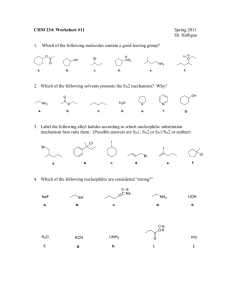
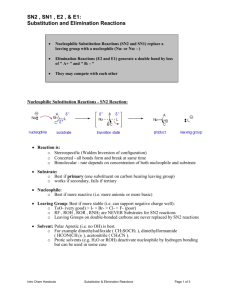
In nucleophilic substitution reactions with alkyl halides the leaving

1) In nucleophilic substitution reactions with alkyl halides the leaving group is?
A hydroxide group.
A halide anion.
A halide cation.
A carbon atom.
An ester.
2) Rank the following ions in terms of their leaving group reactivity. Br
-
, Cl
-
, I
-
, F
-
.
Br
-
> Cl
-
> F
-
> I
-
.
I
-
> Br
-
> Cl
-
> F
-
.
Cl
-
> Br
-
> F
-
> I
-
.
F
-
> Cl
-
> Br
-
> I
-
.
F
-
> Cl
-
> Br
-
> I
-
.
3 How are basicity and leaving group ability related?
They are not related to each other.
Good leaving groups are strong bases.
Good leaving groups are weak bases.
4) The term S
N
2 stands for?
A solvation reaction.
An electrophilic addition reaction.
A nucleophilic reaction.
A unimolecular substituent reaction.
A bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
5) The transition state geometry in an S
N
2 reaction is?
Trigonal planar.
Tetrahedral.
Pentagonal.
Trigonal bipyramidal.
Octahedral.
6) The nucleophile in an S
N
2 reaction approaches the alkyl halide from?
Anywhere, is does not matter.
The same side of the carbon atom that the halide atom is attached to.
The backside of the carbon-halide bond.
The side of the carbon-halide bond.
The top of the carbon-halide bond.
7) Which of the following compounds is least reactive in an S
N
2 reaction?
A B C D E
A
B
C
D
E
8) The order of carbocation stability is?
1
0
> 2
0
> 3
0
2
0
> 1
0
> 3
0
2
0
> 3
0
> 1
0
3 0 > 2 0 > 1 0
3 0 > 1 0 > 2 0
9) Which statement about the solvent effects on substitution reactions is false?
S
N
1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents.
S
N
2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents.
1
0
alkyl halides still react S
N
2 in polar protic solvents.
3
0
alkyl halides still react S
N
1 in non-polar solvents.
10) Which statement about competing elimination reactions is false?
Elimination is favored by nucleophiles which are also strong bases.
Elimination occurs as the result of the loss of a proton on a beta carbon.
Elimination occurs only for S
N
2 reactions.
The structure of the alkyl halide can affect the amount of the elimination product.
The structure of the base can affect the amount of the elimination product.
11) Which statement about substitution reactions with alcohols is true?
Substitution can be done directly on the alcohol.
Substitution always results in an inversion of configuration.
Substitution always results in a retention of configuration.
Substitution can only be done with hydrohalide acids.
Substitution is best achieved by first generating a better leaving group.
12) Is the following molecule chiral?
Yes.
No.
13) Assign the absolute configuration to:
R
S
14) Assign the absolute configuration to:
R
S