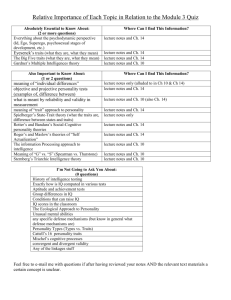
MAN 103 CHAPTER 2 Personality, Stress, Learning and Perception
advertisement

MAN 103 CHAPTER 2 Personality, Stress, Learning and Perception -Different people behave differently in their lives. Personality or personal style is a very complex subject -In our daily lives we use adjective traits like, warm, agressive, easygoing and so on -Personality is the word commonly used to describve an individual’s collection (total person) of such behavioral traits and characteristics Personality: Is a relatively stable set of traits that aids in explaining and predicting individual behavior. -In short is a person’s total mental makeup Personality Development -Traits are distinguishing personal characteristics -It is based on genetics and environmental factors. The genes a person receives before his birth influence his/her traits -Family, school and work also influence the personality -In sum, personality is the sum of genetics and a lifetime of learning -However, personality traits can be changed with work, e.g. people who are shy can be more outgoing Personality Classification Methods 1-Type A and Type B personalities -One of the personality classification methods is the Type A and Type B. -Type A personality is characterized as fast moving, time conscious, competitive, impatient, and preoccupied with work. He is associated with a high level of stress. -Type B personality is the opposite of Type A personality, he is often called laid-back or easygoing 2-Locus of control -It is a continuum representing one’s belief as to whether external or internal forces controls one’s destiny. -People with an external locus of control (externalizers) believe that they have little control over their performance and they are closed to new experiences. -On the other extent, internalizers believe that they are in control and are open to new experiences to improve performance Exercice 2.1. 3-The Big Five Model of Personality This model categorizes traits into the dimensions of surgency, agreeableness, adjustment, conscientiousness and openness to experience. a) Surgency: This dimension involves leadership and extroversion traits. -People strong in leadership (in other words dominance) are also energetic, assertive, active and ambitious with an interest in getting ahead and leading through competing. -People weak in surgency want to be followers, and they do not like to compete or influence -Extroversion is on a continuum between being an extrovert and introvert. -Extroverts are outgoing and sociable, like to meet new people, whereas introverts are shy. b) Agreeableness: This dimension involves traits related to getting along with people. -Agreeable personality is strong when someone is called warm, easygoing, cooperative and tolerant. It is weak when somebody is called cold, difficult, unfriendly. c) Adjustment: This dimension includes traits related to emotional stability. -Adjustment is on a continuum between emotionally stable and being emotionally unstable. -Here, stability refers to self-control, calmness, good under pressure, relaxed and secure. -Being emotionally unstable refers to being out of control, poor under pressure, nervous, insecure, moody, etc. d) Conscientiousness: This dimension includes traits related to achievement. -Conscientiousness is on a continuum between being responsible and dependable and being irresponsible and undependable. -Other traits of high conscientiousness include persistence, credibility and organization -This trait characterized as the willingness to work hard and put extra time and effort to accomplish goals to achieve success. e) Openness to Experience: This dimension includes traits related to being willing to change and try new things. -People strong in openness to experience are imaginative, intellectual, open-minded, autonomous and creative, they seek change and they are willing to try new things, while those are weak in this dimension avoid change and new things. Stress Stress is an emotional and/or physical reaction to environmental activities and events. -Situations in which too much pressure exists are known as stressors. Stressors are situations in which people feel anxiety, tension and pressure. The positive side: Some stress helps improve performance by challenging and motivating us. Many people work better under pressure (e.g. when deadlines are approaching) Problems associated with too much stress: It affect personal health, morale, productivity, organizational efficiency, absenteeism etc. Causes of Stress 1-Personality type: As noted before, Type A personality is characterized by fast moving, hard driving, time conscious etc, whereas Type B personality is not. -In such a case, Type A personality could end up with some problems associated with stress. 2-Organizational climate: The amount of cooperation, the level of motivation, and the overall morale in the organization affect stress levels. -The more positive the organizational climate, the less stress there is. 3-Management Behavior: Calm, participative management styles produce less stress. -Tight control through autocratic management tends to create more stress. 4-Degree of job satisfaction: People who enjoy their jobs and derive satisfaction from them handle stress better than who do not. Signs of Stress -For example when someone looks at the calendar and fear about not meeting a deadline, he is under stress. -People often lose interest in and motivation to do their work because of stress. Stress that is constant, chronic, and severe can lead to burnout over a period of time. Burnout: It is the constant lack of interest and motivation to perform one’s job because of stress. Following stress-controlling techniques can prevent stress and burnout; 1-Exercice 2-Nutrition 3-Relaxation 4-Positive Thinking 5-Support system Intelligence, Emotional Intelligence and Learning Intelligence: It is often called as mental ability -Intelligence is the level of one’s capacity for new learning, problem solving, and decision making. -Today it is agreed that intelligence is a product of both genetics and environment. -Intelligence is also a strong predictor of many important outcomes in life such as educational and occupational attainment. Emotional Intelligence (Emotional Quotient (EQ) -EQ is an offshoot of IQ. It has five components 1) 2) 3) 4) Self awareness (being conscious of your emotions within you) Managing emotions (not letting emotions get in the way of getting the job done) Motivating yourself (being optimistic despite obstacles, setbacks and failure) Empathy (putting yourself in someone else’s situation and understanding that person’s emotions) 5) Social skills (to build relationships, respond to emotions, and influence others) Learning Styles In this section we will describe the four learning styles 1-Accomodator: People who are accommodators prefer learning by doing and feeling. -They tend to act on gut feelings rather than logical analysis. -When making decisions they tend to rely heavily more on other people for information than on their own technical analysis. -They enjoy new and challenging experiences Pros: They are generally good leaders, they take risks Cons: They do not always set clear goals and develop practical plans. 2-Diverger: They learn by observing and feeling -They have the ability to view concrete situations from many different points of view. When soling problems they enjoy brainstorming. -They take time and analyze many alternatives -They are imaginative and sensitive to the needs of other people Pros: They tend to be able to recognize problems They work well with other people Cons: They tend to overanalyze problems and are slow to act. They often miss opportunities 3-Converger: They prefer learning by doing and thinking -They seek practical uses for information and focus on solutions -They tend to deal with technical tasks(e.g. production engineering) and problems rather than social or interpersonal issues Pros: They are good in deductive reasoning, solving problems and decision making Cons: They tend to make hasty decisions without reviewing all the possible alternatives 4-Assimilator: They prefer learning by observing and thinking -They are effective at understanding a wide range of information and putting it into concise logical form. It is more important for them to have a theory rather than practice Pros: They are skilled in creating models and theories Cons: They are not too idealistic and practical, they often repeat mistakes Learning Organization -For competitiveness, organization need to be fast and innovative. -There is a relationship between learning or intelligence, and innovation. -When employees work together, the learning process is optimized, they learn by working together and foster innovations. -The learning organization cultivates the capacity to learn, adapt, and change with the environment to be innovative and speed. A learning organization does; 1-Avoid to make the same mistakes 2-Make continuous performance improvements 3-Share information.