Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Quiz Review
advertisement

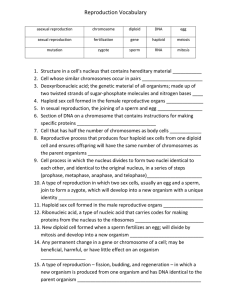
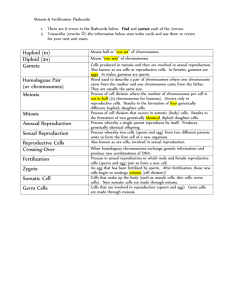
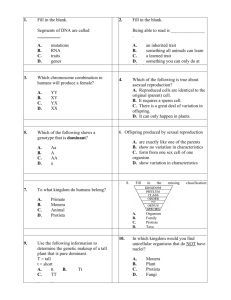
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Quiz Review 1. List and describe the 5 types of asexual reproduction. Binary Fission – one cell breaks into two cells with the same DNA. Example – bacteria. Budding – Offspring begins to form on parent organism and breaks off when it is mature enough to survive on its own. Example – Hydra Fragmentation – Parent organism breaks and each piece forms a new organism. Example – star fish Spore Formation – Parent organism undergoes frequent cell division to produce many identical cells. Example – Mushrooms or mold Vegetative Reproduction – Offspring are formed from runners that the parent organism sends out. Example – strawberry, spider plant, mint 2. List and describe the 3 types of sexual reproduction. Separate Sexes – Male and female organisms are separate and are required to reproduce. Males are XY and Females are XX. Example – most mammals Conjugation – two cells come into contact and exchange small pieces of DNA. Example – Bacteria Hermaphrodites – The organism is able to produce both male and female sex cells. Example – earth worms, tomatoes 3. Match the columns with the correct description ___ Haploid - E A. The product when a sperm cell joins an egg cell ___Diploid B. Sperm meets egg outside the body -C ___External fertilization - B C. Number of chromosomes in a normal body cell ___Internal fertilization - F D. The event of sperm joining egg ___Asexual reproduction - H E. The number of chromosomes in a gamete ___Sexual reproduction F. Sperm meets egg inside the body ___Zygote ___Fertilization -G -A G. Reproduction involving two parents -D H. Reproduction involving only one parent 4. What makes up the sides of a DNA molecule? Sugars and phosphates 5. What makes up the “rungs” on the ladder in a DNA molecule? Nitrogen bases – Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine 6. What nitrogen bases match up together in DNA? A and T, C and G 7. Put the following things in order from Smallest to Biggest – Chromsomes, DNA, Genes DNA, GENES, CHROMOSOMES 8. Compare and contrast MITOSIS with MEIOSIS! Use the words haploid, diploid, and include the numbers of chromosomes before the process begins, and after the process is finished.