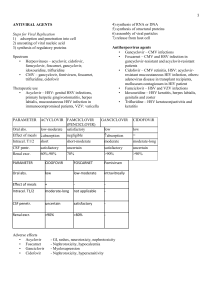
Drug Table Antibiotics, Antivirals, TB, AIDS
advertisement

Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: Antibiotics Affecting the Bacterial Cell Wall - penetrate the cell wall and bind to targets on the cytoplasmic membrane - disrupts the synthesis and maintenance of the cell wall, killing the bacterium through an increase in osmotic pressure Drug Penicillins Beta-Lactamases (Penicillinases) Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors Cephalosporins Carbapenems Mechanism of Action - affects the bacterial cell wall=>cell is crushed Uses Target Populations Routes Side Effects Drug Interactions Other Examples - therapeutic: kill g+ and a few g(ngonorea and syphilis) -prophylactic: prevent bacteremia in pts at risk for endocarditis - gram-positive - may or may not bacteria, such as be orally active Staph and Strep - depot forms - some, but not all, will cover anaerobes, such as Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, and Klebsiella - GI symptoms - suprainfections due to loss of normal flora - overdose --neurologic problems (seizures) - synergistic with aminoglycosides, but not in the same IV line - most have a short halflife - excrete in the kidneys - do not cross the BBB well - Depot forms/deep IM: benzathine penicillin G procaine penicillin G - cut the betalactam ring, inactivating beta lactam antibiotics - bind to the active site of beta-lactamases, preventing them from cutting the beta-lactam rings Similar to penucillins, weaken the bacterial cell wall - broad spectrum -Skin test is a BAD IDEA (can cause anaphlax) - can be administered along with betalactams - gram positive cocci - gram negative cocci and bacilli - anaerobes - IV only - suprainfection - increased bleeding with warfarin (cefmetazole, cefoperazone, cefotetan) - disulfiram-like reaction when taken with alcohol (vomit) - cross allergy with penicillin - widely distributed to body fluids and bone - 1st and 2nd generations do not cross the BBB, 3rd and 4th do Cross - eliminated by the kidneys - used to treat gram - Clostridium - ototoxicity - synergism with - cephalothin - cefamandole - cefotaxime - cefepime - cefeperazon - cefemetazole - cefetetan - imipenem - meropenem - ertapenem Non-Beta Lactam Antibiotics: Antibiotic Affecting the Bacterial Cell Wall - not a beta- Lots of orals: ie amoxicillin - augmentin - unasyn - timentin - zosyn Azetronam Vancomycin IV/Inject potassium penicillin G - poor penetration into lactam - interferes with cell wall synthesis positive infections difficile in penicillinallergic patients - used for serious infections - nephrotoxicity aminoglycosides - multiple drug interactions - rapid infusion leads to flushing, tachycardia, and hypotension - irritating to the skin the CSF Bacteriostatic Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis Drug Tetracyclines Macrolides Clindamycin Mechanism of Action - bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit and prevent the elongation of the peptide chain Uses - braod spectrum - Chlamydia - rickettsial diseases (rocky mountain spotted fever) - acne - periodontal disease - inhibit protein - Chlamydia synthesis by - Legionella inhibiting the (Legeneir’s 50S ribosomal disease) subunit - alternative to penicillin in allergic patients - inhibits the 50S - reserved for ribosomal serious infections subunit Target Populations Routes - mainly oral - rarely Iv - gram positive bacteria - gram negative bacteria - gram positive aerobes - anaerobes Side Effects Drug Interactions - discolor developing teeth - suprainfection with bowedl organisms or Candida - form insoluble - porr CSF penetration compounds with calcium, iron, magnesium, aluminum, and zinc (no laxatives, antacids, dairy, or iron) - corrosive to the GI - erythromycin and tract clarithromycin are - IV erythromycin is strong inhibitors of corrosive to the veins cytochrome P450 - hepatotoxicity Other - poor CSF penetration Examples - tetracycline - doxycycline - minocycline - erythromycin - clarithromycin - azithromycin - IV infusion must - suprainfection with - should not be given - poor penetration of the be slow C. diff with a macrolide brain because they work by the same MOA Chloramphenicol Bacteriocidal Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis Drug Aminoglycosides Mechanism of Uses Action - bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit - promote the formation of abnormal proteins whose Target Populations Routes - gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, and Serratia - do not work against anaerobes Side Effects - IV - otoxicity - topic to sterilize - nephrotoxicity the gut, skin, or eye - is not absorbed Drug Interactions Other Examples - tobromycin - gentamycin - amakacin abnormal functioning kills the cell Antibiotics Affecting DNA Drug Sulfamethoxazoletrimethropim (Bactrim) Fluoroquinones Metronidazole (Flagyl) Mechanism of Uses Target Populations Routes Action - blocks bacterial - broad spectrum - gram negative enzymes - UTI - gram positive important in the - Pneumocystis synthesis of carinii pneumonia DNA, RNA, and of AIDS proteins - inhibit DNA gyrase important in bacterial DNA replication - aerobic organisms - most gram negative - some gram negative - C. difficile - Bacteriodes - Entameba histolytica - anaerobic organisms - parasites - bacteria Side Effects - hypersensitivity reactions - Stevens Johnson - blood dyscrasias (abnormal amounts of the components of blood) - crystalluria - CNS effects – headaches, sudden psychosis - irreversible joint disease in children under 18 - tendon rupture - photosensitivity - Candida suprainfections, especially of the oropharynx - infrequent but serious CNS effects - darkening of the urine CNS effects - avoid during pregnancy Drug Interactions Other Examples - combination of a sulfa drug (sulfamethoxazole)and an inhibitor of a bacterial enzymes called dihydrofolate reductase (trimethroprim) - the two drugs combine to form bactrim and block different steps in the pathway (synergistic) - should not be taken with aluminum, iron, calcium, or zinc supplements - can increase plasma levels of theophylline and warfarin - ciprofloxacin - levoflaxacin - oxofloxacin - cytochrome p450 interactions - prodrug that is activated only in anaerobic cells Side Effects Drug Interactions Other - infusion reactions – phlebitis, fever, chills, rigors, nausea, headache - nephrotoxic - use with caution - binds to the cholesterol with aminoglycosides in cell membranes so it is because they are also toxic to mammalian cells nephrotoxic - drug reduction when used with flucytosine Antifungals Drug Amphotericin B Mechanism of Uses Action - binds to sterols - systemic fungal in the fungal infections membrane and increases permeability - the fungal cell swells and bursts Target Populations Routes Examples Ketaconazole - inhibits the - oral alternative to synthesis of a amphotericin B sterol component - systemic fungal of the fungal cell infections membrane - oral - hepatic necrosis (synergistic) - strong inhibitor of cytochorme p450 enzymes Antivirals Drug Acyclovir Ganciclovir Mechanism of Action - suppresses the synthesis of viral DNA Uses - herpes viruses – herpes simplex, herpes zoster, CMV - herpes viruses – herpes simples, herpes zoster, CMV Target Populations Routes - topical - oral - IV Side Effects - nephrotoxic - granulocytopenia - thrombocytopenia - terotogenic - embyrotoxic Drugs for Influenza Amantidine Rimantadine Neurominidase Inhibitors Drug Interactions - prophylaxis during epidemics - treatment - only effective against influenza A - prophylaxis during epidemics - treatment - only effective against influenza A - must be taken - tamiflu – oral soon after drug used as symptoms appear prophylaxis or to to be effective shorten duration of the flu - relenza is inhaled but is NOT approved for prophylaxis HIV Drugs Other Examples - resistance is common - valacyclovir (Valtrex) is a due to thymidine kinase prodrug that is more deficiency bioavailable - poor bioavailability is slightly increased by food Drug Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs) Mechanism of Uses Action - inhibit the viral enzyme, reverse transcriptase, that converts viral RNA into DNA - inhibit human DNA polymerase so that the drugs are toxic to dividing cells Non-nucleoside - bind to the Reverse Transcriptase active site of the Inhibitors (NNRTIs) reverse transcriptase enzyme - more specific for the viral reverse transcriptase - do not affect human DNA polymerase the way that NRTIs do Protease Inhibitors - inhibit viral (PIs) protease, which is responsible in the final step in maturation of the infective virus - cannot cut the long viral proteins into functional units so the virus remains immature and non-infective Entry Inhibitors - inhibits entry of HIV into CD4 positive cells Target Populations Routes Side Effects Drug Interactions Other Examples - mitochondrial toxicity in the liver - hepatomegaly - failing liver - lactic acidosis - bone marrow depression - anemia - neutropenia - GI toxicity - peripheral lipoatrophy (d4t) - peripheral neuropathy - Stevens Johnson - cytochrome p450 syndrome interactions - severe hepatotoxicity - delavirdine and efavirenz are inhibitors - nevirapine is an inducer - avoid St. John’s wort - AZT - ddi - ddc - 3tc - d4t - central obesity - metabolized by - hyperglycemia/ cytochrome p450 diabetes enzymes - hyperlipidemia - avoid St. John’s - increased bleeding in wort patients with - avoid garlic hemophilia preparations - reduced bone mineral density - elevation of serum transaminases (liver enzymes) - ECG changes with atazanavir (prolonged QT) - GI effects - idinavir - ritonavir - saquinavir - nelfinavir - amprenavir - fosamprenavir - atazanavir - tirpranavir - lopinavir - nevirapine - delaviridine - efavirenz - includes fusion inhibitors and attachments inhibitors Fusion Inhibitors - binds to gp41, a - for patients who viral envelope have failed more protein standard HAART with RT inhibitors and protease inhibitors Attachment Inhibitors - blocks the CCR5 receptor so that HIV does not attach to the CD4 cell Integrase Inhibitors - blocks integrase, which integrates HIV viral genetic information into the host cell DNA, turning the host cell into a viral factory - must be given subcutaneously twice a day - given twice per day - injection site reactions - increased risk of bacterial pneumonia - extremely expensive - hard to manufacture - limited supply - pregnancy category - dosage depends on B whether or not it is - cough given with a - fever cytochrome p450 - rash inducer or inhibitor - muscle and joint pain - stomach pain - dizziness - liver toxicity - diarrhea - plasma - there is only one - nausea concentrations may opportunity for this to be - headache be reduced by effective because after - pregnancy category enzyme inducers, the first time the virus is C particularly already incorporated into rifampin the host cell - the only fusion inhibitor on the market is enfuvirtide - the only CCR5 antagonist is Maraviroc (Selenztry) - raltegravir is the only approved drug Tuberculosis Drugs Drug Isoniazid Rifampin Mechanism of Action - inhibits the formation of the mycobacterial cell wall Uses - used to treat latent TB - used along with at least one other drug for active TB - used with at least one other drug for active TB Target Populations Routes Side Effects Drug Interactions Other - hepatotoxic - increases the level - distributed to all body of phenytoin tissues and fluids - crosses the BBB to achieve therapeutic levels - hepatotoxic - turns the body fluids red - increases the - distributed to the CSF hepatotoxicity of isoniazif and pyrazinamide - decreases the levels of birth control pills, Examples seizure meds, and others Pyrazinamide - often combined with isoniazid, rifampin, and ethambutol - hepatotoxic Ethambutol - optic neuritis - allergic reactions - NOT HEPATOTOXC!! - distributed widely but does not penetrate the brain Diuretics Drug Thiazide Mechanism of Uses Action edema PREVENT Reabsorb NA and Cl in early distal tubule High Ceiling/loop (Lasix) K sparing Osmotic Inhibit RAAS Target Populations Routes Side Effects Too little K, too little NA, too little Cl, dehydration Drug Interactions Other Examples ALL DIURETICS are BAD for Lithium. All K losing are bad for Digoxin. ALL Avoid in Preg, If possible. Same OTOTOXIC Can Cause Too much K/Hyperkalemia Endocrine effects Prevent reabsorb NA (no kick out of K) in collecting duct Osmosis Too much fluid in Brain, Eye Watch with ACE/ARB Can cause paradoxical edema Can cause too much K/ Hyperkalemia Angioedema Preg cat D Spironolactone prolongs life in CHF pts Not metabolized- inert. All RAAS, Preg Cat D Ace Inhibitors “–opril” Dry Cough Prevent renal failure, Death from MI or CHF. ARBs “-sartan”– prevent nephropathy