The Blood
advertisement

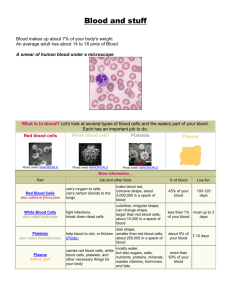
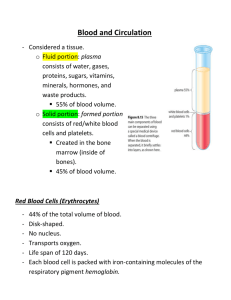
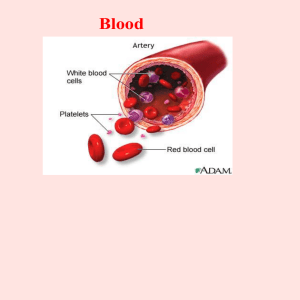
Write down what you know about the blood. Write down what you know is NOT true about the blood. Blood minus its cells Composition › Water containing many dissolved substances (foods, salts, hormones) Amount of blood = 4-6 L (7%-9% of body weight) Slightly alkaline Blood sample spun down using centrifuge RBCs (erythrocytes) WBCs (leukocytes) Platelets (Thrombocytes) Formed in bone marrow from myeloid tissue Artery showing size relation of formed elements in the blood (red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets Cell maturation chart Electron scanning microscope images of formed elements in blood in relation to each other Red blood cells (RBCs) 4.5-5 million per mm3 of blood Disc shaped Structure: › Without nuclei Function: › Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide Image showing red blood cells in relation to other cells White blood cells (WBCs) 5,000-10,000 per mm3 of blood Structure: › Granular: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils › Non-granular: lymphocytes and monocytes Function: › defense Microscope, stained image of red blood cells and white blood cells. This is a normal blood sample. This is a after colored image from an electron scanning microscope showing the white blood cell in relation to the red blood cell Also called platelets 300,000 per mm3 of blood Play an essential role in blood clotting Stained, microscopic image of a blood sample showing platelets and red blood cells Electron scanning microscope showing a red blood cells surrounded by platelets ABO system › Type A – type A antigens in RBCs; anti-B type antibodies in blood › Type B – type B antigens in RBCs; anti-A type antibodies in blood › Type AB – type A and type B antigens in RBCs; no anti-A and no anti-B antibodies in blood › Type O – no type A and no type B antigens in RBCs; anti-A and anti-B antibodies in blood Chart showing characteristics in blood, plasma and what the coordinating blood type would be Chart showing the percentages of blood type availability Rh-positive blood – Rh factor antigen present in RBCs Rh-negative blood – no Rh factor antigen present in RBCs; no anti-Rh antibodies present unless exposed Rh factor showing blood surface antigens and antibodies Myel/o – bone marrow Plasm/o – plasma Splen/o – spleen Thromb/o - clot Anemia – reduction in the amount of hemaglobin in the red blood cells Embolus – blood clot or foreign material Hemophilia – inherited blood disease most commonly caused by a deficiency of coagulation factor VIII Leukemia – malignant disease characterized by excessive increase in abnormal white blood cells formed in bone marrow Bone marrow aspiration – a syringe used to aspirate bone marrow from ilium Bone marrow biopsy – a needle puncture to obtain bone marrow sample Bone marrow transplant – infusion of normal bone marrow cells from a donor for patient with leukemia Coagulation time – blood test to determine time it takes for blood to form a clot Complete blood count – basic blood screening Differential count – explains the number of different kinds of cells Hematocrit – blood test to measure volume and number of red blood cells Hemoglobin – blood test to determine the concentration of oxygen carrying components (hemoglobin) in red blood cells Prothrombin time – used to determine certain coagulation activity defects and to monitor anticoagulation therapy Hyperlipidemia – excessive amounts of fats in the blood Anticoagulant – agent that shows the clotting process Hemorrhage – rapid loss of blood Disease/disorders › Hematoma Complementary terms › Multiple myeloma › Hematologist › Pancytopenia › Hematology › Thrombosis › Hematopoiesis › Thrombus › Hemolysis › splenomegaly › Hemostasis › Myelopoiesis › Plasmapherisis › Thrombolysis