6.6 Types of Chemical Reactions: Single and Double Displacement
advertisement

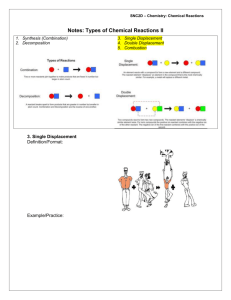
6.6 Types of Chemical Reactions: Single and Double Displacement Magnesium metal is one of the most combustible substances in your school’s chemical storeroom. Most fires can be extinguished with a standard carbon dioxide fire extinguisher. A magnesium fire is particularly dangerous because spraying carbon dioxide onto it only makes it worse (Figure 1). single Displacement Reactions Figure 1 The beaker contains solid carbon dioxide that quickly sublimates to release carbon dioxide gas. This gas then reacts vigorously with hot magnesium metal. single displacement reaction a reaction in which an element displaces another element in a compound, producing a new compound and a new element The word and chemical equations for the reaction of magnesium with carbon dioxide are magnesium + carbon dioxide → magnesium oxide + carbon 2 Mg(s) + CO2(g) → 2 MgO(s) This reaction is an example of a single displacement reaction. In a single displacement reaction, one element displaces or replaces an element in a compound (Figure 2). The general pattern for this type of reaction is A + BC → AC + B A represents an element; BC represents a compound. A BC AC + To see a dramatic video of the reaction of magnesium and carbon dioxide, Go to NElsoN sCIENCE LeaRning Tip Non-Metals Place Second Remember that the second element in a chemical compound is almost always a non-metal. That is why, in Figure 2, element C is written second in both compounds: BC and AC. + C(s) B + Figure 2 In a single displacement reaction, one element, A, displaces element B in a compound, BC. The new compound, AC, is one product. The displaced element, B, is the second product. Notice how the chemical equation for the reaction of magnesium with carbon dioxide is similar to this general pattern. In single displacement reactions involving an ionic compound and a metal, it is always the positive ion (cation) that is replaced in the compound. Singledisplacementreactionsoftenoccurinaqueoussolution.Figure3 shows what happens when a coiled copper wire is placed into a solution of silver nitrate: copper + silver nitrate → copper(II) nitrate + silver Cu(s) + 2 AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 Ag(s) Figure 3 (a) A coil of copper wire is placed into a solution of the silver nitrate. (b) The fuzzy coating on the copper wire is silver metal. The solution is blue because of dissolved Cu2+(aq) ions. 240 Chapter 6 • Chemicals and Their Reactions (a) (b) NEL Single displacement reactions also occur when metals are placed into acids. The chemical formula of any acid includes one or more hydrogen atoms. (For example, the chemical formula for hydrochloric acid is HCl(aq).) In these reactions, metal atoms displace the hydrogen atoms in the compound. Figure 4 shows the reaction of zinc metal and hydrochloric acid: zinc + hydrochloric acid → hydrogen + zinc chloride Zn(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq) Hydrogen, you will recall, forms diatomic molecules. That is why the chemical formula for hydrogen is H2 rather than H. Displacement Reactions in Mining Metals rarely occur naturally as pure elements. Instead, they combine with other elements to form rock deposits called ores. Nickel, for example, occurs in rock as nickel sulfide. The processing of nickel ore is called smelting. The first step in smelting is converting nickel sulfide into nickel oxide. Nickel oxide is then burned with coke (carbon) to produce pure nickel and poisonous carbon monoxide: Figure 4 Zinc reacts in hydrochloric acid. As zinc displaces the hydrogen in the acid, bubbles of hydrogen gas appear on the surface of the zinc. C(s) + NiO(s) → Ni(s) + CO(g) Note that the chemical equation for smelting fits the general pattern of single displacement reactions. The factory in which this process occurs is called a smelter. Another of the products of processing nickel is sulfur dioxide. As you will learn in the next chapter, sulfur dioxide emissions from nickel smelters are responsible for some of the damage caused by acid precipitation. RESEARCH THIS WHen gOLd LOSeS iTS gLiTTeR SKILLS: Defining the Issue, Researching, Communicating The cyanide process is one of the most effective methods of extracting gold from rock. However, it is controversial because it uses sodium cyanide—a highly toxic substance. The used cyanide must be collected, stored, and treated to keep it out of the environment (Figure 5). SKILLS HANDBOOK 4.A., 4.C. Consider this scenario. A company wants to mine a newly discovered gold deposit near a remote town in northern Ontario. The president of the company has invited the following people to discuss the project: • the mayor of the town • a representative from the Ministry of the Environment • the leader of a First Nations group • a member of a local non-governmental environmental group 1. Take the role of one of the four people at the meeting. 2. Research background information to support your role, including the history of cyanide use in gold processing. Figure 5 Water from gold mines is treated to remove the cyanide before being released into the environment. NEL A. In your role, summarize your perspective on the development of the mine. Present your perspective as an opening argument. T/I C 6.6 Types of Chemical Reactions: Single and Double Displacement 241 Double Displacement Reactions double displacement reaction a reaction that occurs when elements in different compounds displace each other or exchange places, producing two new compounds Double displacement reactions occur when two elements in different compounds trade places (Figure 6). The general pattern for these reactions is: AB + CD → AD + CB The symbols A, B, C, and D represent atoms, single ions, or polyatomic ions. LeaRning Tip Polyatomic Ions Treat polyatomic ions as a single unit in a chemical equation. In a double displacement reaction, a polyatomic ion (such as the nitrate ion, NO3−) can change places with an ion composed of only one atom (such as chloride, Cl−). DID YOU KNOW? Heavy Metals Banned Heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury are very toxic. Solutions containing cations of these metals are also dangerous. For this reason, many school boards have banned their use. Even in schools where they are not banned, they are generally only used in very small quantities. After use, they are collected in special containers so that as little as possible is released into the environment. What is your school’s policy on heavy metals? Figure 7 (a) When silver nitrate solution is added to sodium chloride solution, specks of silver chloride appear. (b) When silver nitrate solution is added to tap water, a faint haze appears. This haze indicates that chloride ions are present in the water—perhaps from road salt. AB CD AD + CB + Figure 6 In a double displacement reaction, the two non-metals, B and D, trade places. Alternatively, you could think of it as the two metals, A and C, switching over. Many double displacement reactions occur between two ionic compounds in solution. For example, Figure 7 shows the reaction of a solution of silver nitrate with a solution of sodium chloride. In this reaction, nitrate ions and chloride ions trade places. The word and chemical equations for this reaction are as follows: silver nitrate + sodium chloride → silver chloride + sodium nitrate NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) AgNO3(aq) + Notice that both the word and chemical equations fit the general pattern for this reaction: AB + CD → AD + CB (a) (b) Forming a Precipitate precipitate a solid formed from the reaction of two solutions 242 Look closely at the chemical equation for the reaction in Figure 7. Note that the reactants are both in solution (aq), and so is one of the products: sodium nitrate. The other product, silver chloride, is a solid (s). Chemists have discovered, through experimentation, that some ionic compounds do not dissolve in water. If these insoluble compounds are formed during a reaction, they become visible as a precipitate: tiny specks of solid material in the solution. The silver chloride formed in Figure 7 is a precipitate. Chapter 6 • Chemicals and Their Reactions NEL Not all double displacement reactions result in the formation of a precipitate, but many do. Lead(II) nitrate and potassium iodide are both soluble in water. When their solutions are mixed, a bright yellow precipitate of lead(II) iodide appears (Figure 8). AB + CD → AD + CB lead(II) nitrate + potassium iodide → lead(II) iodide + potassium nitrate Figure 8 The bright yellow precipitate is insoluble lead(II) iodide. It is produced when a solution containing Pb2+ ions is mixed with a solution containing I− ions. in Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2 KI(aq) → PbI2(s) + 2 KNO3(aq) Potassium iodide can be used to test for Pb2+ ions in water: a yellow precipitate indicates that lead ions are present. SUMMARY •Inasingledisplacementreaction,anelementand a compound react to produce a different element and compound and have the general pattern A + BC → AC + B. •Sometimes,inareactionofaqueous reactants, one of the products is insoluble. This product, called a precipitate, appears as a solid in the solution. •Inadoubledisplacementreaction,two compounds react to produce two different compounds and have the general pattern AB + CD → AD + CB. CHECK YOUR LeaRning 1. Compare single and double displacement reactions. K/U 2. What types of reactants are likely to be involved in (a) a single displacement reaction? (b) a double displacement reaction? K/U 3. Classify the following word equations as representing either single or double displacement reactions: K/U (a) aluminum + iron(III) oxide → aluminum oxide + iron (b) barium chloride + sodium sulfate → barium sulfate + sodium chloride (c) zinc + copper(II) sulfate → zinc sulfate + copper (d) silver nitrate + sodium phosphate → silver phosphate + sodium nitrate (e) calcium + water → hydrogen + calcium hydroxide 7. The dark tarnish that sometimes forms on silver is silver sulfide, Ag2S. A common home remedy for tarnish is represented by the chemical equation 3 Ag2S(s) + 2 Al(s) → 6 Ag(s) + Al2S3(s) (Figure 9) K/U A (a) Classify the reaction as a single displacement or a double displacement reaction. (b) Which method do you think is better for cleaning silverware: the method described in (a) or scrubbing and polishing? Why? 4. Rewrite the word equations in question 3 as balanced chemical equations (without state symbols). K/U T/I 5. Consider the chemical equation CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s). K/U A (a) Classify the reaction as a single displacement or a double displacement reaction. (b) Copper compounds such as copper(II) sulfate are toxic. Before disposal, these compounds must be treated to reduce their toxicity. Describe how to use steel wool (which is made mostly of iron) to remove the Cu2+ ions from an aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate. 6. Firefighters suggest that the best way to put out a magnesium fire is to pour sand or salt over it. Why is this better than using a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher? A NEL Figure 9 To remove the tarnish from silverware, soak it in a hot solution of baking soda in an aluminum pan. 8. The fuzzy silver coating in Figure 3 of this section is impure silver. It can be converted back into silver nitrate by reacting it with nitric acid, HNO3(aq), as shown: Ag(s) + HNO3 (aq) → AgNO3(aq) + NO2(g) + H2O(l) K/U T/I A (a) Balance the equation. (b) What has to be done to the reaction mixture to recover solid silver nitrate? (c) Why must this process be done in a well-ventilated area? (Hint: see Figure 1 in Section 5.10.) 6.6 Types of Chemical Reactions: Single and Double Displacement 243