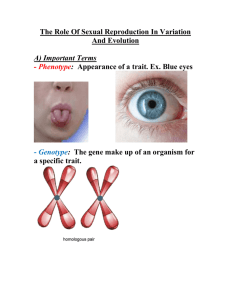
LA MISE EN CONTEXTE
advertisement

Name: Class: Date: ANSWER KEY Checkup 1 • Chapter 5 The cell (pp. 126–131) © ERPI Reproduction and adaptation permitted solely for classroom use with Observatory. 1. Look at the following illustration. a) What three cell components are visible under a light (optical) microscope? Cell membrane. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. 2. Cell organelles allow a cell to perform various functions. a) What organelles produce energy in the cell? Mitochondria. b) What organelles are responsible for digesting certain nutrients? Lysosomes. c) What organelle packages material inside the cell? Golgi apparatus. d) What organelle transports material produced by the cell from one place to another inside the cell? Endoplasmic reticulum. 3. What is the difference between DNA, genes and genome? DNA is a molecule shaped like a double helix. Genes are segments of DNA. A genome is the complete set of genetic information of an individual or species. Observatory/Guide 11071-B 1 CHECKUP OF CHAPTER 5 Name: Class: Date: ANSWER KEY 4. What is the function of genes? Genes contain the genetic information required to manufacture proteins, each of which has a specific job to carry out. 5. Complete the following DNA sequence. G A G C G A Cell division (pp. 131–135) © ERPI Reproduction and adaptation permitted solely for classroom use with Observatory. 2 T 6. Give three reasons why cells divide. To increase the organism’s cell count (growth). To replace damaged or broken tissue (regeneration). To make sexual reproduction possible. 7. What are the two types of cell division? Mitosis. Meiosis. 8. Some human cells are said to be diploid while others are said to be haploid. a) What distinguishes a diploid cell from a haploid cell? CHECKUP OF CHAPTER 5 2 Observatory/Guide 11071-B Name: Class: Date: ANSWER KEY A diploid cell possesses two sets of chromosomes while a haploid cell contains only one set of chromosomes. b) How many chromosomes does a human diploid 23 pairs of chromosomes. cell contain? c) How many chromosomes does a human haploid cell contain? 23 chromosomes. 9. What kind of cells are formed during meiosis? Gametes (male or female). 10. Look at the two following illustrations. They show a simplified version of the types of cell division. Name the type of division represented in a) and in b), then explain your answer. a) Type of division: © ERPI Reproduction and adaptation permitted solely for classroom use with Observatory. Meiosis. Explanation: The daughter cells are haploids. b) Type of division: Two successive mitosis. Explanation: In each case, the daughter cells are diploids. Observatory/Guide 11071-B 3 CHECKUP OF CHAPTER 5 Name: Class: Date: ANSWER KEY 11. Answer the following questions. a) What does a cell do when it is not dividing? It performs various functions to ensure the organism is in good working order. b) Why do cells replicate their DNA? So that each daughter cell can have a complete copy of DNA. c) What is a gamete? A gamete is a haploid cell (or sex cell). 3 Cellular specialization (pp. 136–139) © ERPI Reproduction and adaptation permitted solely for classroom use with Observatory. 12. Look at the illustration at right. It presents various tissues found in the arm. a) Name each type of tissue indicated in the illustration. b) Indicate one function for each type of tissue. NAME OF TISSUE FUNCTION OF TISSUE A Epithelial tissue Protects other tissues. B Nerve tissue Receives and transmits information. C Muscle tissue Produces movement. D Connective tissue Supports other tissues. (bone tissue) CHECKUP OF CHAPTER 5 4 Observatory/Guide 11071-B Name: Class: Date: ANSWER KEY 13. What is a system? A system is a group of organs and tissues working together to accomplish a common function in the body. © ERPI Reproduction and adaptation permitted solely for classroom use with Observatory. 14. Each of the following statements describes one of the body’s vital functions. In each case, name the system that manages this function. a) Eating well is important to keep our bodies healthy. Digestive system. b) Nutrients carried by red blood cells provide energy for our cells. Cardiovascular system. c) When we urinate, we eliminate certain waste products. Excretory system. d) Our sense of smell allows us to distinguish various odours. Nervous system. Observatory/Guide 11071-B 5 CHECKUP OF CHAPTER 5