Review—Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, & Fungi
advertisement
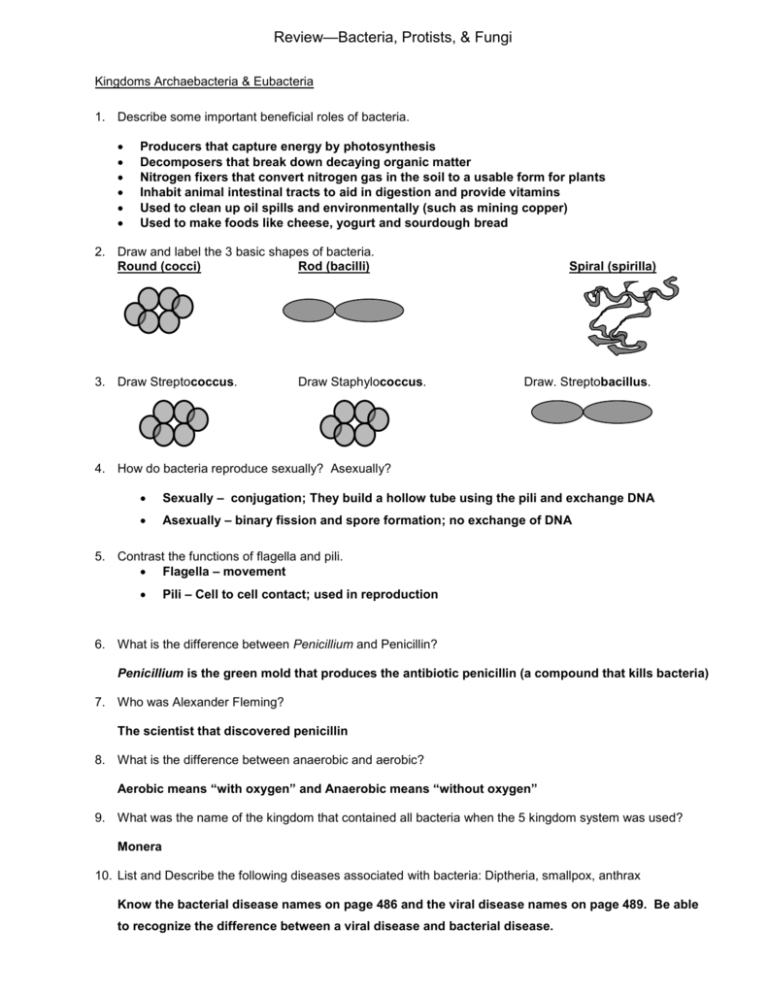
Review—Bacteria, Protists, & Fungi Kingdoms Archaebacteria & Eubacteria 1. Describe some important beneficial roles of bacteria. Producers that capture energy by photosynthesis Decomposers that break down decaying organic matter Nitrogen fixers that convert nitrogen gas in the soil to a usable form for plants Inhabit animal intestinal tracts to aid in digestion and provide vitamins Used to clean up oil spills and environmentally (such as mining copper) Used to make foods like cheese, yogurt and sourdough bread 2. Draw and label the 3 basic shapes of bacteria. Round (cocci) Rod (bacilli) 3. Draw Streptococcus. Draw Staphylococcus. Spiral (spirilla) Draw. Streptobacillus. 4. How do bacteria reproduce sexually? Asexually? Sexually – conjugation; They build a hollow tube using the pili and exchange DNA Asexually – binary fission and spore formation; no exchange of DNA 5. Contrast the functions of flagella and pili. Flagella – movement Pili – Cell to cell contact; used in reproduction 6. What is the difference between Penicillium and Penicillin? Penicillium is the green mold that produces the antibiotic penicillin (a compound that kills bacteria) 7. Who was Alexander Fleming? The scientist that discovered penicillin 8. What is the difference between anaerobic and aerobic? Aerobic means “with oxygen” and Anaerobic means “without oxygen” 9. What was the name of the kingdom that contained all bacteria when the 5 kingdom system was used? Monera 10. List and Describe the following diseases associated with bacteria: Diptheria, smallpox, anthrax Know the bacterial disease names on page 486 and the viral disease names on page 489. Be able to recognize the difference between a viral disease and bacterial disease. Kingdom Protista 11. Name, draw and Label the protist with pseudopods. nucleus The amoeba. Contractile vacuole 12. Draw and Label a Euglena and explain how it moves. The flagellum propels it through the water. flagellum 13. Draw and label a paramecium. What are the two uses for its cilia? cilia 1. movement 2. to sweep food into the mouth 14. The protists with silica shells are diatoms silica that is used in everyday things. . Why are they useful to us? They provide us with 15. Why are algae important to us? They provide the majority of the oxygen in the atmosphere. They are also the main source of food for many aquatic animals. 16. In what ways are diatoms used in everyday things? In abrasive cleaners, to make road paint sparkle, in glass 17. What causes malaria? The bite from a mosquito infected with Plasmodium Kingdom Fungi 18. What is the most important role of a fungus? Decomposer 19. What are other important roles of fungi? Sources of food, produce antibiotics, symbiotic relationships with plants 20. What is the only unicellular fungus and what is one of its main uses? How do they reproduce? Yeast. By budding. 21. How do fungi eat? Absorption 22. Explain mutualism and one example involving a fungus. Mutualism – a symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit. Ex. Lichens – fungus and a photosynthetic bacteria (p. 540) 23. What is the importance of spores in fungi? Reproduction 24. Draw and Label a mushroom. Page 528 25. Fill in the chart. Add as much as you can to each box. Domain Archea Bacteria Bacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Cell Type Cell Structure Prokaryote Cell walls w/o peptidogylcan Prokaryote Cell walls w/ peptidoglycan Body Form Unicellular Unicellular Nutrition Auto/Heterotroph Habitat/Location Found Examples Protista Eukarya Fungi Eukaryote Cell walls of cellulose; some have chloroplasts Most Unicellular, some Multicellular Eukaryote Cell wall with chitin Heterotrophic & Autotrophic Auto/Heterotroph Heterotrophic only Extreme environments Soil, water, air, intestines of animals Water Damp, moist places Methanogen, halophiles Escherichia coli, Algae, Eulgena, Paramecium, Amoeba, diatoms Mushrooms, Yeast (unicellular), mold Benefits Cycle nutrients Aid Digestion in animals, decomposers Provide oxygen, food Decomposers, source of food, antibiotics Diseases None known Lyme, tetanus, diphtheria, strep throat, tuberculosis Malaria, amebic dysentery Athlete’s Foot Ringworm Lactobacillus, Streptococcus Multicelluar, one Unicellular









