TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
advertisement

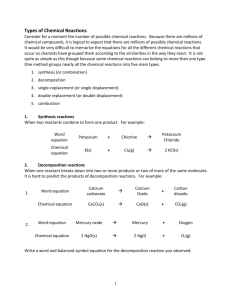
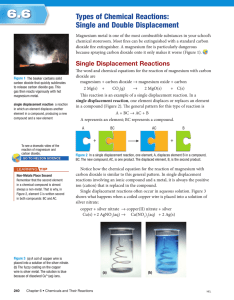
Grade 10 Academic Science - Chemistry Types of Reactions There are several types of chemical reactions 1. combustion 2. synthesis reactions 3. decomposition reactions 4. displacement reactions Combustion This is a reaction where a substance reacts with oxygen to produce something called an oxide. Oxides are compounds that contain oxygen. The reaction usually releases heat in the form of heat and/or light. An example is a lighter butane + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy C4H10 + O2 CO2 + H2O NOTE: You must BALANCE this equation (i.e., number of reactants must equal number of products 2C4H10 + 13O2 8CO2 + 10H2O * If there is not enough oxygen available, CO (carbon monoxide) is produced which is dangerous to humans.* Synthesis Reactions During a synthesis reaction, two things attach to make one new substance: A + B AB An example is placing a magnesium ribbon in Bunsen burner flame magnesium + oxygen magnesium oxide Mg + O2 MgO Again, balance the chemical equation 2Mg + O2 2 MgO Decomposition Reactions During decomposition reactions, a larger compound is broken down: AB A + B The example is electrolysis of water with splint tests of gases water oxygen gas + hydrogen gas 2H2O O2 + 2H2 Displacement Reactions In a displacement reaction, elements trade places and recombine. There are two kinds of displacement reactions: Single Displacement Reactions In this kind of reaction an element will displace another element from a compound: A + BC B + AC This reaction can be demonstrated by combining magnesium + silver nitrate silver + magnesium nitrate Mg + 2AgNO3 2Ag + Mg(NO3)2 the magnesium displaces (takes the place of) the silver Another example is bromine + calcium iodide iodine + calcium bromide Br2 + CaI2 I2 + CaBr2 NOTE: metals displace metals / non-metals displace non-metals Double Displacement Reactions In a double displacement reaction two compounds are mixed and the metals switch places: AB + CD AD + CB A demonstration is lead (II) nitrate + potassium iodide lead (II) iodide + potassium nitrate Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI PbI2 + 2KNO3