Blood and stuff
advertisement
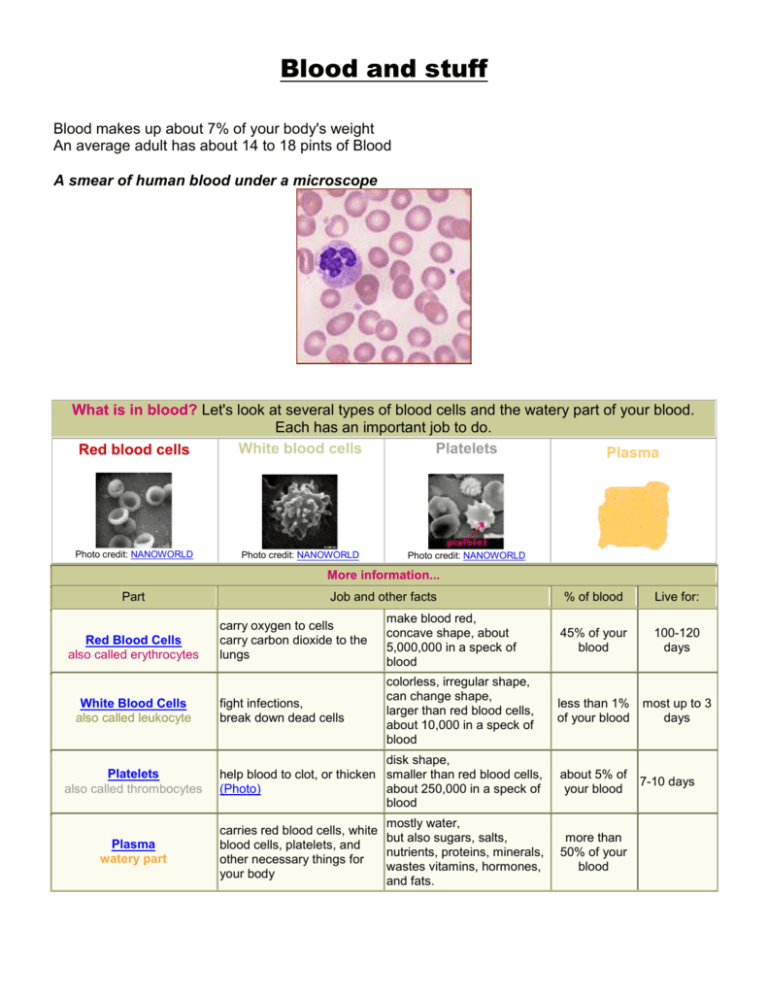
Blood and stuff Blood makes up about 7% of your body's weight An average adult has about 14 to 18 pints of Blood A smear of human blood under a microscope What is in blood? Let's look at several types of blood cells and the watery part of your blood. Each has an important job to do. Platelets White blood cells Red blood cells Plasma Photo credit: NANOWORLD Photo credit: NANOWORLD Photo credit: NANOWORLD More information... Part Red Blood Cells also called erythrocytes White Blood Cells also called leukocyte Job and other facts % of blood Live for: carry oxygen to cells carry carbon dioxide to the lungs make blood red, concave shape, about 5,000,000 in a speck of blood 45% of your blood 100-120 days fight infections, break down dead cells colorless, irregular shape, can change shape, larger than red blood cells, about 10,000 in a speck of blood less than 1% of your blood most up to 3 days 7-10 days Platelets also called thrombocytes disk shape, help blood to clot, or thicken smaller than red blood cells, (Photo) about 250,000 in a speck of blood about 5% of your blood Plasma watery part mostly water, carries red blood cells, white but also sugars, salts, blood cells, platelets, and nutrients, proteins, minerals, other necessary things for wastes vitamins, hormones, your body and fats. more than 50% of your blood White Blood cells have a rather short life cycle, living from a few days to a few weeks One drop of Blood can contain from 7,000 to 25,000 white Blood cells. If an invading infection fights back and persists, that number will significantly increase. Red Blood Cells (RBCs) make up approximately 40% of Blood volume There are five types of White Blood Cells (WBCs): basophil - acts on smooth muscle and Blood cell walls; eosiniphil - acts against infestations of parasitic larvae; lymphocyte - recognizes surface markers on cells and targets them for destruction if foreign to the body; monocyte - formed bone marrow, monocytes migrate into connective tissue and become macrophages; and, neutrophil - the first line of defense, 100 billion mature neutrophils are released into the body everyday Red Blood cells live about 120 days in our bodies Plasma, the fourth major component of Blood, is a sticky, pale yellow fluid mixture of water, protein and salts. It is 95% water. The other 5% is made up of nutrients, proteins and hormones Red blood cells are most common in blood Women average about 4.8 million of these cells per cubic millimeter (mm3) of blood. Men average about 5.4 million per mm3 These values can vary over quite a range depending on such factors as health and altitude. (Peruvians living at 18,000 feet may have as many as 8.3 million per mm3) Functions of the blood Blood performs two major functions: transport through the body of o oxygen and carbon dioxide o food molecules (glucose, lipids, amino acids) o ions (e.g., Na+, Ca2+, HCO3−) o wastes (e.g., urea) o hormones o heat defense of the body against infections and other foreign materials. All the WBCs participate in these defenses. Where are blood cells made? Blood cells are made in the bone marrow. The bone marrow is the soft, spongy material in the center of the bones that produces about 95 percent of the body's blood cells. There are other organs and systems in our bodies that help regulate blood cells. The lymph nodes, spleen, and liver help regulate the production, destruction, and differentiation (developing a specific function) of cells. The production and development of new cells is a process called hematopoiesis. Blood cells formed in the bone marrow start out as a stem cell. A "stem cell" is the initial phase of all blood cells. As the stem cell matures, several distinct cells evolve such as the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Immature blood cells are also called blasts. Some blasts stay in the marrow to mature and others travel to other parts of the body to develop into mature, functioning blood