- What are the responsive organs? 1 _________________ Both = los dos NAME:_________________________________________ DATE:__________ 2º ESO___ (Bilingual) HOW DO RECEPTORS WORK? Receptors are sensory structures which detect external and internal stimuli. The sense organs are: Sight: The eyes detect light. Smell: The nose detects chemical substances dissolved in the air. Taste: The tongue detects chemical substances dissolved in water. Hearing: The ears detect sound. Touch: The skin detects pressure, touch, pain and temperature changes. 1.- Copy this information: 2.- Translate these words: Receptor: Touch: Taste: Sight: Hearing: Sense organs: Smell: stimuli: 3.- Match the columns with arrows Touch Taste Sight Smell Hearing 4.- Match the two columns with arrows Nose Touch Ear Taste Eye Sight Skin Smell Tongue Hearing 5.- Fill-in the blank: a) The _________ detect sound. b) The _________ detect light. c) The _________ and ___________ detects chemical substances d) The __________ detects pressure, touch, pain and temperature changes. 6.- What are the different senses: 7.- What are the sense organs: 8.- Draw a picture to represent the sense of sight: 9.- Draw a picture to represent the sense of hearing: 10.- Match the columns with arrows: Hearing eyes Touch nose Sight tongue Smell ears Taste skin pain and temperature sound chemical substances chemical substances light NAME:_________________________________________ DATE:__________ 2º ESO___ (Bilingual) HOW DOES COORDINATION WORK IN ANIMALS? Coordination systems work together to process information received from stimuli, and to produce appropriate responses. Animals have two coordination systems: The nervous system regulates and coordinates the body’s activities and responses. The endocrine system regulates and coordinates the body’s functions by means of chemical substances called hormones. 1.- Copy this information in the box 2.- Translate these words: Stimuli: Response: Hormone: Nervous system: Endocrine system: Chemical substances: 3.- Match the two columns with arrows Nervous system Endocrine system Coordinates the body functions Produce appropriate responses Process information received Hormones 4.- Write ‘T’ if the statement is true or ‘F’ if it is false. a) Coordination systems work to process information received from stimuli. b) Coordination systems produce appropriate responses. c) The nervous system regulates the body’s activities and responses. d) The endocrine system regulates and coordinates the body functions by means of chemical substances. 5.- Fill-in the blank The ____________ system regulates the body’s __________________________. The ____________ system regulates and _________________ the body ________________ by means of ____________________ called _______________. 6.- Complete with vowel: Th__ n__rv__ __s syst__m r__g__l__t__s th__ b__dy’s __ct__v__t__ __s __nd r__sp__ns__s. Th__ __nd__cr__n__ f__nct__ __ns by syst__m m__ __ns r__g__l__t__s __f ch__m__c__l __nd c__ __rd__n__t__s s__ubst__nc__s th__ c__ll__d b__dy h__rm__n__s. 7.- What is the nervous system useful for?: The nervous system is useful because ___________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 8.- What is the endocrine system useful for?: 9.- What are the differences between the nervous system and the endocrine system? 10.- What are the similarities between the nervous system and the endocrine system? NAME:_________________________________________ DATE:__________ 2º ESO___ (Bilingual) HOW DOES THE NERVOUS SYSTEM WORK? The nervous system receives information, interprets it, and transmits a response to the responsive organs effectors. The nervous system in vertebrates includes: The central nervous system: This consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The brain analyses information and decides on a suitable response. The peripheral nervous system: This consists of nerves which originate in the brain and in the spinal cord. The nerves carry nerve impulses from the nerve centres to all other parts of the body. The nerves can be classified as: - Afferent (sensory) nerves: They carry information from the sense organs to the central nervous system. - Efferent (motor) nerves: They carry information about the responses from the central nervous system to the responsible organs. 1.- Copy below: 2.- Translate this words: Nervous system: Brain: Spinal cord: Nerves impulses: Afferent nerves: Efferent nerves: Central nervous system: Peripheral nervous system: Nerves: Nerve centres: sensory nerves: Motor nerves: 2.- What is the Central Nervous System?: 3.- How are the nerves be classified?: ________________________________ and _________________ ____________________________________ 4.- What is the difference between Afferent and Efferent nerves? 5.- a) What is the other name for afferent nerves? b) What is the other name for efferent nerves? 6.- Fill-in the blank: a) The _____________________________: This consists of the _________ and the _____________. b) The _____________________________: This consists of ________ which originate in the ______ and in the ___________________. c) The _____________ analyses information and decides on a suitable response. d) The _____________ carry _________________ from the _____________ to all other parts of the body. 7.- Write “T” if the sentence is true or “F” if the sentence is false. a) The nervous system receives information, interprets it, and transmits a response to the responsive organs affectors. b) The central nervous system consists of the nerves, the brain and the spinal cord. c) The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves which originate in the brain and in the spinal cord. d) The efferent nerves carry information from the sense organs to the central nervous system. 8.- Correct the mistakes in the previous activity. Be rewriting the sentences. a) b) c) d) 9.- What are the differences between sensory nerves and motor nerves? 10.- What are the similarities between afferent and efferent nerves? NAME:_________________________________________ DATE:__________ 2º ESO___ (Bilingual) HOW DO THE RESPONSIVE ORGANS WORK? There are two types of response to stimuli. Motor responses: The response is movement. The motor system consists of a skeletal system (bone support the body) and a muscular system (muscles are contractile organs attached to the bone by tendons). Endocrine responses: The response is the release of hormones. It is controlled by glands in the endocrine system. These glands produce hormones which are released into the blood and control and coordinate activities throughout the body. 1.- Copy the text: 2.- Translate these words: Responsive organs: Skeletal system: Endocrine responses: Hormones: Blood: Bones: Motor system: Muscular system: Endocrine system: Glands: body: Muscles: 3.- Fill-in the blank: a) ____________________: The response is ______________. b) The ________________ consists of a ___________ system and a ____________ system c) ____________________: The response is the release of _______________. d)These __________ produce ______________ which are released into the ________ and _______ and _____________ activities throughout the __________. 4.- Match the two columns with arrows Motor response Endocrine response Muscular system Movement Endocrine system Skeletal system Motor system Hormones Glands 5.- Complete The motor system The endocrine system The response is … Consists of … 6.- Correct the mistakes: a) The endocrine system consists of a muscular system and a skeletal system. b) The glands, in the endocrine system, produce blood. c) The bones are contractile organs. d) The muscular system consists of bones. 7.- Put in order this sentences: a) motor system The consists skeletal system of a muscular system. and a b) contractile Muscles are the bone organs tendons. attached to by c) the blood. The hormones glands produce released into which are d) bone The body. support the 8.- Complete with vowels: a) Th__ m__t__r syst__m s__pp__rt th__ c__ntr__ct__l__ b__dy) __rg__ns c__ns__sts __nd __ __f __ m__sc__l__r __tt__ch__d b) Th__ h__rm__n__s __r__ __nd c__ __rd__n__t__ __ct__v__t__ __s t__ r__l__ __s__d sk__l__t__l Some muscles: (b__n__ syst__m (m__scl__s th__ b__n__ by t__nd__ns). __nt__ th__ thr__ __gh__ __t 9.- Look for the names of some glands of the endocrine system: 10.- Look for the names of… Some bones: syst__m bl__ __d th__ __r__ __nd b__dy. c__ntr__l NAME:_________________________________________ DATE:__________ 2º ESO___ (Bilingual) HOW DOES COORDINATION WORK IN PLANTS? Plants do not have a nervous system or an endocrine system. Responses to stimuli in plants are coordinated by hormones. Plants respond to many factors such as: light, gravity, water and temperature. 1.- Copy this text. 2.- Translate: Nervous system: Plant: Gravity: Temperature: Endocrine system: Light: Water: Stimuli 3.- What are coordinated by hormones? 4.- Correct the mistakes: a) Plants have a nervous system. b) Plants have a endocrine system. c) Plants do not respond to any factors. d) Plants do not respond to many factors such as: light, gravity, WHAT IS TROPISM? Tropism is a type of response in plants which permanently changes the direction of a plant’s growth. There are two types of tropism: Positive tropism: The plant grows in the direction of the source of the stimulus. Negative tropism: The plant grows away from the source of the stimulus. Some tropisms are: geotropism (gravity), phototropism (light), hydrotropism (water), thigmotropism (contact), etc. 5.- Copy only the two types of tropism. 6.- What is a tropism? 7.- a) What is the difference between positive and negative tropism? b) Write the names of the various tropisms: 8.- Look at the picture and respond. What types of tropism does each part of the plant have? a) The stem grows towards light: b) The stem grows in the opposite direction of the Earth: c) The root grows towards the Earth: d) The root grows in the opposite direction of to the light: e) Draw the root of this plant WHAT ARE NASTIC MOVEMENTS? There are temporary responses of particular parts of a plant to external stimuli. The plant later returns to its original position. Nastic movements are, for example: - Some flowers open at dusk and close during the day, others flowers do the opposite. - Tulips open and close according to the temperature. - Some plants move when they are touched, etc. 9.- What are the differences between tropism and nastic movements? 10.- What are the similarities between tropism and nastic movements?