Lab: Immune and Lymphatic Systems
advertisement

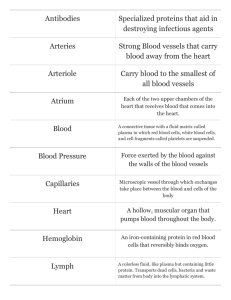
Lab: Immune and Lymphatic Systems NAME________________________ PER_____ Lymphatic Organs and Tissues 1. The lymphatic system is a specialized subdivision of the circulatory system. Although the cardiovascular system has a pump (the heart) and arteries, veins, and capillaries, the lymphatic system lacks two of these structures: the ______________ and the ___________. Like the ___________ of the cardiovasculae system, the vessels of the lymphatic system are equipped with _________ to prevent backflow. The lymphatic vessels act primarily to pick up leaked fluid, now called _________, and return it to the bloodstream. About _______ of fluid is returned every 24 hours. 2. Label the following diagram using these terms: axillary node, appendix, right lymphatic duct, thymus gland, pharyngeal tonsils, inguinal nodes, Peyer’s patches, intestinal nodes, red bone marrow, mammary plexus, cervical nodes, thoracic duct, spleen 3. Choose one of the following slides: lymph node, thymus, spleen, or tonsil. Examine it under the microscope and draw what you see in color. Label the major structures as well. Slide:____________________ Magnification:_______ 4. Match the term to the description. ___The largest lymphatic organ ___ Filter lymph ___ Particularly large and important during youth; produces hormones that help to program the immune system ___ Removes aged and defective red blood cells ___ Includes the adenoids ___ Acts against bacteria breaching the intestinal wall ___ Lack a complete capsule and have crypts in which bacteria can be trapped A. B. C. D. E. Lymph node Peyer’s patches Spleen Thymus Tonsils 5. The figure below provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A, the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular system is depicted schematically. Part B show the different types of lymphatic vessels in a simple way. First, color code and color the following: Heart Arteries Veins Blood capillaries Lymphatic vessels/ lymph node Loose connective tissue around the blood and lymph capillaries 6. Then, identify by labeling these specific structures in part B: Lymph capillaries, lymph duct, lymphatic collecting vessels, lymph trunks, lymph node, valves, veins Immune Cells and Response 7. The major elements of the body’s nonspecific defense system are: the ___________, consisting of the skin and ________; defensive cells, such as _____________ and phagocytes; and a whole deluge of __________. 8. The basic structure of an antibody is diagrammed below. Select 2 different colors and color the heavy chains and the light chains. Add labels to the diagram to identify the type of bonds that hold the polypeptide chains together, the complement binding site, and the macrophage binding site. Also label the constant (c) and the variable (v) regions of the antibody, adding polka dots to the variable portions. Which part of the antibody, v or c, is its antigen binding site? _____ Which part determines antibody class and specific function? ______ 9. The figure below diagrams the events involved in the inflammatory response. Events depicted in A precede those shown in B. Each event is represented by a square with one or more arrows. From the list below, write the correct number in each event square in the figure. Then, color code and color the structures that appear in the numbered list. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. WBCs are drawn to the injured area by the release of inflammatory chemicals. Tissue repair occurs. Tissue injury occurs and microbes enter the injured tissues. Local blood vessels dilate and the capillaries become engorged with blood. Phagocytosis of microbes occurs. Fluid containing clotting proteins is lost from the bloodstream and enters the injured tissue area. Mast cells degranulate, releasing inflammatory chemicals. Margination and diapedesis occur. Mast cells Mast cell granules Monocyte Epithelium Erythrocytes Neutrophils Macrophage Subcutaneous tissue Endothelium of capillary Microorganisms Fibrous tissue repair 10.Use the following terms to complete the concept map on the Immune System. Active immunization, transfer of antibodies, acquired, nonspecific immunity, inflammation, passive immunization, active, phagocytic cells, specific immunity, innate 11.Fill in the blank to describe the type of immune cell. Killer T cells, antibodies, natural killer cells, viruses, helper T cells, suppressor T cells, B cells, macrophages, memory T and B cells