1 ANTIVIRAL AGENTS Steps for Viral Replication 1) adsorption and

1
ANTIVIRAL AGENTS
Steps for Viral Replication
1) adsorption and penetration into cell
2) uncoating of viral nucleic acid
3) synthesis of regulatory proteins
Spectrum
•
Herpesviruses – acyclovir, cidofovir, famcyclovir, foscarnet, gancyclovir, idoxouridine, trifluridine
•
CMV – gancyclovir, fomivirsen, foscarnet, trifluridine, cidofovir
Therapeutic use
•
Acyclovir – HSV: genital HSV infections, primary herpetic gingivostomatitis, herpes labialis, mucocutaneous HSV infection in immunocompromised patients, VZV: varicella
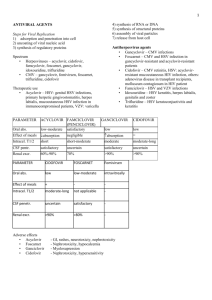
PARAMETER ACYCLOVIR FAMCICLOVIR
(PENCICLOVIR)
Oral abs. low-moderate satisfactory
4) synthesis of RNA or DNA
5) synthesis of structural proteins
6) assembly of viral particles
7) release from host cell
Antiherpesvirus agents
•
Gancyclovir – CMV infections
•
Foscarnet – CMV and HSV infection in gancyclovir-resistant and acyclovir-resistant patients
•
Cidofovir – CMV retinitis, HSV: acyclovirresistant mucocutaneous HIV infection, others: adenovirus disease in transplant recipients, molluscum contagiosum in HIV patient
• Famciclovir – HSV and VZV infections
•
Idoxouridine – HSV keratitis, herpes labialis, genitalis and zoster
•
Trifluridine – HSV keratoconjuctivitis and keratitis
GANCICLOVIR CIDOFOViR low low
Effect of meals
absorption negligible
absorption =
Intracel. T1/2 short short-moderate moderate moderate-long
CSF pentr.
Renal excr. satisfactory
60%-90% uncertain
70% satisfactory
>90% uncertain
>90%
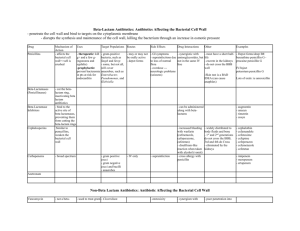
PARAMETER CIDOFOViR FOSCARNET Fomivirsen
Oral abs. low low-moderate intravitreally
Effect of meals =
Intracel. T1/2
- moderate-long not applicable
-
-
CSF penetr.
Renal excr. uncertain
>90% satisfactory
>80%
-
-
Adverse effects
•
Acyclovir - GI, rashes, neurotoxiciy, nephrotoxicity
• Foscarnet - Nephrotoxicity, hypocalcemia
•
Ganciclovir - Myelosupression
• Cidofovir - Nephrotoxicity, hypersensitivity
Antiretroviral agents
Nucleoside RT inhibitors
Nonnucleoside RT inhibitors
HIV protease inhibitors
Entry inhibitors
Fusion inhibitors
Integrase inhibitors
Nucleoside RT inhibitors – bind to the catalytic site of the enzyme
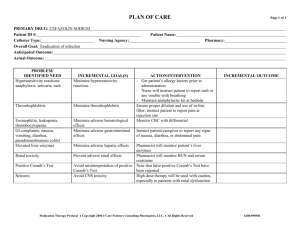
ZIDOVUDINE LAMIVUDINE STAVUDINE DIDANOSINE
Oral bioavailability
Effect of meals satisfactory
(high fat) excellent
excellent
satisfactory
(acidity)
Intracellular T1/2 3-4 12 3.5 8-24
Metabolism
Renal excr. % intensive
15
ABACAVIR moderate
70 intensive
40 moderate
20-50
ZALCITABINE TENOFOVIR EMTRICITABE
Oral bioavailability
Effect of meals
Intracell. T1/2
Metabolism good
3 intensive excellent
2-3 mild acceptable
(fat)
11-49 excellent
39 negliglible negliglible
Renal excr. % <5 70 80 80
Adverse effects
•
Zidovudine - anemia, granulocytopenia, malaise, myalgia, nausea, insomnia, hyperpigmentation, lactic acidosis-steatosis syndrome
•
Didianosine, stavudine - neuropathy, pancreatitis, diarrhea
•
Zalcitabine - nephropathy
•
Lamivudine - well tolerated
• Abacavir - hypersensistivity
•
Tenofovir - well tolerated, flatulence
2
3
Nonnucleoside RT inhibitors - bind to the site distant from the catalytic site of the enzyme
PARAMETER NEVIRAPINE EFAVIRENZE DELAVIRDINE
Oral bioavailability
Plasma protein binding, %
Metabolism
Renal excretion (%) excellent
60
Extensive
Negliglible satisfactory
99
Extensive
Negliglible excellent
98
Extensive
Negliglible
Adverse effects
Rashes (Stevens-Johnson syndrome),sedation,hepatotoxicity
Efavirenz- psychiatric reactions
Attention: cytochrome P450 Nevirapine - induction
HIV protease inhibitors
• Saquinavir, ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir,
• amprenavir, lopinavir, atazanavir
Active against HIV-1 and HIV-2
• Mechanism: inhibit protease which is responsible for cleaving precursor molecules necessary to produce final structural proteins of the virion core
• Pharmacokinetics: bioavailability depends on preparation, high protein-bound, metabolized in the liver, CNS penetration (indinavir)
• Adverse effects: altered body fat distribution, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, liver function impairement,
GI symptoms, nephrolithiasis (Indinavir), skin rashes
Boosted terapy – the addition of ritonavir to other PI to prologe their action (P450 inhibitor)
Fusion inhibitors - enfuvirtide
Blocks gp 41 subunit of the viral envelope glycoprotein – involved in fusion
Active: against HV-1
Pharmacokinetics: given parenterally only
Adverse effects: injection-site reactions
Integrase inhibitors - Raltegravir
Prevents DNA strand transfer by binding divalent cations into the catalytic core of integrase
Given orally without regard to food. No effect on
P450.
Headache or GI problems.
Immune reconstitution syndrome - patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, which includes raltegravir-containing regimens.
During the initial phase of treatment, a patient whose immune system improves may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (e.g., Mycobacterium avium , cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis pneumonia, tuberculosis, varicella zoster virus), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Entry inhibitors - Maraviroc
Inhibitor (antagonist) of CCR5 co-receptor
Recomended for treatment of HIV infection caused by resistant strains
Caution: patients with liver dysfunction (CYP2A4) and at increased risk of cardiovascular events, can cause upper respiratory tract symptoms
Highly active antiretroviral therapy
Regimens for initial treatment of HIV in adults and adolescens
•
NNRTI-based regimen: efavirenz + tenofovir
+ emtricitabine or lamivudine
•
Protease inhibitor-based regimen: ritonavir + tenofovir + emtricitabine or lamivudine
•
Integrase inhibitor-based regimen: raltegravir
+ tenofovir + or lamivudine
Regimen fo pregnant women: ritonavir + zidovudine
(reduces in utero transmission) + lamivudine or emtricitabine
NNRTI are antimetabolites of different (not the same) endnogenous nucleosides = drugs combination is possible- no overlapping mechanism of action!
4
Antiinfluenza Agents
AMANTADINE RIMANTADINE ZANAMIVIR OSELTAMTViR
Type of influenza A
Route Oral
A
Oral
A,B
Inhaled
A,B
Oral
Oral abs. moderateexcellent excellent negliglible very good
Metabolism < 10% ~75% Negligible Negligible
Renal excr. % 50%-90% ~25% 100% 95%
Neuraminidase inhibitors
• Active against influenza virus A and B
•
Mechanism: inhibit neuraminidase which is an essential viral glycoprotein for replication and release
• Adverse effects: well tolerated
•
Therapeutic use: uncomplicated influenza infection, given intranasally (z) or orally (o)
Anti-hepatitis agents
Lamivudine -Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase
Inhibitor (NRTI)
Adefovir -Nucleotide Inhibitor
Interferon Alfa
Pegylated Interferon Alfa
Ribavirin
Interferon Alfa
Intracellular effects
1.
Transcription inhibition (inhibits Mx protein and mRNA synthesis)
2. Translation inhibition: activated 2’-5’oligoadenylate [2-5(A)] synthetase – vRNA cleaved, protein kinase - intiation of mRNA inhibited, phosphodiesterase – tRNA function blocked
3. Proteins posttranslational modyfication glycosylation of proteins inhibited
4. Inhibition of virus maturation – glycoproteins maturation inhibited, changes in membrane – budding inhibited
Spectrum - Most of viruses except few of DNA types
Pharmacokinetics - parenerally only, given 3-times weekly, pegIFN (polyethylene glycol) once a week, steady-state levels 5-8 weeks after initiation of weekly dosing, eliminated by the liver and/or kidneys (endstage renal disease)
Therapeutic uses - chronic hepatitis type C and B
Adverse effects
• Influenza-like symptoms
• Bone marrow depression
• Autoimmune effects: hypothyreosis
• Neurotoxicity: somnolence confusion, behavioral disturbances, neurasthenia, depression
•
Hair loss
•
Nephritis
•
Cardio, - hepatotoxicity
•
Impaired fertility
Ribavirin
Mechanism of action: intracellulary phosphorylated
• Inhibits inosine-5’-dehydrogenase – synthesis of GTP
• Inhibits GTP-dependent 5’capping of viral mRNA
• Inhibits influenza virus transcriptase
• Enhances viral mutagenesis – lethal mutagenesis
Spectrum: Influenza and parainfuenza viruses, RSV,
HCV, adenoviruses, paramyxoviruses, arenaviruses, bunyaviruses, flaviviruses
Pharmacokinetics: well absorbed, large volume of distribution, hepatic metabolism and renal elimination
Therapeutic use: chronic HCV infection, RSV bronchiolitis and RSV pneumonia in children
(aerosol), in immunocompromised patients, occasionaly – influenza, vaccinia, parainfuenza, measles, Lassa fever, SARS, Congo hemorrhagic fever
Adverse effects: irritation, wheezing, anemia
(hemolysis and bone marrow depression), nausea,
insomnia, depression, embryotoxic, teratogenic and oncogenic (cat. X)
Adefovir
Spectrum – HBV
•
inhibits DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptases, serves as chain terminator
Pharmacokinetics: well absorbed, small volume of distribution, eliminated by the kidneys
Adverse effects: nephrotoxicity, diarrhea, hepatitis exacerbation, genotoxic, embryotoxic
Therapeutic use: chronic HBV infections
New agents
• Boceprewir - inhibitors of HCV protease – effective in infection due to viral genotype 1
•
Telaprevir, symeprevir – peptidomimetic inhibitors of NS3/4A serine kinase HCV – inhibits viral replication (effective in infection due to viral genotype 1)
•
Daklataswir – inhibitor of jest inhibitorem 5A
(NS5A) protein involved into the replication process of vRNA and virion assembly
• Sofosbuwir - pan-genotypic inhibitor of the
HCV NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which is essential for viral replication.
Imiquimod
• Topical treatment of condylomata acuminata
(genital and perisanal warts)
• Induces cytokines with antivirial and immunomodulatory effects
• Skin irritations
5