ECONOMICS 101, Fiscal Problem without equations Prof. Dohan
advertisement

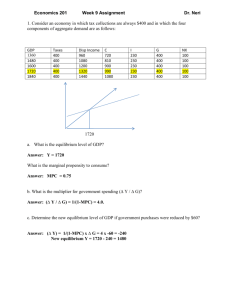
1 ECONOMICS 101, Fiscal Problem without equations Prof. Dohan Fall 2010 Answer Key for this homework. The numbers are a bit different but the principles are the same. Try it on the original homework. MACRO ECONOMIC POLICY FOR UKRANRUS The current president of Ukranrus, a large emerging industrial economy, wants to have both fullemployment and maintain price stability as soon as possible so that he is reelected “President”. The Ukranrus economy has the following characteristics (millions of Ukrans) YFE = potential output at full employment. Ya* = the equilibrium level of GDP output. It is the value of the GDP output where Ya= Yd . Yd is the demand for that output. If Ya* is less then the potential full employment output YFE, the output will goes toward Ya* which causes unemployment. If Ya* > Yfe then output stops growing at YFE and our attempt to by more than YFE causes inflation. Yd (AE in the book) = the components of final demand: Yd = C+Id+G+X-M (Id = planned investment demand which is also influenced by interest rates and the level of output), C = consumption which depends mostly on disposable income (Ydi). G = government spending on goods and services excluding transfer payments, X.= exports. M= imports. Ydi (disposable income) = Ya – Tx + TR (that is output minus taxes plus transfer payments.) A. The equilibrium output is currently Y a* = Too little demand to get to full employment 13,000 Assume we have found this value by finding the Ya where Ya=Yd And that we know all the equation for C, and the values for I, G, T, X and M B. Full employment level of output YFE = Yd = C+Id+G+X-M 15,000 C. Marginal propensity to consume MPC = 0.8 D. Currently, its exports and imports cannot be changed because of trade agreements with its strong neighbors. E. Export and imports are currently fixed. +2,000 Ya* = Yfe = 13,000 15,000 Write out the “Yd function” in letters taking into account that C = C -.8Ydi and remember that Ydi = (Ya –Tx + Tr). Now sketch a sample of the aggregate demand function Yd. Then identify the equilibrium output Ya* and the full employment output YFE on the horizontal axis and draw vertical lines from these two points to the 45oYa line and write their numbers underneath. Yd = C+Id+G+X-M = C + .8Ya-.8*Tx + .8*Tr + I + G +X - M 2._On the graph, show the output gap between full employment level YFE = 15,000 and the equilibrium level of output which is 13,000. Use a arrow ( or ) to indicate the direction of desired change. Ya* -Yfe = ∆Ya* 15,000 -13,000= +2000 3. What is the horizontal "output gap (ΔYa* = YFE - Ya*) = +2000 (from above) (That is, the amount between YFE (Full employment output) and Ya* (current equilibrium output where Ya = Yd) and what does it mean in economic terms. This is GDP output that is permanently lost because of the lack of aggregate demand. It lowers the per capita income and the average income of households. Unemployment So now you can describe in one word the one major economic issue in this political campaign. (Observation by professor: Gee, I thought the election was about Obama, Obamacare, too much government spending, high taxes, too much government interference in the financial markets, etc., but this only an observation, and not “official” for this class to read or know..) 4. Calculate the regular multiplier showing work and explain the principle reason for the multiplier effect in words. (Hint: additional disposable income and consumption) M=1/(1-MPC M=1/(1-MPC) = 1/(1-.8) = 5 2 6. What is the vertical shift in ΔYd, that is what is “Aggregate demand gap” between Ya and Yd at YFE. It is also called the “AE gap” or aggregate expenditure gap. Explain what it measures. How did you calculate it? Show work. Hint: (ΔYd = (YFE - Ya*)/M ΔYd = (YFE - Ya*)/M => (15,000-13,000)/5 = +400 = ΔYd 7. VIP: What fiscal policies do we have to reach full employment with price stability (FEWPS)? That is, what variables can we use to shift ΔYd up or down by the required amount (from Question 6) so that the income gap between full employment and aggregate expenditure is closed. Fiscal policies refer to changes in government spending on goods and services (G), or using changes in the tax system (Tx) or transfers (Tr) to influence consumptions spending (We shall also see how changes in the taxes on business can influence investment and other behavior.) Here we are going to assume we can only change “lump sum” Tx or Tr, rather than changing the tax rate, tr. 8. What is the amount of the shift in Yd (or AE) (which we call ΔYd ) so that ΔYd times M, the multiplier) closes the output gap ΔYa*? On the graph indicate the amount and what direction they should move. ΔYd*/ M = ΔYa* ΔYd * M = ΔYa* +400*5 = +2000 +400 = the vertical upward shift in ΔYd* 9. What changes in government spending could be used at the Federal level to reach FEWPS? Explain why such small changes might have a large impact on the economy. (Extra Credit: What realistic problems does the President have in getting quick results from this policy before 2012 election?) ΔYd*= +400, so since Yd = C+Id+G+X-M so that and increase in G = +400 together with the multiplier effect resulting from the secondary expansion of demand from the spending of income on consumer goods by the people who are now earning more income – called the multiplier effect – causes the equilibrium level of income to rise by $2000 from $13,000 to $15,000. The Republican Party will block any attempt to increase government spending even though it is for the good of the people. They will deny Obama of any ability to govern and succeed. Extra Credit Today. What changes in taxes are necessary to reach FEWPS? Explain how taxes work through changing Ydi to change C which shifts Yd and this has a multipler effect on Y*a. Explain your calculations and answer. EXPLAIN HOW THIS POLICY WOULD BE IMPLEMENTED IN PRACTICE and what are the economic and political advantages and disadvantages of implementing such a tax policy? Remember that consumers save or dissave as Ydi goes up or down! ΔYd*= Δ C = MPC*ΔYdi = +400, the necessary upward shift in C before the secondary expansioin of C from higher incomes. ΔYdi is changed by change taxes in the opposite (-1) direction or transfers in the same direction as the shift in aggregate demand. MPC*ΔYdi = +400 => .8*ΔYdi = +400 so that ΔYdi = +400/.8 = +500, so Δ C = Δ Tx* (-1)*.8=400 Or -500*(-1)*.8 = 400, so cut taxes by 500 to shift C upward by 400 at any level of Ya* 11. What about using changes in transfer payments in this case. The analysis is the same as for taxes but without the -1 sign. 12. In using changes in taxes, does it make any difference in the effectiveness of the policy if the tax changes are imposed only on the rich high income household or only on the poor low income households. Explain why. Yes, the MPC of the lower income households is higher than of the rich high income households so that the multiplier effect of reducing taxes on lower income households is higher than on higher income households. If the MPClow = .9, then the multiplier is 10. If the MPChigh is .5, then the multiplier is 5.