a. Solve for the equilibrium level of income.
advertisement
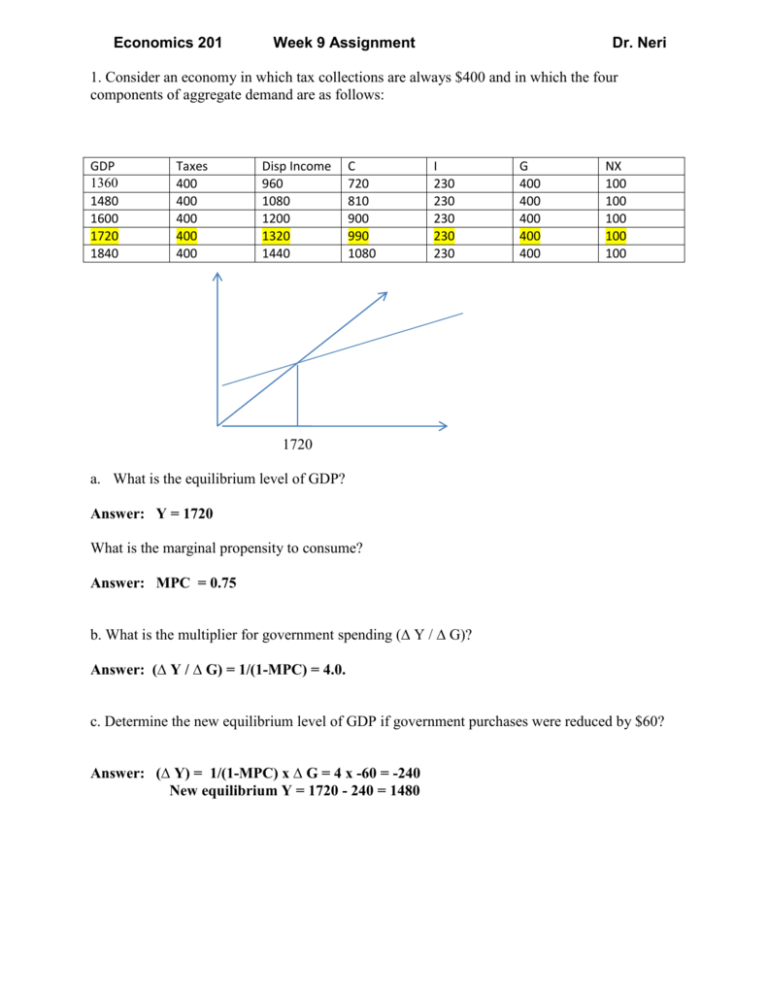
Economics 201 Week 9 Assignment Dr. Neri 1. Consider an economy in which tax collections are always $400 and in which the four components of aggregate demand are as follows: GDP 1360 1480 1600 1720 1840 Taxes 400 400 400 400 400 Disp Income 960 1080 1200 1320 1440 C 720 810 900 990 1080 I 230 230 230 230 230 G 400 400 400 400 400 NX 100 100 100 100 100 1720 a. What is the equilibrium level of GDP? Answer: Y = 1720 What is the marginal propensity to consume? Answer: MPC = 0.75 b. What is the multiplier for government spending (∆ Y / ∆ G)? Answer: (∆ Y / ∆ G) = 1/(1-MPC) = 4.0. c. Determine the new equilibrium level of GDP if government purchases were reduced by $60? Answer: (∆ Y) = 1/(1-MPC) x ∆ G = 4 x -60 = -240 New equilibrium Y = 1720 - 240 = 1480 2. Bernankistan is a small country ruled by Sir Alan of Greenspan. You are given the following information about the economy: C = 75 + 0.6Yd I = 125 G = 81 T = 81 ( Lump-Sum) Yd = Y – T Bernankystan does not have Imports (M) or Exports (X). a. Solve for the equilibrium level of income. Answer: Y = 581. Substitute and solve. b. Calculate the government spending multiplier (∆ Y / ∆ G). Answer: (∆ Y / ∆ G) = 1/(1-MPC) = 2.5 c. Calculate the investment spending multiplier (∆ Y / ∆ I). Answer: (∆ Y / ∆ I) = 2.5, the same as the spending multiplier d. Sir Alan wants to increase government spending by 8 from 81 to 89. What will happen to the equilibrium income? Solve for the new equilibrium level of income? (∆ Y) = 1/(1-MPC) x ∆ G = 2.5 x 8 = 20 New equilibrium Y = 581 + 20 = 601 e. Sir Alan says “let’s not increase G, Let’s reduce T by 8 from 81 to 73. What will happen to the equilibrium income? Solve for the new equilibrium level of income? Calculate (∆ Y / ∆ T). This called the tax multiplier. Answer: GDP = Y = 593 Answer: (∆ Y / ∆ T) = -1.5 e. Suppose Sir Alan’s advisors tell him G should be increased by 20 to from 81 to 101. Sir Alan says that’s ok as long as the increased spending is financed by raising T by 20. Solve for the new equilibrium level of income if G increases by 20 from 81 to 101 and the increase in G is financed by an increase in taxes (T) by 20 from 81 to 101. Answer: GDP = Y = 601 f. What is the multiplier effect of the increase in G financed by and equal increase in T aimed at keeping the budget balanced? Answer: Multiplier = 1.0











