Introduction to Animal Nutrition Study Guide answers
advertisement

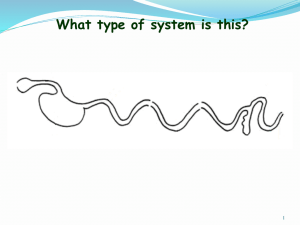
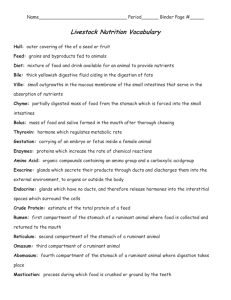
Name:_______________________________ Introduction to Animal Nutrition Study Guide Worksheets/Notes Worksheet 1C Monogastric Digestive System Process Notes Pages Function of Monogastric Digestive System Organs (chart) Worksheet 2A 1 Ruminant Digestive System Notes Pages forages, ground concentrates, and light grains. (Had pictures that you colored) Notes Pages Nutritional Needs of Animals—Part 1 (had a box that you drew pictures for each nutrient) Quiz Nutritional Needs of Animals – Part 1 Quiz Evaluations *Look at all evaluations Appendix A,B,C,D Worksheet Balancing a Ration *Look at all worksheets, quizzes, evaluations, and notes pages. You are responsible for the information. 1. What are the two types of Digestive systems? Name an example of each. a. Monogastric –human, dogs, pigs b. Ruminant- Cow, sheep, goats 2. Define digestion. a. The process of breaking down food into smaller particles 3. What is the process of digestion? (Start to end) a. Mouth, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small intestine, cecum, colon, rectum, anus 4. List each organ in the monogastric digestive system and tell the function of each. (Notes Pages Chart. If you have the chart from your notes just attach to study guide) 5. Chemical Reactions in the Monogastric Digestive Process Organ Function of Enzyme/Acid Mouth Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Breaks down starch Example: Gastric Acid Maltase Amylase Pepsin Sucrase Lipase Lipase Lactase Trypsin Amylase Rennin Peptidase Chymotrypsin 6. What is the difference in the saliva of a ruminant compared to a Monogastric animal? a. The saliva in a monogastric has amylase to start breaking down food, the saliva in a ruminant does not have amylase so it doesn’t start breaking down food in the mouth. 7. What are the four compartments in the ruminant stomach? Describe each. a. Rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum 8. What path do ground concentrates, light grains, and forages take through the ruminant stomach? a. 9. Can Monogastric animals digest forages? a. no 10. List the 6 basic nutrients then describe each. a. Water, vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates, minerals, fats 11. What are the 4 life stages? Describe each. a. Maintenance- maintaining weight (no weight gain or loss), nutrient requirements low b. Gestation- female is pregnant, nutrient requirements are higher, 3rd trimester needs most nutrients c. Lactation- female is producing milk d. Growth and Development – growing larger and stronger, developing tissues and muscles, require additional nutrients 12. In which trimester of gestation will the female need the most nutrients? a. 3rd 13. In which life stage will an animal need less nutrients? a. maintenance 14. List sources of information on nutritional requirements. a. Texrtbooks, computer, National Research Council (NRC), extension agents, feed companies 15. Identify sources of nutrients. Water Pond, well Protein Grains, legumes, amino acids in animal tissues Carbohydrates Sugars, starches, and fibers in grain and forages Fats Fatty acids in animal tissues, fats, and grains Vitamins Grass, sun-cured hay, and commercial feeds Minerals Plant and animal tissue and commercial feeds 16. Know how to balance a ration. Look at worksheets.