BBB4M – Barriers to Trade - ital-biz
advertisement

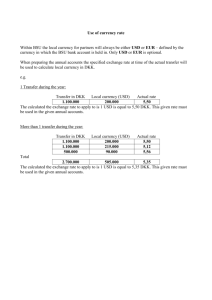
BBB4M – International Business 1. Currency Exchange Worksheet Visit www.xe.com or www.x-rates.com . Using the Quick Cross Rates given below, and with pencil and calculator only, perform the following currency conversions. Use the proper currency symbols wherever possible. Example: Euros €. Use the Quick Currency Converter to check your answers. a) b) c) d) e) f) 2. 25 Swiss Francs British Pounds 50 USD Russian Rubles 100 Euros Mexican Pesos 1000 Chinese Yuan British Pounds 100 Mexican Pesos USD Japanese Yen An American tourist buys Euros at today’s rate (1 USD = 0.769349 €) for a trip in the summer. Suppose decides not go and converts her Euros to USD at a later date when 1 USD = 0.759900 €. (i) Did the Euro strengthen or weaken against the dollar? (ii) How much did she gain/lose in this situation? A Canadian tourist visits Vietnam and spends 183 million VND (Vietnamese Dong) during her stay. When she returns to Canada she converts the remaining VND she has to CAD and receives 1,225 CAD at today’s exchange rates. How much did she spend during her stay in CAD? An American manufacturer agrees to sell 10,000 air conditioning units to a South African importing firm and retailer in Johannesburg. The agreed price per unit is $375 USD. Payment will be made today. a) What is the exchange rate value of each air conditioner in Rand? b) What is the total import cost per unit if the importer must pay an import duty of 5%, a 15% charge for shipping and handling, and a Value Added Tax of 12% (all charges apply to the import cost per unit)? c) What is the final retail price to South African consumers if a 50% mark-up per unit for profit is applied to the total import unit cost? d) CHALLENGE QUESTION Suppose payment to the American suppliers is not made until 30 days later at which time the Rand is expected to weaken against the USD by 10%. Use the percent change formula to determine the new 30 day exchange rate then calculate the impact the new currency exchange rate will have on the importer’s profits. (Hint: What is the added cost per unit? This will have to come out of profits unless the company increases its retail price, which it may not be able to do without upsetting its customers.) [percent change = new value – old value x 100%] old value 3. 4. On the xe.com site, under Tools, Click on Current and Historical Rate Tables. On the x-rates.com site click on Historic Lookup under Menu. (a) Find the CAD/USD exchange rate on Feb 1 2000. Compare this conversion rate with today’s latest exchange rate. Calculate the percent increase in the value of the CAD relative to the USD. (b) Beginning Dec 01 2004 and ending Dec 31, did the CAD strengthen or weaken against the AUD during this period? Why? (c) How much would a Canadian importer have to spend in CAD to buy a shipment of goods worth 1000,000 Yen on August 1, 1997? (d) Suppose an investor has two options: Invest 1000 000 CAD on Sept 01, 2004, @ 4% for 1 year in a Canadian bank; or, convert the money into Pounds Sterling on Sept 01, 2004 and invest the Pounds @ 5% for 1 year in a U.K. bank. Perform the necessary calculations and decide which option is best for the investor given that she must convert the Pounds Sterling into CAD on Sept 01, 2005? Use historical exchange rate information. (e) Suppose a company is considering expanding its manufacturing operations internationally and budgets 50 million CAD to do so. One of the countries it is considering in Ireland. The original start date for constructing a new plant at a cost of 22 million CAD was set for Sept 01 2007, but delays and issues with government regulations delayed the start date to April 01 2008. What was the effect of the delay in the start date on the cost of construction? (a) Summarize the main points in Currency Risk Factors, Page 293. You should be familiar with the terms: floating rate, currency devaluation, currency revaluation, and exchange controls. (b) Describe what is meant by currency speculation. Exchange rates for 30 November 2010 on www.xe.com .