First Grade Curriculum Map
advertisement
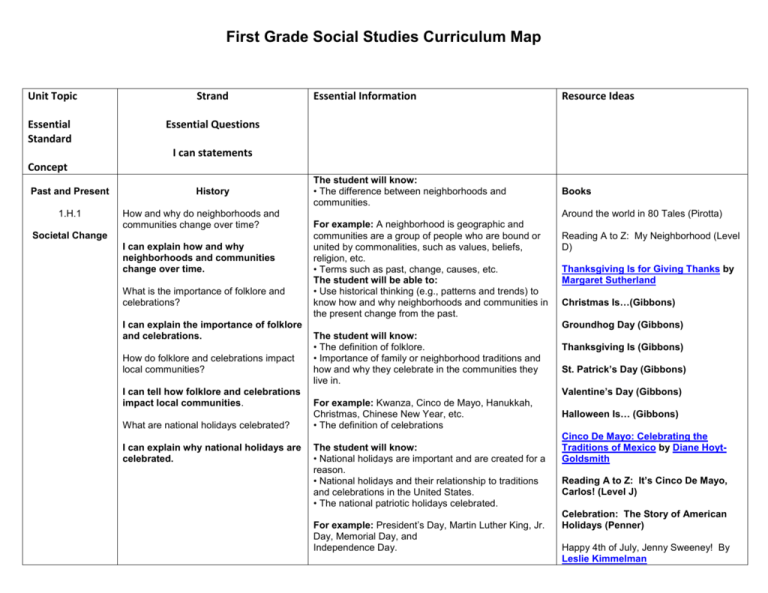
First Grade Social Studies Curriculum Map Unit Topic Strand Essential Standard Essential Questions Essential Information Resource Ideas The student will know: • The difference between neighborhoods and communities. Books I can statements Concept Past and Present 1.H.1 History How and why do neighborhoods and communities change over time? Societal Change I can explain how and why neighborhoods and communities change over time. What is the importance of folklore and celebrations? I can explain the importance of folklore and celebrations. How do folklore and celebrations impact local communities? I can tell how folklore and celebrations impact local communities. What are national holidays celebrated? I can explain why national holidays are celebrated. Around the world in 80 Tales (Pirotta) For example: A neighborhood is geographic and communities are a group of people who are bound or united by commonalities, such as values, beliefs, religion, etc. • Terms such as past, change, causes, etc. The student will be able to: • Use historical thinking (e.g., patterns and trends) to know how and why neighborhoods and communities in the present change from the past. Reading A to Z: My Neighborhood (Level D) Thanksgiving Is for Giving Thanks by Margaret Sutherland Christmas Is…(Gibbons) Groundhog Day (Gibbons) The student will know: • The definition of folklore. • Importance of family or neighborhood traditions and how and why they celebrate in the communities they live in. Thanksgiving Is (Gibbons) St. Patrick’s Day (Gibbons) Valentine’s Day (Gibbons) For example: Kwanza, Cinco de Mayo, Hanukkah, Christmas, Chinese New Year, etc. • The definition of celebrations The student will know: • National holidays are important and are created for a reason. • National holidays and their relationship to traditions and celebrations in the United States. • The national patriotic holidays celebrated. For example: President’s Day, Martin Luther King, Jr. Day, Memorial Day, and Independence Day. Halloween Is… (Gibbons) Cinco De Mayo: Celebrating the Traditions of Mexico by Diane HoytGoldsmith Reading A to Z: It’s Cinco De Mayo, Carlos! (Level J) Celebration: The Story of American Holidays (Penner) Happy 4th of July, Jenny Sweeney! By Leslie Kimmelman The 4th of July Story (Dalgliesh) President’s Day (Rockwell) Folktales: American Children's Folklore (American Folklore Series) by Simon J. Bronner Classic American Folk Tales (Zorn) Activity Holidays around the world Have students think of as many holidays as possible. What are they for, when do they happen, and how are they celebrated? Weblinks www.wilmington.patch.com/columns/thenand-now-18 (shows pictures of Wilmington from the past and the present) www.brainpopjr.com – Great clip on President’s Day Who needs a GPS? 1.G.1 Location, Land Forms, and Water Forms Geography How can one use geographic tools to identify landforms and bodies of water? I can use geographic tools to identify landforms and bodies of water. How do I find locations on a map? I can find locations on a map. How do I use cardinal directions and map symbols? I can use cardinal directions and map symbols. The student will know: • Geographic tools are used to identify and describe the physical features of landforms and bodies of water. For example: The ocean is a large body of water and a mountain is a landform. • Examples of geographic tools such as maps globes, and atlases (e.g., paper and electronic forms), global positioning systems (e.g., GPS), keys, legends, compass rose, etc. • Maps and globes are different representations of Earth. The student will be able to: • Create simple maps showing landforms and bodies of water. • Use geographic terms in work and play to describe and find places. Books Geography from A to Z: A Picture Glossary (Knowlton) Follow that Map! (Ritchie) Me on the Map (Sweeney) Map Keys (Adburg) North, South, East, and West (Fowler) The Four Oceans (Mara) The Seven Continents (Mara) Armadillo from Amarillo (Cherry) Maps and Globes (Knowlton) Where do I Live? (Chesanow) Reading A – Z: I Looked Everywhere (Level C) Reading A – Z: My Neighborhood (Level d) There is a Map on my Lap (Rabe) The student will know: • How to find specific location of places on a map such as home, classroom, playground by using map symbols. • Maps and other geographic tools are used to locate familiar contexts of home, classroom, school and community. • People use geographic terms, tools, and technology in work and play to describe and find places. For example: maps are used to find unfamiliar places and compasses are used to find direction, etc. The student will know: • Symbols represent features on a map. • Essential basic elements of geographic representations. For example: cardinal directions and map symbols, etc. The student will be able to do: • Identify and use map symbols to represent streets, roads, lakes, etc. • Create and interpret a basic map including the key with symbols from the map. What the earth gives me? 1.G.2 HumanEnvironment Interaction and Natural Resources Geography In what ways do people change the environment? I can describe ways people change the environment. What are natural resources and how do human use them? I can identify natural resources and how humans use them. How do people use the natural resources in the community? I can tell how people use natural resources in the community. The student will know: • People may change the environment to meet their needs. For example: the use of land, building of homes, and ecosystems, etc. The student will know: • People use and conserve natural resources in their community. • Examples of basic natural resources include air, water, sunlight, animal, minerals, oceans, wildlife, coal, sand, and many more. • Natural resources are always found in or on the earth. • Environment does not always stay the same due to changes. The student will know: • People live in environments that are conducive to their living needs whether it is weather conditions, Books The Little House (Burton) Where once there was a Wood (Fleming) Why Should I Recycle? (Green) Why Should I Save Water? (Green) Why Should I Save Energy? (Green) Why Should I Protect Nature? (Green) Earth and Me (Artel) Where Once There Was A Wood (Flemming) One Little Monster Learns to Reduce, Reuse, and Recyle (Lanczak) Recycling (True Books: Environment) by Rhonda Lucas Donald Investigate Earth’s Resources How does the environment impact where people live? ways of travel, city or country, etc. • People live differently in various regions according to the environment. I can explain how the environment impacts where people live. For example: People who live in the city may travel on public transportation such as a city bus, etc (Barraclough) Reading A to Z: Where we get Energy (Level K) Trees to Paper (Snyder – Level G) Activity Fieldtrip to Airlie Gardens The economy and me. 1.E.1 Goods and Services and Supply and Demand Book Economics What are the ways in which people earn money? I can state examples of the ways people earn money. How do people use money they earn for goods and services? I can tell how people use money they earn for goods and services What is the difference between goods and services? I can explain the difference between goods and services. What are examples of goods and services in the home, school, and community? I can name examples of goods and services in the home, school and community. What is meant by supply and demand? I can explain the terms supply and demand. How does supply and demand affect the choices families and communities make? I can explain how supply and demand affect choices made by families and The student will know: • People use money they earn to buy goods and services. • Businesses incur costs by hiring individuals and earn revenue by selling goods and services • Individuals earn income by working for various businesses. • Distinguish between goods and services. • Individuals receive income by working at a job. • The difference between income and money. • People make decisions about jobs based on education, skills, interests, etc. • Producers and consumers impact goods and services. What are goods and services? (Andrews) Who is buying? Who is selling? (Larson) Corduroy (Freeman) One Cent, Two Cents, Old Cent, New Cent: All About Money (Worth) What Can I Buy? (Vaughn) Math at the Store (Amato – Level G) Bunny Money (Wells) People Working (Florian) In a People House (LeSieg) Richard Scarry's Busiest People Ever and Richard Scarry's What Do People Do All Day The Goat in the Rug (Blood) Tony's Bread (dePaola) The student will know: • Goods are food, clothing, etc. • Services are firemen, policemen, lawn maintenance caretakers, banking, etc. • The difference between goods and services. The student will know: • The process of making choices using available resources and why people cannot have everything they want. • The definition of supply and demand. Activity Take pictures from a magazine and have students sort goods and services. communities. Civics and Governance The Role of Rules 1.C&G.1 Authority, Citizenship, and Conflict Why are rules needed in the home, school, and community? I can explain why rules are needed in the home, school and community. How do authority figures play a role in the home, school, and community? I can explain how authority figures play a role in the home, school, and community. How can conflict be resolved in the home, school, classroom, and community? I can tell how conflict can be resolved in the home, school, classroom and community. The student will know: • Rules are made to ensure a safe society in the home, school and community. For example: taking care of oneself, respect for the rights of others, following rules, and getting along with others, etc. • How to distinguish appropriate rules and why they are used. • The importance of home, school and community rules to a society. The student will know: • The roles and responsibilities of people with authority in home, school and community. For example: teachers, principal, parents, mayor, park rangers, wardens, etc. • Notable authority leaders of home, school and community. Books The Rainbow Fish (Marcus Pfister) www.storylineonline.net You can hear book read aloud. The 7 Habits of Happy Kids (Sean Covey) The Recess Queen (O’Neill) Do onto Otters (Keller) A Bad Case of Tattle Tongue by Julia Cook Know and Follow Rules by Cheri J. Meiners M.Ed. Don't Squeal Unless It's a Big Deal: A Tale of … by Jeanie Franz Ransom First Day Jitters by Julie Danneberg For example: to include but not limited to teacher, principal, parents, mayor, park rangers, game wardens, law enforcement, etc. Unity in our differences 1.C.1 Diversity and Values and Culture What are the different types of languages, traditions, and holidays, of various cultures? I can name examples of different types The student will know: • There are various ways to solve differences in conflicts. • Conflicts might be settled in fair and just ways in homes, schools, classrooms and communities (e.g., majority rules). • There are various ways that individuals, groups, and communities manage conflict and promote equality, justice and responsibility in homes, schools, classrooms and communities The student will know: • There are individual differences in languages, beliefs and customs that may be unique to one’s culture. • Comparisons of the beliefs, customs, ceremonies, traditions and social practices of the varied cultures in their local community. • Comparisons of how people from other cultures live, work, and play. Books A Day in the Life of Children around the world (Kirk) Holidays (Level H – Sundance Publishing) Beliefs of languages, traditions, and holidays of various cultures. • Similarities and differences in the ways various cultures address human needs and concerns How are people influenced by different values and beliefs? The student will know: • Reading about diverse cultures will help to identify with one’s culture and be exposed to other cultures. • Learning about diverse cultures through literature, art and music. I can explain how people are influenced by different values and beliefs. This is my House (Dorros) Music Around the World, Level 3: A Musical Adventure (Level 3) by John Lithgow and Teresa Domnauer You and Me Together : Moms, Dads, and Kids Around the World (Kerley) Children Around the World: The Ultimate Class Field Trip (Woodfield) We are Different, We are the Same (Kates) A Rainbow of Friends (Hallinan) Throw Your Tooth on the Roof: Tooth Traditions from Around the World (Beeler) This Is the Way We Go to School: A Book About Children Around the World by Edith Baer Children Around the World by Montanari People (Spier) Activity: Have students bring