Dihybrid Cross Problems
advertisement

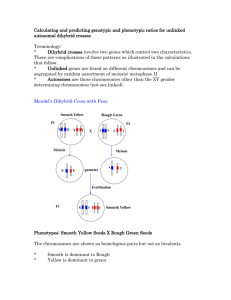
Sample Dihybrid Crosses Example1: Capercaille (simple dominance/ recessive) The Capercaille is a ground dwelling bird of the pine forest of Scotland. The length and color of the primary feather is controlled by two unlinked genes. Using the allele key to the right calculate the phenotypic ratio of an F2 generation beginning with a cross between a hen bird that is homozygous recessive for both genes and a cock bird that is homozygous dominant for both genes. Allele Key: Q- Long feather q-short feather A- dark feather color a-light feather color Example2: Sweet peas (Incomplete/Dominance) Sweet pea flowers color is controlled by an incomplete dominant pair of alleles. The flowers are white, pink and red. The height of the mature plant is controlled by a gene showing dominance. Calculate the F2 phenotypic ratio for a cross between two heterozygous plants at both gene loci. Allele key: A1= white, A2= red B= Tall, b= short Example3: Dihybrid Test Cross A suspect heterozygote Guinea pig for coat color and length is crossed with a double homozygote recessive. As with a monohybrid test cross there is a predictable dihybrid test cross ratio which is 1:1:1:1. Calculate the genotypes of the offspring resulting from a test cross with a heterozygote Guinea pig. Allele key: L = long hair coat l =short hair coat B =Black coat b =brown coat Example4: Dihybrid with Sex linkage at one gene loci. Colorblind allele loci is found on the non-homologous region of the X chromosome. Tongue rolling alleles are carried on an autosomal chromosome Calculate the phenotypic ratio of a cross between a male tongue roller (heterozygous) with normal vision and a female who is heterozygous at both loci. Allele Key: XB= Normal vision Xb= Colorblind Y = Male chromosome T= Tongue roller t = non-tongue roller Example5: Epistasis/ Mouse color: Here two genes interact to control one characteristic. Mouse coat color is controlled by two genes. The first produces the pigment and the second controls the banding of the coat color pigment. Mouse coat is either Black(not banded), Agouti(banded) or albino(no color or banding). Agouti is actually a black hair that has a yellow tip and represents the color of wild mice. Calculate the phenotypic ratio from a cross between two agouti mice who are heterozygous at both gene loci. Allele key: C= Color produced c = no color produced A = Banding (agouti/back yellow tip) a =Non banding (black) Chi Square calculation on dihybrid data In one of Mendel's dihybrid crosses, the following types and numbers of pea plants were recorded in the F2 generation: Yellow round seeds (289)Yellow wrinkled seeds(122) Green round seeds(96) Green wrinkled seeds(36) According to theory these should be in the ratio of 9:3:3:1. Do these observed results agree with the expected ratio?